DRS: Draft registration statement submitted by Emerging Growth Company under Securities Act Section 6(e) or by Foreign Private Issuer under Division of Corporation Finance policy
Published on February 2, 2024
Table of Contents
As confidentially submitted to the Securities and Exchange Commission on February 1, 2024
Registration No. 333-
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
Confidential Draft Submission No. 1
Form S-1
REGISTRATION STATEMENT
UNDER
THE SECURITIES ACT OF 1933
Tamboran Resources Corporation
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
| Delaware |
1311 |
93-4111196 |
||
| (State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) |
(Primary Standard Industrial Classification Code Number) |
(I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) |
Suite 01, Level 39, Tower One, International Towers Sydney
100 Barangaroo Avenue, Barangaroo NSW 2000
Australia +61 2 8330 6626
(Address, including zip code, and telephone number, including area code, of registrants principal executive offices)
C T Corporation System
1209 Orange Street, Wilmington, County of New Castle, Delaware 19801
(302) 658-7581
(Name, address, including zip code, and telephone number, including area code, of agent for service)
Copies to:
| Michael Chambers David J. Miller Latham & Watkins LLP 300 Colorado St., Suite 2400 Austin, Texas 78701 (737) 910-7300 |
Andrew S. Epstein Trevor Lavelle Clifford
Chance US LLP Houston, TX 77002 |
Approximate date of commencement of proposed sale of the securities to the public:
As soon as practicable after the effective date of this Registration Statement.
If any of the securities being registered on this Form are to be offered on a delayed or continuous basis pursuant to Rule 415 under the Securities Act of 1933, check the following box: ☐
If this Form is filed to register additional securities for an offering pursuant to Rule 462(b) under the Securities Act, check the following box and list the Securities Act registration statement number of the earlier effective registration statement for the same offering. ☐
If this Form is a post-effective amendment filed pursuant to Rule 462(c) under the Securities Act, check the following box and list the Securities Act registration statement number of the earlier effective registration statement for the same offering. ☐
If this Form is a post-effective amendment filed pursuant to Rule 462(d) under the Securities Act, check the following box and list the Securities Act registration statement number of the earlier effective registration statement for the same offering. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, a smaller reporting company, or an emerging growth company. See the definitions of large accelerated filer, accelerated filer, smaller reporting company, and emerging growth company in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
| Large accelerated filer | ☐ | Accelerated filer | ☐ | |||
| Non-accelerated filer | ☒ | Smaller reporting company | ☐ | |||
| Emerging Growth Company | ☒ | |||||
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 7(a)(2)(B) of the Securities Act. ☐
The registrant hereby amends this registration statement on such date or dates as may be necessary to delay its effective date until the registrant shall file a further amendment that specifically states that this registration statement shall thereafter become effective in accordance with Section 8(a) of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, or until this registration statement shall become effective on such date as the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission, acting pursuant to said Section 8(a), may determine.
Table of Contents
The information in this preliminary prospectus is not complete and may be changed. These securities may not be sold until the registration statement filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission is effective. This preliminary prospectus is not an offer to sell these securities and it is not soliciting an offer to buy these securities in any jurisdiction where the offer or sale is not permitted.
Subject to Completion, dated , 2024
Preliminary Prospectus
Shares

Tamboran Resources Corporation
Common Stock
This is the initial public offering of common stock of Tamboran Resources Corporation, a Delaware corporation. We are offering shares of our common stock. We have granted the underwriters a 30-day option to purchase up to additional shares from us at the initial public offering price, less the underwriting discounts and commissions.
Depositary shares, referred to as CHESS Depository Interests (CDIs), representing units of beneficial interests in shares of our common stock, are listed on the Australian Stock Exchange (ASX) under the symbol TBN. This prospectus does not constitute an offer to sell, or the solicitation of any offer to buy, any CDIs.
We anticipate that the initial public offering price of our common stock will be between $ and $ per share. We intend to apply to list our common stock on the New York Stock Exchange (the NYSE) under the symbol TBN.
We are an emerging growth company as the term is used in the Jumpstart Our Business Startups Act of 2012 (JOBS Act) and, as such, have elected to comply with certain reduced public company reporting requirements. See Prospectus SummaryEmerging Growth Company Status.
Investing in our common stock involves risks, including those described under Risk Factors beginning on page 18 of this prospectus.
| Per Share | Total | |||
| Public offering price |
$ | $ | ||
| Underwriting discount and commissions(1) |
$ | $ | ||
| Proceeds to us before expenses |
$ | $ |
| (1) | The underwriters will also be reimbursed for certain expenses incurred in this offering. See Underwriting for additional information regarding underwriting compensation. |
Neither the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission nor any state securities commission has approved or disapproved of these securities or determined if this prospectus is truthful or complete. Any representation to the contrary is a criminal offense.
The underwriters expect to deliver the shares of our common stock on or about , 2024.
Joint Book-Running Managers
| BofA Securities | Citigroup |
Co-Managers
The date of this prospectus is , 2024.
Table of Contents

Table of Contents
| Page | ||||
| 1 | ||||
| 16 | ||||
| 18 | ||||
| 57 | ||||
| 60 | ||||
| 61 | ||||
| 62 | ||||
| 63 | ||||
| MANAGEMENTS DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS |
65 | |||
| 78 | ||||
| 87 | ||||
| 115 | ||||
| 121 | ||||
| 129 | ||||
| 130 | ||||
| 132 | ||||
| 140 | ||||
| 142 | ||||
| MATERIAL U.S. FEDERAL INCOME TAX CONSEQUENCES TO NON-U.S. HOLDERS OF OUR COMMON STOCK |
145 | |||
| 149 | ||||
| 153 | ||||
| 154 | ||||
| 155 | ||||
| INDEX TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION |
F-1 | |||
Through and including , 2024 (the 25th day after the date of this prospectus), all dealers that effect transactions in our common stock, whether or not participating in this offering, may be required to deliver a prospectus. This delivery requirement is in addition to a dealers obligation to deliver a prospectus when acting as an underwriter and with respect to unsold allotments or subscriptions.
You should rely only on the information contained in this prospectus or in any free writing prospectus that we authorize to be distributed to you. We and the underwriters have not authorized anyone to provide you with any information other than that contained in this prospectus or in any free writing prospectus prepared by or on behalf of us or to which we have referred you, and neither we, nor the underwriters take responsibility for any other information others may give you. We are offering to sell, and seeking offers to buy, shares of our common stock only in jurisdictions where such offers and sales are permitted. The information in this prospectus or any free writing prospectus is accurate only as of its date, regardless of its time of delivery or the time of any sale of shares of our common stock. Our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects may have changed since that date.
For investors outside the United States: We and the underwriters have not done anything that would permit a public offering of the securities offered hereby or possession or distribution of this prospectus, any amendment or supplement to this prospectus, or any applicable free writing prospectus in any jurisdiction where action for that purpose is required, other than in the United States. Persons outside the United States who come into possession of this prospectus, any amendment or supplement to this prospectus, or any applicable free writing prospectus
i
Table of Contents
must inform themselves about, and observe any restrictions relating to, the offering of the securities and the distribution of this prospectus, any amendment or supplement to this prospectus, or any applicable free writing prospectus outside of the United States.
This prospectus, the registration statement of which this prospectus forms a part and the offering have not been, nor will they need to be, lodged with the Australian Securities & Investments Commission. This prospectus and the registration statement of which this prospectus forms a part are not a Prospectus under Chapter 6D of the Corporations Act 2001 (Cth) of Australia, or the Australian Corporations Act. Any offer of shares of our common stock in Australia is made only to persons to whom it is lawful to offer shares of our common stock without disclosure under one or more of certain of the exemptions set out in section 708 of the Australian Corporations Act, or an exempt person. Further details of the exemptions are set out below in Underwriting Notice to Prospective Investors Australia. By accepting this prospectus, an offeree in Australia represents that the offeree is an exempt person. No shares of our common stock will be issued or sold in this offering in circumstances that would require the giving of a Prospectus under Chapter 6D of the Australian Corporations Act.
Industry and Market Data
In this prospectus, we present certain market and industry data. This information is based on third-party sources that we believe to be reliable as of their respective dates. Neither we nor the underwriters have independently verified any third-party information. Some data is also based on our good faith estimates. Expectations of our and our industrys future performance are necessarily subject to a high degree of uncertainty and risk due to a variety of factors, including those described in Risk Factors. These and other factors could cause future performance to differ materially from our expectations. See Cautionary Statement Regarding Forward-Looking Statements.
Presentation of Financial and Operating Data
Unless indicated otherwise, the historical financial information presented in this prospectus is that of Tamboran Resources Limited (our Predecessor) and its consolidated subsidiaries as of and for the year ended June 30, 2023 or 2022, as applicable. The unaudited pro forma financial information presented in this prospectus presents the historical results of our Predecessor on a pro forma combined basis to give effect to this offering, the use of proceeds therefrom, and the corporate reorganization as if they had occurred at the beginning of the period presented. See Corporate Reorganization included elsewhere in this prospectus. Unless otherwise indicated, information presented in this prospectus (i) assumes that the underwriters option to purchase additional common stock is not exercised and (ii) assumes that the initial public offering price of the shares of our common stock will be $ per share (which is the midpoint of the estimated price range set forth on the cover page of this prospectus).
In addition, unless indicated otherwise, the operational data presented in this prospectus is that of our Predecessor and its consolidated subsidiaries on a consolidated basis as of and for the periods presented.
Our historical operating and financial data may not be comparable between periods presented in this prospectus and to future periods. See Managements Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations Factors that Affect Comparability of Our Results of Operations.
Trademarks and Trade Names
We own or have rights to various trademarks, service marks and trade names that we use in connection with the operation of our business. This prospectus may also contain trademarks, service marks and trade names of
ii
Table of Contents
third parties, which are the property of their respective owners. Our use or display of third parties trademarks, service marks, trade names or products in this prospectus is not intended to, and does not imply a relationship with, or endorsement or sponsorship by us. Solely for convenience, the trademarks, service marks and trade names referred to in this prospectus may appear without the ®, or SM symbols, but such references are not intended to indicate, in any way, that we will not assert, to the fullest extent under applicable law, our rights or the rights of the applicable licensor to these trademarks, service marks and trade names.
Rounding and Percentages
The financial information and certain other information presented in this prospectus have been rounded to the nearest whole number or the nearest decimal. Therefore, the sum of the numbers in a column may not conform exactly to the total figure given for that column in certain tables in this prospectus. In addition, certain percentages presented in this prospectus reflect calculations based upon the underlying information prior to rounding and, accordingly, may not conform exactly to the percentages that would be derived if the relevant calculations were based upon the rounded numbers or may not sum due to rounding.
Currency Exchange Rate Data
Our functional currency is the Australian dollar and our consolidated financial statements are presented in U.S. dollar. The functional currency is the currency of the primary economic environment in which an entitys operations are conducted. We translate our consolidated financial statements into the presentation currency using exchange rates in effect on the relevant balance sheet date for assets and liabilities and average exchange rates for the period for statement of operations accounts, with the difference recognized as a separate component of stockholders equity.
The following exchange rates were used to translate our consolidated financial statements and other financial and operational data shown in constant currency:
| Average for the Fiscal Year Ended June 30, |
||||||||
| 2023 | 2022 | |||||||
| Australian dollar |
$ | 0.67 | $ | 0.73 | ||||
The following table lists, for each period presented, the high and low exchange rates, the average of the exchange rates on each business day during the period indicated and the exchange rates at the end of the period for one U.S. dollar, expressed in Australian dollars, based on the closing midrate as reported by FactSet.
| Fiscal Year Ended June 30, |
||||||||
| 2023 | 2022 | |||||||
| High for the period |
0.712x | 0.762x | ||||||
| Low for the period |
0.622x | 0.688x | ||||||
| End of the period |
0.666x | 0.688x | ||||||
| Average for the period(1) |
0.673x | 0.726x | ||||||
| (1) | Average represents the average of the rates on each business day during the period. |
The above rates may differ from the actual rates used in the preparation of the financial statements and other financial information appearing in this prospectus. Our inclusion of these exchange rates is not meant to suggest
iii
Table of Contents
that the Australian dollar amounts actually represent such U.S. dollar amounts or that such amounts could have been converted into U.S. dollars at any particular rate, if at all.
Other Considerations
This prospectus contains forward-looking statements that are subject to a number of risks and uncertainties, many of which are beyond our control. See Risk Factors and Cautionary Statement Regarding Forward-Looking Statements for additional information regarding these risks.
You should read this prospectus and any written communication prepared by us or on our behalf in connection with this offering, together with the additional information described in the section of this prospectus titled Where You Can Find More Information. We have not authorized anyone to provide you with information or to make any representation in connection with this offering other than those contained herein. If anyone makes any recommendation or gives any information or representation regarding this offering, you should not rely on that recommendation, information or representation as having been authorized by us, the underwriters or any other person on our behalf. The information contained in this prospectus is accurate only as of the date of which it is shown, or if no date is otherwise indicated, the date of this prospectus, regardless of the time of delivery of this prospectus or of any sale of our shares of common stock. We are offering to sell, and seeking offers to buy, shares of common stock only in jurisdictions where offers and sales are permitted. Our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects may have changed since that date. Information contained on our website is not part of this prospectus.
No action is being taken in any jurisdiction outside the United States to permit a public offering of shares of common stock or possession or distribution of this prospectus in that jurisdiction. Persons who come into possession of this prospectus in jurisdictions outside the United States are required to inform themselves about and to observe any restrictions as to this offering and the distribution of this prospectus applicable to that jurisdiction.
Glossary of Natural Gas Terms
The following are abbreviations and definitions of certain terms used in this prospectus, which are commonly used in the natural gas industry:
Bcf refers to one billion cubic feet.
Btu refers to British thermal unit, which is the heat required to raise the temperature of one pound of liquid water by one degree Fahrenheit.
CCUS refers to carbon capture, utilization and sequestration.
CO2 refers to carbon dioxide.
CO2e refers to carbon dioxide equivalent.
gross acres or gross wells refers to the total acres or wells, as the case may be, in which a working interest is owned.
Henry Hub refers to a natural gas pipeline located in Erath, Louisiana that serves as the official delivery location for futures contracts on the NYMEX. The settlement prices at the Henry Hub are used as benchmarks for the North American natural gas market.
iv
Table of Contents
Mcf refers to one thousand cubic feet.
Mcf/d refers to one thousand cubic feet per day.
MMboe refers to one million barrels of oil equivalent.
MMBtu refers to one million Btus.
MMcf refers to one million cubic feet.
MMcf/d refers to one million cubic feet per day.
Mtpa refers to million metric tons per year.
net acres refers to the gross acres on which an owner holds an interest, proportionally reduced by the working interest in such acreage. For example, an owner who has 50% interest in 100 acres owns 50 net acres.
ORRI refers to overriding royalty interest.
Scope 1 emissions refers to direct GHG emissions that occur from sources that are controlled or owned by an organization.
Scope 2 emissions refers to indirect GHG emissions associated with the purchase of electricity, steam, heat or cooling.
Scope 3 emissions refers to GHG emissions that result from the end use of an organizations products, as well as emissions from other business activities from assets not owned or controlled by the organization but that the organization indirectly impacts in its value chain.
working interest refers to the right granted to the lessee of a property to explore for and to produce and own natural gas or other minerals. The working interest owners bear the exploration, development, and operating costs on either a cash, penalty, or carried basis.
Commonly Used Defined Terms
As used in this prospectus, unless the context indicates or otherwise requires, the terms listed below have the following meanings:
Beetaloo refers to the Beetaloo Basin of the Northern Territory, Australia.
Beetaloo Joint Venture refers to the unincorporated joint venture in respect to EPs 76, 98 and 117, between the TB2 Joint Venture (77.5% working interest) and Falcon (22.5% non-operated working interest).
bp refers to BP Singapore Pte. Ltd, a subsidiary of BP plc.
bylaws refers to the bylaws of Tamboran Resources Corporation.
CDI refers to a CHESS Depository Interest.
certificate of incorporation refers to the certificate of incorporation of Tamboran Resources Corporation.
Code refers the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended.
v
Table of Contents
corporate reorganization refers to the transactions pursuant to which, among other things, we (i) issued to eligible shareholders of our Predecessor one CDI of our common stock for every one ordinary share of Tamboran Resources Limited, in each case, as held on the scheme record date, (ii) amended the terms of each of the outstanding options to acquire ordinary shares of Tamboran Resources Limited so that the entitlements of option holders to be issued ordinary shares in Tamboran Resources Limited instead became entitlements to be issued CDIs in the Company, (iii) maintained an ASX listing for our CDIs, with each CDI representing 1/200th of a share of our common stock, (iv) delisted our Predecessors ordinary shares from the ASX, and (v) became the parent company to Tamboran Resources Limited.
Corporations Act refers to the Australian Corporations Act, 2001 (Cth).
Daly Waters or DWE refers to Daly Waters Energy, LP, which is 100% owned by Formentera Australia Fund, LP, which is managed by Formentera Partners, LP, a private equity firm of which Bryan Sheffield serves as managing partner.
ESG refers to environmental, social and governance.
Falcon or Falcon Oil & Gas or FOG refers to Falcon Oil and Gas Australia Ltd, a wholly owned subsidiary of Falcon Oil and Gas Limited (TSX.V: FOG, London AIM: FO).
Federal Government refers to the federal government of Australia.
GAAP refers to generally accepted accounting principles in the United States.
GHG refers to greenhouse gases.
governing documents refers to our certificate of incorporation and our bylaws.
H&P refers to Helmerich & Payne International Holdings, LLC.
McArthur Joint Venture refers to the unincorporated joint venture in respect to EP 161 between us (25% non-operated working interest) and Santos (75% working interest).
Northern Territory refers to the Northern Territory of Australia.
NSAI refers to Netherland, Sewell & Associates, Inc., an independent third-party provider of petroleum consulting services.
operational net zero refers to the full elimination and/or offset of Scope 1 and Scope 2 emissions in our owned and operated upstream businesses.
Origin Retail refers to Origin Energy Retail Pty Ltd.
Origin B2 refers to Origin Energy B2 Pty Ltd.
Petroleum Act refers to the Petroleum Act 1984 (NT).
Predecessor refers to Tamboran Resources Limited, an Australian corporation and wholly owned subsidiary of Tamboran Resources Corporation.
vi
Table of Contents
Santos QNT or Santos Ltd refers to Santos QNT Pty Ltd, a wholly owned subsidiary of Santos Ltd (ASX: STO).
scheme of arrangement refers to a statutory scheme of arrangement under Australian law under Part 5.1 of the Corporations Act.
Shell refers to Shell Eastern Trading (Pte) Ltd, a subsidiary of Shell plc.
Tamboran or the Company refers to Tamboran Resources Corporation, a Delaware corporation and Predecessor, as context requires.
Tamboran B2 refers to Tamboran B2 Pty Ltd.
TB2 Joint Venture refers to Tamboran (B1) Pty Ltd, a 50 / 50 joint venture between us and Daly Waters that holds a 77.5% working interest in the Beetaloo Joint Venture through its wholly owned subsidiary, Tamboran B2 Pty Ltd.
vii
Table of Contents
This summary highlights information contained elsewhere in this prospectus. You should read the entire prospectus carefully before making an investment decision in shares of our common stock, including the information under the headings Risk Factors, Cautionary Note Regarding Forward-Looking Statements and Managements Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations and the historical and pro forma consolidated and combined financial statements and the related notes thereto appearing elsewhere in this prospectus. Except where the context suggests otherwise, the information presented in this prospectus (i) assumes that the underwriters do not exercise their option to purchase up to an additional shares of our common stock and (ii) reflects the completion of our corporate reorganization described in this prospectus under Corporate Reorganization. In this prospectus, unless the context otherwise requires, the terms we, us, our and the Company refer to (i) Tamboran Resources Limited, an Australian public company formed in 2009, and its subsidiaries (our Predecessor), which is our predecessor entity before the completion of our corporate reorganization described in this prospectus and (ii) Tamboran Resources Corporation, a Delaware corporation formed in 2023, and its subsidiaries (Tamboran), which is our successor entity after the completion of our corporate reorganization described in this prospectus. Please read Corporate Reorganization. We have provided definitions for some of the natural gas industry terms used in this prospectus in the Glossary. References to dollars, $, U.S. dollars and US$ refer to United States dollars; and references to Australian dollars and A$ refer to Australian dollars.
Our Company
Overview
We are an early stage, growth-driven independent natural gas production company focused on an integrated approach to the commercial development of the natural gas resources in the Beetaloo located within the Northern Territory of Australia. We and our working interest partners have exploration permits (EPs) to approximately 4.7 million gross (1.9 million net to Tamboran) contiguous prospective acres, and are currently the largest acreage holder in the Beetaloo. We believe natural gas will play a significant role in the transition to cleaner energy and are committed to supporting the global energy transition by developing commercial production of natural gas in the Beetaloo with net zero equity Scope 1 and 2 emissions.
Our Assets
The Beetaloo, located approximately 300 miles southeast of the city of Darwin in the Northern Territory of Australia, covers approximately 10,800 square miles (or approximately 7 million acres) of outback and is believed to contain significant quantities of unconventional natural gas. To date, more than $600 million has been invested by various public and private companies in the exploration, appraisal and development of the Beetaloo. Based on data from our appraisal wells, we believe the most productive sections of the Beetaloo to be those at greater than 6,000-foot vertical depth. Initial data suggests that these sections demonstrate the highest productivity and reservoir pressures and exhibit the lowest decline rates in the Beetaloo. To date, our appraisal and development activities have focused on the dry gas shale target of the Middle Velkerri-B formation, although we expect to eventually evaluate other benches for future development. Regional data from exploration wells, initial results from our appraisal wells, including well log and core data, as well as available 2-D seismic data, indicate that the geological properties of the Middle Velkerri section in the Beetaloo are widespread and contiguous across an area encompassing approximately 950 square miles and that the Beetaloo has geology similar to those of the Marcellus Shale of the Appalachian Basin in the northeastern United States.
1
Table of Contents
We have participated in six appraisal wells over the last 18 months, four of which we drilled as the operator:
| Well Name |
Operator | Non-Operator(s) | Exploration Permit |
Date Drilled | Tamboran Working Interest |
|||||||
| Tanumbirini #2 (T2H) |
Santos | Tamboran | 161 | 2021 | 25 | % | ||||||
| Tanumbirini #3 (T3H) |
Santos | Tamboran | 161 | 2021 | 25 | % | ||||||
| Maverick 1V (M1V) |
Tamboran | N/A | 136 | August 2022 | 100 | % | ||||||
| Amungee NW-2H (A2H) |
Tamboran | DWE & FOG | 98 | November 2022 | 38.75 | % | ||||||
| Shenandoah South 1H (SS1H) |
Tamboran | DWE & FOG | 117 | August 2023 | 38.75 | % | ||||||
| Amungee NW 3H (A3H) |
Tamboran | DWE & FOG | 98 | September 2023 | 38.75 | % | ||||||
We anticipate that flow test results from our operated well SS1H will be available during the first quarter of 2024. Flow test results from the two wells in which we participated on a non-operated basis, the T2H and T3H, delivered initial 30-day gross production (IP30) rates of 2.1 MMcf/d and 3.1 MMcf/d, respectively, over approximately 2,200-foot and 2,000-foot horizontal sections. Normalizing those production rates (a common practice in U.S. shale operations) to our optimal development plan of 10,000-foot horizontal sections, we expect the IP30 rates in T2H and T3H would have been approximately 9.5 MMcf/d and 15.5 MMcf/d, respectively.
T2H and T3H were drilled with low intensity, shorter lateral lengths (approximately 2,000 feet), while SS1H and A3H were drilled with Helmerich & Payne International Holdings, LLCs (H&P) modern US FlexRig® that was imported into Australia in 2023 and will increase spacing between well pads. In our next phase of drilling and completion, we anticipate increasing frac stages by extending the horizontal length of our wells. Our contiguous acreage position and the scarcity of other operators or urban areas near the Beetaloo will provide us with the space necessary to eventually drill pad wells with up to three to four-mile horizontal laterals, greatly increasing efficiencies and production from a relatively smaller number of wells. We have experienced geologic complexity, similar to U.S. shale basins in our drilling activities to date, which, based on that experience and seismic data, we believe to be generally characteristic of the Beetaloo. We believe the relative lack of complexity in the geology of the Beetaloo will enable us to achieve more predictable well recoveries and permit greater lateral lengths.
Our key assets are (i) a 25% non-operated working interest in EP 161, (ii) a 38.75% working interest in EP 76, 98 and 117, where we are the operator, and (iii) a 100% working interest in EPs 136, 143 and EP(A) 197, where we are the operator, all of which are located in the Beetaloo. We have an undivided 50% interest in EPs covering 4.7 million gross (1.9 million net) acres through the TB2 Joint Venture with Daly Waters. We hold our rights in the Beetaloo through EPs granted by the government of the Northern Territory for initial periods of five years with a right to renew twice for additional five-year periods, and with a further right to extend the term with Ministerial approval based upon approval of a work program. An EP grants the holder the exclusive right to explore for petroleum and to carry on such operations and execute such works as are necessary for that purpose, in the exploration permit area. We are also entitled to apply for a retention license (RL) in areas where petroleum has been identified but commercial viability is yet to be established. RLs are for a term of five years and may be renewed without a statutory limitation. An RL would provide us with the exclusive right to carry on in the license area geological, geophysical, and geochemical programs and other operations and works, including appraisal drilling, as reasonably necessary to evaluate the potential of the petroleum believed to be present in the license area. Upon commercialization of the natural gas properties subject to an EP or RL, we are eligible to apply to convert relevant productive areas of our EPs (or any future RLs) into production licenses (PL) with an initial term of either 21 or 25 years as determined by the Northern Territory Minister for Environment (the Minister), which can be further renewed. A PL has exclusive rights to explore for petroleum and recover it from the license area and to carry out such operations and execute such works in the license area as are necessary for the exploration for and recovery of petroleum. We will be required to pay a statutory royalty to the Northern Territory Government (NT Government) of 10% of the gross value, at the well-head, of all petroleum produced
2
Table of Contents
in connection with a PL or EP in a project area. The gross value of that petroleum is determined by the Petroleum Royalty Act (NT). Additionally, we will pay royalties of between 6% to 11% to other third parties under certain commercial arrangements. See BusinessOur Assets within the Beetaloo, BusinessEnvironmental Matters and Regulation and Certain Relationships and Related Party Transactions.
Our Business Plan
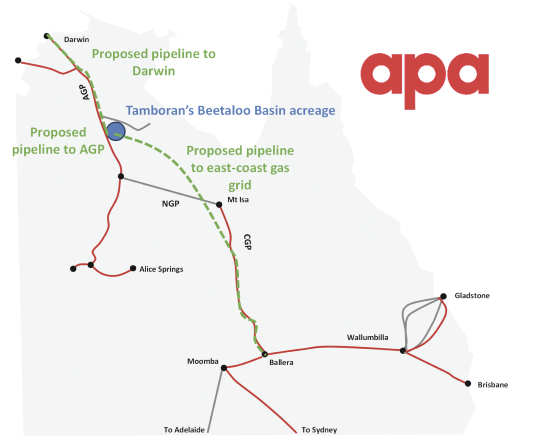
Our business plan consists of three distinct phases in the development of the Beetaloo. The focus of the first phase will be on the transition from exploration activities to the commercialization of our Beetaloo properties. In furtherance of that goal, we expect to drill and complete an additional six to 10 appraisal wells by the end of 2025. Based on our review of seismic data, well logs, rock core and production data from completed appraisal wells, we have already identified what we believe to be the most productive acreage and shale benches to target for our first stage wells. Beginning in 2026, subject to approval by the Minister responsible for the Petroleum Act, we plan to market the gas from the appraisal wells, which is expected to be modest, in the Northern Territory, with the goal of generating operating cash flow for further development. The Beetaloo is currently serviced by two open-access pipelines that are sized to accommodate the ~60 MMcf/d local market and also provide access to the deeper Australian East Coast market. We have early development agreements with APA Group, Australias largest gas infrastructure company by volume (ASX: APA) whereby APA has commenced preliminary work on a project to ultimately build, own, and operate a new ~20 mile pipeline to connect our appraisal wells to the existing gas transmission network through the Amadeus Gas Pipeline (AGP), subject to the terms of definitive development agreements. In parallel, Tamboran, through the Beetaloo Joint Venture, is aiming to sanction a 40 MMcf/d compression facility at Shenandoah South that would upgrade the raw gas to meet sales gas quality. We expect the compression facility, together with the associated wells and gathering infrastructure, to require approximately $350 million ($135 million net to Tamboran) in capital costs. Gas sales are expected to commence from our appraisal wells in the first quarter of 2026. Through the course of the completion of the additional six to 10 appraisal wells, we believe we can reduce costs through greater efficiency while simultaneously providing us sufficient data to confirm the estimated ultimate recovery (EUR) for wells drilled in the Beetaloo. Our development plan seeks to efficiently drill from pad wells, utilizing long laterals and modern completion techniques employed by U.S. onshore operators. We expect the cost structure and production profiles achieved with our appraisal wells to lead to a financial investment decision (FID) for an initial large scale drilling program in our second phase.
The second phase of our business plan involves building our drilling program to produce natural gas to supply the Australian East Coast and Northern Territory markets. We anticipate drilling as many as 100 to 200 wells during this second phase, which may commence as early as 2026, subject to the completion of certain third-party infrastructure projects. The current pipeline infrastructure, the AGP in the Northern Territory, can export ~50 MMcf/d northbound and ~50 MMcf/d to the East Coast. We have a set of early development agreements with APA whereby APA will commence work on a project to ultimately build, own, and operate a new approximately 1,000 mile pipeline to connect the Beetaloo to the main trunk line of the East Coast Gas Grid, subject to the terms of definitive development agreements. The new pipeline is anticipated to reduce the cost of transporting gas from the Northern Territory to the East Coast by up to 50%. We have non-binding letters of intent
3
Table of Contents
from six of Australias largest energy retailers to purchase natural gas from us, with an aggregate volume of 875 MMcf/d for a period of up to 10 to 15 years.
In the third phase of our business plan, following commercialization of the Beetaloo, we intend to drill additional wells with the intent to supply natural gas for export through the existing liquified natural gas (LNG) plants in Darwin and our proposed 6.6 Mtpa Northern Territory LNG export facility (NTLNG) to South and East Asian markets. Depending on the quantum of ullage in the existing LNG plants in Darwin, this phase may occur before or in parallel with the second phase. In consideration of our proposed NTLNG project, the government of the Northern Territory of Australia has awarded us exclusive use of a 170-hectare (approximately 420 acres) site for a 12-month term (which commenced June 2023) for a construction study with respect to our proposed NTLNG project within the Middle Arm Sustainable Development precinct (MASD). The MASD, an industrial complex adjacent to the city of Darwin, seeks to provide infrastructure focused on low emissions operations, for the export, processing, storage, shipping and rail transportation of LNG and other hydrocarbons. The MASD precinct is currently home to an export hub with two existing and operational LNG export terminals, the Darwin LNG terminal with a capacity of 3.7 Mtpa and the Ichthys LNG terminal with a capacity of 8.9 Mtpa. The Australian government has committed A$1.5 billion in investments commencing in 2025 to further develop MASD infrastructure and access, including dredging of the deepwater port, construction of road and rail access and distribution of electricity. We estimate total time required for construction of the NTLNG project to be between three to five years and have non-binding memoranda of understanding with each of BP Singapore Pte. Ltd (bp) and Shell Eastern Trading (Pte) Ltd (Shell) for 20-year LNG purchase contracts. We could additionally sell our future production if, for example, our NTLNG project faces any delays,
4
Table of Contents
through the two existing and operational LNG terminals near Darwin. We intend to seek additional strategic partners for the financing and development of these and other infrastructure projects.
Our business and development plans include the continuous focus on reducing cost while increasing production efficiencies. We believe that importing U.S. unconventional drilling and completion techniques, best-practices and technology, together with the right personnel, will reduce the incremental cost to drill and complete each subsequent well. We currently have on contract one H&P FlexRig® until August 2025 with a 10-year option to contract for up to five additional rigs. The drilling and completion costs for our most recent SS1H and A3H wells are expected to be approximately $30.3 million, on average per well. We estimate the drilling and completion costs of each of the remainder of our additional appraisal wells will be approximately $26 million as a result of our application of U.S. practices, longer lateral lengths and increased number of stimulated stages. We are targeting long-term development well costs of $16 million per well at depths of approximately 9,800 feet with 60 stages. We believe by taking advantage of efficiencies related to economies of scale, continued infrastructure development in the Beetaloo and resource maturation, over time we will significantly reduce the cost to drill and complete our wells.
The Opportunity
We believe there is significant opportunity to supply natural gas to both domestic Australian markets and select South and East Asian markets. According to the International Energy Agency, 70% of future growth in global electricity demand will come from high-growth and high-demand markets in Asia. Demand from Australias East Coast natural gas market has increased significantly in recent years, as a result of the construction of export projects during the 2010s and underinvestment in natural gas production and infrastructure on the East Coast, and is now expected to result in gas shortages through the remainder of this decade, according to the Australian Competition and Consumer Commission. Meeting this forecasted demand will require significant investment in new natural gas production and infrastructure.
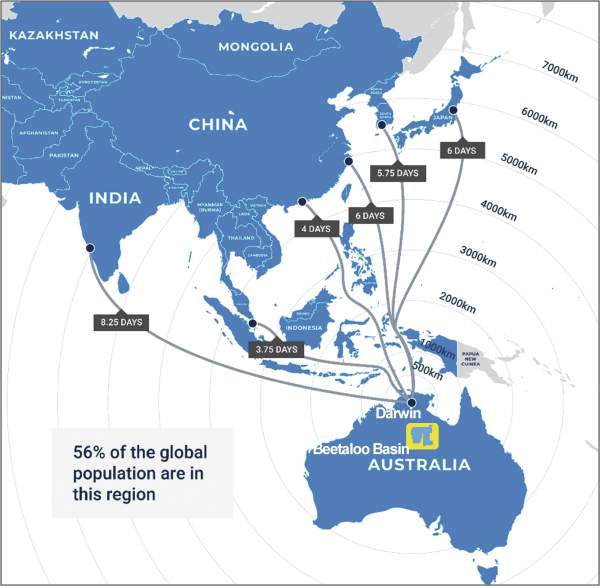
The relative geographic proximity of the existing and planned LNG export terminals in northern Australia to Asian markets provides Northern Territory operators with competitive advantages over current LNG suppliers from the Middle East and the United States. For example, LNG can be delivered from Darwin to Singapore in less than four days, and to China and Japan within six days. Shipments from the Middle East must travel through the Red Sea, while shipments from the United States must travel around the southern cape of Africa or through the Panama Canal, all of which often result in delays or higher costs. The cost to ship LNG from Darwin to Japan is approximately 40% lower than the cost to ship LNG from Qatar. Additionally, spot prices in certain South and East Asian regional markets have historically been significantly higher than spot prices at Henry Hub. For example, during the calendar year ended 2023, spot prices for natural gas delivered to Henry Hub averaged $2.54 per MMBtu while over that same period the Japan Korea Marker (JKM) continuous futures price for LNG averaged $14.45 per MMBtu.
5
Table of Contents
The following image illustrates the delivery times of LNG from Australia to select South and East Asian markets:
Preliminary results and third-party data indicate that natural gas produced in the Beetaloo generally has lower carbon dioxide content compared to natural gas produced elsewhere in Northern Australia and major fields supplying Australias East Coast gas market. We believe our application of U.S. drilling and completion technology will provide us with a competitive advantage to achieve natural gas production in compliance with the Australian governments recently enacted GHG regulations. The Australian governments current policy is to target net zero carbon emissions economy-wide by 2050. Additionally, the Australian government requires all shale gas production in the Beetaloo following commercialization to be conducted on a Scope 1 net zero emissions basis. We have set a target to exceed these requirements by reaching net zero equity Scope 1 and 2 GHG emissions upon commencement of commercial production. We expect there to be a variety of means in
6
Table of Contents
which we could achieve our operational net zero equity goals, including but not limited to, utilizing carbon offsets, for which the prices are capped by applicable law, exploring opportunities to power our facilities with renewable energy sources, implementing methane minimization technology in the design of our facilities and integrating a carbon capture storage hub with our proposed NTLNG project.
We believe natural gas produced in the Beetaloo can play a key role in supporting the emissions reduction targets of many regional markets through the transition of coal-to-gas fired power plants. The domestic Australian market is primarily reliant on coal with over 60% of electricity generation across Victoria, New South Wales and Queensland supplied from coal-fired power, according to the Australian Department of Industry, Science, Energy and Resources. According to the U.S. Energy Information, in 2021, coal supplied a majority of the total energy consumption in China as well as Southeast Asia generally.
Competitive Strengths
We have a number of strengths that we believe will help us successfully execute our business strategy, including:
| | Leading acreage holder and operator in the high-quality Beetaloo. As a result of a series of opportunistic acquisitions, including through the TB2 Joint Venture, we have established the largest contiguous acreage position in the Beetaloo of any natural gas production company. Our Beetaloo assets cover approximately 4.7 million gross prospective acres (1.9 million contiguous net acres), the most extensive position reported in the Beetaloo. To date, 21 wells have been drilled in the Beetaloo intersecting the Middle Velkerri shales. Of those wells, only six have been horizontal wells and 15 have been vertical wells that were either exploring for other plays (liquids) or delineating the shale. Approximately 5,000 miles of 2-D seismic data has been collected over the Beetaloo. Based on the extensive 2-D seismic data available to us as well as our own preliminary well results, we believe our acreage position consists of significant quantities of high-quality natural gas in what we believe to be the core of the Velkerri shale gas play. Our initial development area of the Middle Velkerri-B shale shows an average shale thickness of 230 feet across a 610,473-acre area. Our independent reserve engineers, Netherland Sewell & Co., estimate the Middle Velkerri section to be continuous across an approximately 160 mile area. The Beetaloo has very few operators and no urban areas. The geographical features of the Beetaloo, our expansive contiguous prospective acreage position and very few restrictive boundaries support 10,000-ft. laterals and U.S. style unconventional drilling techniques. In addition, we believe our position as the leading acreage holder in the Beetaloo will support our efforts to establish commercial production in volumes sufficient to stimulate investment in in-basin frac sand and other services. |
| | Premium Markets. We expect the relative geographic proximity of the Beetaloo to the major population centers on the Australian East Coast and the Asian LNG markets to provide us the opportunity to potentially obtain attractive prices for our natural gas relative to markets in North America based on historical pricing. For example, during the calendar year ended 2023, spot prices for natural gas delivered from Henry Hub averaged 2.54 per MMBtu. Over that same period, the Japan Korea Marker (JKM) continuous futures price of LNG averaged $14.45 per MMBtu. Although production costs in the Beetaloo are currently significantly higher than U.S. onshore operations, upon full commercialization of the Beetaloo, we expect those costs to decline. If the Australian East Coast and the Asian LNG markets maintain elevated prices relative to North America and we achieve our cost targets, we believe we will have an opportunity to potentially capture higher margins as compared to natural gas produced in the Marcellus Shale of the Appalachian Basin. |
| | High caliber and experienced management team with a track record of success. We maintain a highly experienced and knowledgeable management team with an average of over 25 years of experience among our senior management team. Our leadership team has significant experience |
7
Table of Contents
| managing integrated energy and power assets for large-scale enterprises, including companies such as Unocal, Chevron, Apache, and ExxonMobil. We also have a management team with extensive experience with vertical and horizontal drilling in unconventional plays. Joel Riddle, our CEO since 2013, has more than 25 years experience in the upstream oil and gas industry, and Faron Thibodeaux, our COO, has over 40 years of technical and operations experience in the energy industry. The board includes our Chairman Dick Stoneburner, the former co-founder, President and Chief Operating Officer of Petrohawk Energy Corporation and President North America Shale Production Division for BHP Billiton Petroleum, and Fredrick Barrett, co-founder and former CEO of Bill Barrett Corporation, each of whom have more than 35 years of experience raising capital and operating assets in the oil and gas industry. The Company has raised more than A$350 million to date through an initial public equity offering listed on the ASX, follow-on offerings, and private placements. |
| | Net Zero Equity Scope 1 and Scope 2 Emissions. Australian law requires that natural gas reserves in the Beetaloo be produced on a Scope 1 net zero basis upon achieving commercial production. We have a comprehensive sustainability program, which is overseen and directed by a Sustainability Committee composed of board members. We believe natural gas delivered from the Beetaloo will provide an attractive alternative for domestic and Asian economies seeking to reduce reliance on coal and reduce their own GHG emissions. |
| | High quality, blue-chip strategic partners. We have contracted H&P to exclusively provide drilling services for our wells in the Beetaloo. Our agreements with APA Group contemplate providing access to existing natural gas transmission pipelines to transport initial gas production and the construction of additional pipelines to connect with systems on the Australian East Coast and to Darwin in the Northern Territory. Our memoranda of understanding with each of bp and Shell contemplate 20-year LNG purchase agreements from our proposed NTLNG development. We have non-binding letters of intent from six of Australias largest energy retailers to purchase natural gas from us, with an aggregate volume of 875 MMcf/d for a period of up to 10 to 15 years. We are seeking to enter into definitive agreements with these strategic partners as we execute on subsequent phases of our business plan, and we will continue to seek additional strategic partnerships in the development of the Beetaloo. See BusinessAgreements Relating to the Development of our Assets and Certain Relationships and Related Party Transactions. |
Business Strategies
We intend to execute the following business strategies:
| | Commercialize our resources in the Beetaloo. We intend to commercialize our natural gas resources in the Beetaloo in accordance with the first phase of our business plan over the next two to three years. Leveraging the experience and data derived from our appraisal well program, we anticipate commencing a multi-year drilling program as early as 2026 for as many as 100 to 200 wells, subject to our ability to obtain the necessary capital and completion of certain third-party infrastructure projects, including the proposed pipelines with APA Group. |
| | Pursue an integrated approach to the development and scale of natural gas production and transportation projects. We aim to build additional infrastructure with partners to support the take-away of up to 2.0 Bcf/d of gross production following the initial commercialization of the Beetaloo. Adjacent to the Beetaloo are currently two natural gas pipelines, one running north to Darwin and another pipeline to the Australian East Coast. We are in discussion with APA Group to construct two larger diameter pipelines to each of Darwin and the Australian East Coast, and we anticipate commencing construction of our NTLNG project as early as 2027, subject to receiving the necessary approvals. Additionally, there are two LNG export terminals in operation near Darwin through which we can eventually sell additional production. |
8
Table of Contents
| | Import U.S. best practices to become a low-cost provider of natural gas to the Australian domestic market and regional Asian markets. We will continue to import best practices from the U.S. E&P industry to enhance production and reserve recovery per well while simultaneously reducing capital and operating costs. To date, horizontal drilling and completion techniques and pad drilling have not been widely used in the Australian E&P industry. Based on analysis of our preliminary results and seismic data, we believe the geology of the Beetaloo is conducive to U.S.-style unconventional drilling, and we have entered into an agreement with H&P to bring U.S. unconventional drilling rigs to the Beetaloo. We currently have on contract an H&P FlexRig® until August 2025 with an option to contract for additional rigs. Our A3H well was drilled to a total depth of 12,589 feet in less than 18 days, the fastest rate of any well drilled with a horizontal section in the Beetaloo, where wells have historically been drilled to depth in 45 days or more. |
| | Lower Emissions from Natural Gas Production. We aim to fulfill the Australian governments requirements in the achievement of net zero for our equity share of Scope 1 and 2 emissions from natural gas production. We intend to participate in an open-access, multi-user CCUS (carbon capture utilization and sequestration) project at the proposed NTLNG facility and will seek to power our gathering and processing facilities from renewable sources, including solar and wind, to the extent available. Our goal is to deliver LNG to global markets from net zero equity Scope 1 and 2 facilities in an effort to replace coal consumption, particularly in Australian and East Asian markets, with lower-emissions natural gas from the Beetaloo. |
Our Joint Venture Partner
Our largest shareholder is Bryan Sheffield. Mr. Sheffield, through Sheffield Holdings, LP (Sheffield), first began acquiring interests in Tamboran in November 2021, has made three subsequent equity investments and has now grown to become Tamborans largest shareholder, currently holding approximately 17% of outstanding common shares. Mr. Sheffield has significant investment experience in the U.S. unconventional energy sector. He previously served as the Chairman, CEO and Founder of Parsley Energy Inc., a major independent unconventional oil and gas producer in the Permian Basin in Texas. Parsley Energy was acquired by Pioneer Natural Resources Company in January 2021 for $7.3 billion. He is currently the Managing Partner of Formentera Partners, an energy private equity firm, which has raised $1.2 billion in equity since 2021.
In September 2022, Mr. Sheffield, through Daly Waters Energy, LP (Daly Waters), partnered with Tamboran through a newly formed 50 / 50 joint venture, Tamboran (B1) Pty Ltd (the TB2 Joint Venture), to acquire a 77.5% interest in EPs 76, 98, and 117 covering approximately four million gross prospective acres (1.5 million net prospective acres). We and Daly Waters each hold a 38.75% interest in these EPs. Daly Waters interest in the TB2 Joint Venture will be transferred to Mr. Sheffields private equity firm, Formentera Partners, where they intend to participate in the assets continued development. Mr. Sheffield, through Daly Waters Royalty LP (Daly Waters Royalty) also holds a 2.3% overriding royalty interest (ORRI) over all of our Beetaloo assets. See BusinessAgreements Relating to the Development of our Assets and Certain Relationships and Related Party Transactions.
Corporate Reorganization
Tamboran Resources Corporation, the issuer of the common stock being sold in this offering, was incorporated in Delaware on October 3, 2023 for the purpose of effecting our corporate reorganization pursuant to a scheme of arrangement under Australian law between the Company and Tamboran Resources Limited, an Australian public company, which we refer to as the corporate reorganization. On December 13, 2023, the Company acquired all of the outstanding ordinary shares of our Predecessor in exchange for 1,716,672,600 CDIs representing beneficial interests in 8,583,363 shares of our common stock. After giving effect to this offering, our Predecessors former shareholders will hold an economic interest equivalent to % of the Companys
9
Table of Contents
outstanding common stock, in the form of CDIs and shares of common stock. Upon consummation of the corporate reorganization, our Predecessors ordinary shares were delisted from the ASX. Other than the CDIs, the Companys common stock will not be listed on any Australian securities exchange. For additional information concerning our CDIs, see Description of Capital Stock CHESS Depositary Interests. Following the closing of the corporate reorganization transactions, the Companys assets consist primarily of 100% of the ordinary shares of our Predecessor.
The description of our business and our consolidated financial statements and other financial information included in this prospectus as of the dates and for the periods prior to the corporate reorganization reflect the business, results of operations and financial position of our Predecessor, and the description of our business and our consolidated financial statements and other financial information as of the dates and for the periods from and after the corporate reorganization reflect the business, results of operations and financial condition of the Company and its consolidated subsidiaries, in each case unless otherwise expressly stated or the context otherwise requires.
10
Table of Contents
Our Structure
The following diagram shows our simplified ownership structure immediately following this offering and the transactions related thereto (assuming that the underwriters option to purchase additional shares is not exercised):
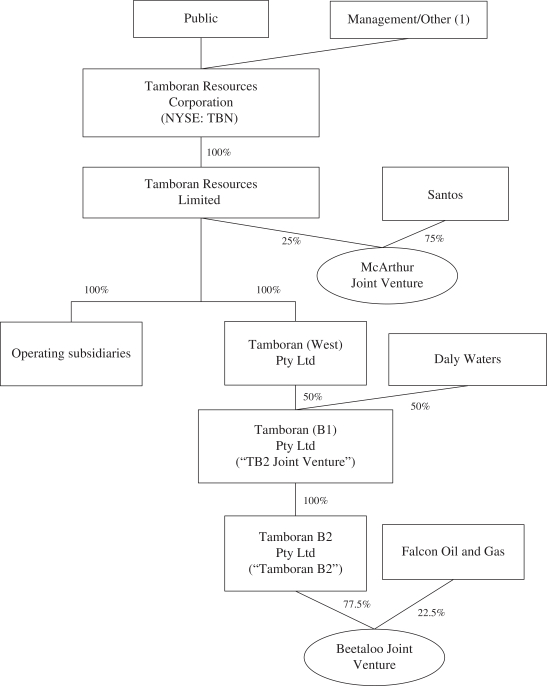
| (1) | Consists of Mr. Sheffield and his controlled funds, H&P, management, directors, and other employee stockholders. |
11
Table of Contents
Emerging Growth Company Status
We are an emerging growth company within the meaning of the federal securities laws. For as long as we are an emerging growth company, we may not be required to comply with certain requirements that are applicable to other public companies that are not emerging growth companies including, but not limited to, the auditor attestation requirements of Section 404 of the U.S. Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, as amended (the SOX), the reduced disclosure obligations regarding executive compensation in our periodic reports and proxy statements and the exemptions from the requirements of holding a nonbinding advisory vote on executive compensation and stockholder approval of any golden parachute payments not previously approved. Additionally, an emerging growth company can also take advantage of the extended transition period provided in Section 7(a)(2)(B) of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the Securities Act), for complying with new or revised accounting standards.
We intend to take advantage of these exemptions until we are no longer an emerging growth company. We will cease to be an emerging growth company upon the earliest of: (i) the last day of the fiscal year in which we have $1.235 billion or more in annual revenues, (ii) the date on which we become a large accelerated filer (the fiscal year-end on which the total market value of our common equity securities held by non-affiliates is $700.0 million or more as of December 31 of such year), (iii) the date on which we issue more than $1.0 billion of non-convertible debt over a three-year period or (iv) the last day of the fiscal year following the fifth anniversary of this offering.
In addition, Section 107 of the JOBS Act provides that an emerging growth company can take advantage of the extended transition period provided in Section 7(a)(2)(B) of the Securities Act, for complying with new or revised accounting standards. We have elected to take advantage of this extended transition period, which means that the financial statements included in this prospectus, as well as any financial statements that we file or furnish in the future, will not be subject to all new or revised accounting standards generally applicable to public companies for the transition period for so long as we remain an emerging growth company. As a result of this election, our financial statements may not be comparable to companies that comply with public company effective dates for such new or revised standards.
For a description of the qualifications and other requirements applicable to emerging growth companies and certain elections that we have made due to our status as an emerging growth company, see Risk FactorsRisks Related to the Offering and our Common StockFor as long as we are an emerging growth company, we will not be required to comply with certain reporting requirements, including those relating to accounting standards and certain disclosure about our executive compensation, that apply to other public companies.
Corporate Information
Headquartered in Sydney, Australia, we have been investing in the development of Australian oil and natural gas reserves since our formation in 2009. Since 2014, we have focused our development activities within the Northern Territory. Our Predecessor completed its initial public offering in Australia in July 2021 and was publicly listed on the Australian Securities Exchange under the ticker TBN. Our Predecessor was removed from the ASX following the corporate reorganization, at which time CDIs representing shares of common stock of Tamboran Resources Corporation were listed on the ASX under the same ticker TBN. We were incorporated in the State of Delaware on October 3, 2023 for the purposes of effecting the corporate reorganization.
Our principal executive offices are located at Suite 01, Level 39, Tower One, International Towers Sydney, 100 Barangaroo Avenue, Barangaroo NSW 2000, Australia and our telephone number at that address is +61 2 8330 6626. Our website address is www.tamboran.com. Following the closing of this offering we will make our periodic reports and other information filed with or furnished to the Securities and Exchange Commission (the SEC), available free of charge through our website as soon as reasonably practicable after those reports and other information are electronically filed with or furnished to the SEC. Information on, or otherwise accessible through, our website or any other website is not incorporated by reference into, and does not constitute a part of, this prospectus.
12
Table of Contents
THE OFFERING
| Issuer |
Tamboran Resources Corporation |
| Common stock offered by us |
shares (or shares if the underwriters option to purchase additional shares is exercised in full). |
| Option to purchase additional shares |
We have granted the underwriters a 30 day option to purchase up to an aggregate of additional shares of our common stock. |
| Common stock to be outstanding immediately after completion of this offering |
shares (or shares if the underwriters option to purchase additional shares is exercised in full). |
| Use of proceeds |
We expect to receive approximately $ million of net proceeds from the sale of our common stock in this offering, based upon the assumed initial public offering price of $ per share (the midpoint of the price range set forth on the cover page of this prospectus), after deducting underwriting discounts and estimated offering expenses (or approximately $ million if the underwriters option to purchase additional shares is exercised in full). Each $1.00 increase (decrease) in the public offering price would increase (decrease) our net proceeds by approximately $ million. |
| We intend to use all the net proceeds of this offering to fund our development plan and for working capital and other general corporate purposes. See Use of Proceeds. |
| Dividend policy |
We currently do not pay a fixed cash dividend to holders of our common stock. Any future determination related to our dividend policy will be made at the sole discretion of our board of directors. See Dividend Policy. |
| Listing and trading symbol |
We intend to apply to list our common stock on the New York Stock Exchange (the NYSE) under the symbol TBN. |
| Risk factors |
Investing in our common stock involves a high degree of risk. You should carefully read and consider the information set forth under Risk Factors beginning on page 18 of this prospectus and all other information set forth in this prospectus before deciding to invest in our common stock. |
Summary of Risk Factors
An investment in our securities involves a high degree of risk. The occurrence of one or more of the events or circumstances described in the section titled Risk Factors, alone or in combination with other events or circumstances, may materially adversely affect our business, financial condition and operating results. In that event, the trading price of our securities could decline, and you could lose all or part of your investment. Such risks include, but are not limited to:
13
Table of Contents
Risks Related to Our Business and Industry
| | Our business plan requires substantial additional capital, which we may be unable to raise on acceptable terms in the future, or at all, which may in turn limit our ability to execute on our plans; |
| | We are an early stage development company with no revenues and have a limited operating history, and our future performance is uncertain. Our ability to successfully drill and complete the wells identified for our current capital plan will depend on a variety of factors; |
| | Our business plan contemplates delivering natural gas to the Australian East Coast as well as select markets in South and East Asia. Our ability to deliver natural gas in significant quantities to these markets depends on the construction of additional pipeline capacity. We cannot assure you that we will be able to secure sufficient take-away capacity on our timing or at all; |
| | We have no proved reserves at this time and areas that we decide to drill may not yield natural gas in commercial quantities or quality, or at all; |
| | Drilling wells is speculative, often involving significant costs that may be more than our estimates, and may not result in any discoveries or additions to our future production or reserves. Any material inaccuracies in drilling costs, estimates or underlying assumptions will materially affect our business; |
| | We intend to import and implement U.S. practices and technology for use in the development of our properties in the Northern Territory. There is limited experience with these practices and technology within the workforce in the areas we operate. The ability to attract and train a qualified workforce could hamper our present operations and limit our ability to grow; |
| | Our inability to access appropriate equipment and infrastructure in a timely manner may hinder our access to natural gas markets and delay the phases of our business plan; |
| | Drilling, completions, workover and hydraulic fracturing operations are operationally complex activities which present certain risks that could adversely affect our business, financial condition or results of operations; |
| | Natural gas prices are volatile. A reduction or sustained decline in prices may adversely affect our business, financial condition or results of operations and our ability to meet our financial commitments or raise capital; |
| | Construction of midstream projects subjects us to risks of construction delays, cost over-runs, limitations on our growth and negative effects on our financial condition, results of operations, cash flows and liquidity; |
| | If our assessments of the Beetaloo are materially inaccurate, it will have a fundamental impact on our business; |
| | All of our assets and operations are located in the Beetaloo, making us vulnerable to risks associated with operating in one geographic area; and |
| | Our recurring losses from operations, negative cash flows and substantial cumulative net losses raise substantial doubt about our ability to continue as a going concern. |
Risks Related to Environmental, Legal Compliance and Regulatory Matters
| | We are subject to complex federal, local and other laws and regulations that could adversely affect the cost, manner or feasibility of conducting our operations or expose us to significant liabilities; |
| | We face community opposition from certain parties with respect to our development of the Beetaloo and related operations, which could result in significant costs and delays and could impede our ability to obtain the government approvals required for such operations; |
14
Table of Contents
| | The exploration and development of natural gas in the Beetaloo can pose native title and heritage risks, potentially leading to legal disputes, operational disruptions, and reputational damage; |
| | Upon commencement of commercial production, we are required by the Australian government to produce natural gas in the Beetaloo on a Scope 1 net zero basis. We also have set an internal goal of producing natural gas with net zero equity Scope 1 and 2 emissions. Meeting these requirements and goals may increase our costs of production, and we may be unable to meet these requirements and goals; and |
| | Increased attention to ESG matters and environmental conservation measures may adversely impact our business. |
Risks Related to our Corporate Structure
| | We are a holding company. Our sole material asset is our equity interest in Tamboran Resources Limited and we will be accordingly dependent upon distributions from Tamboran Resources Limited to pay taxes and cover our corporate and other overhead expenses. |
Risks Related to the Offering, our Common Stock and our CDIs
| | The requirements of being a public company, including compliance with the reporting requirements of the ASX listing rules and the Exchange Act, and the requirements of the SOX, may strain our resources, increase our costs and distract management, and we may be unable to comply with these requirements in a timely or cost-effective manner; |
| | We have engaged in transactions with our affiliates and expect to do so in the future. The terms of such transactions and the resolution of any conflicts that may arise may not always be in our or our stockholders best interests; |
| | We have identified a material weakness in our internal control over financial reporting. Any material weakness may cause us to fail to timely and accurately report our financial results or result in a material misstatement of our financial statements; |
| | Investors purchasing shares of our common stock in this offering will not be able to freely sell those shares, or CDIs representing those shares, in Australia during the 12 months after the issue date of those shares in this offering and therefore will not be able to take advantage of any liquidity that may be available for CDIs traded on the ASX during that period; |
| | All of the shares of our common stock and the CDIs representing those shares to be outstanding following the corporate reorganization and this offering will be freely tradable in the public markets and a substantial majority of the shares of our common stock distributed in the corporate reorganization and the CDIs representing those shares will not be subject to lock-up agreements; |
| | Our ability to raise additional capital may be significantly limited by listing rules of the ASX that limit the amount of common stock that we are permitted to issue without stockholder approval; and |
| | As a result of listing CDIs on the ASX, we will be subject to the listing rules of the ASX, which may strain our resources, divert managements attention and affect our ability to manage our business or raise additional capital. |
15
Table of Contents
SUMMARY HISTORICAL CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL DATA
Tamboran Resources Corporation was incorporated on October 3, 2023 and does not have historical financial operating results. The following table shows summary historical consolidated financial data of our accounting predecessor, Tamboran Resources Limited. The summary historical consolidated financial data has been converted from International Financial Reporting Standards to GAAP in accordance with GAAP.
The summary historical consolidated financial data as of and for the years ended June 30, 2023 and 2022 were derived from the historical audited consolidated financial statements and related notes of our Predecessor included elsewhere in this prospectus.
The following table also shows summary unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial data of Tamboran Resources Corporation as of and for the year ended June 30, 2023, which reflect the historical results of our predecessor on a pro forma basis to give effect to (i) this offering and the use of proceeds therefrom and (ii) the corporate reorganization, each of which are described in further detail below, as if they had occurred on June 30, 2023.
You should read the following table in conjunction with Business, Corporate Reorganization, Use of Proceeds, Managements Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations and our historical and pro forma consolidated and combined financial statements and the related notes thereto included elsewhere in this prospectus. Among other things, our historical and pro forma consolidated and combined financial statements include more detailed information regarding the basis of presentation for the following information. Our historical and pro forma consolidated and combined financial results are not necessarily indicative of results to be expected for any future periods. The unaudited pro forma historical financial data are presented for illustrative purposes only and are not necessarily indicative of the financial position that would have existed or the financial results that would have occurred if this offering and the corporate reorganization had occurred on the dates indicated, nor are they necessarily indicative of the financial position or results of our operations in the future. The pro forma adjustments, as described in the notes to the unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial statements, are preliminary and based upon currently available information and certain assumptions that our management believes are reasonable.
16
Table of Contents
| Year ended June 30, |
||||||||
| 2023 | 2022 | |||||||
| (in thousands, except per share data) | ||||||||
| Revenue and other operating income |
$ | | $ | | ||||
| Other income: |
||||||||
| Interest expense, net |
31 | (6 | ) | |||||
| Foreign exchange gain, net |
130 | 471 | ||||||
| Other expenses |
(337 | ) | (144 | ) | ||||
| Operating costs and expenses: |
||||||||
| Compensation and benefits, excluding stock based compensation |
(5,432 | ) | (2,627 | ) | ||||
| Stock based compensation |
(909 | ) | (1,057 | ) | ||||
| Consultancy, legal and professional fees |
(6,818 | ) | (2,708 | ) | ||||
| Depreciation and amortization |
(118 | ) | (128 | ) | ||||
| Loss on assets classified as held for sale |
(12,585 | ) | | |||||
| Accretion of asset retirement obligations |
(601 | ) | (79 | ) | ||||
| Exploration expense |
(2,793 | ) | (1,707 | ) | ||||
| General and administrative |
(2,764 | ) | (1,637 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Net loss |
$ | (32,196 | ) | $ | (9,622 | ) | ||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Net loss per common share: |
||||||||
| Basic and diluted |
$ | (0.026 | ) | $ | (0.014 | ) | ||
| Weighted average number of common shares outstanding: |
||||||||
| Basic |
1,210,408,816 | 708,265,427 | ||||||
| Diluted |
1,210,408,816 | 708,265,427 | ||||||
| Cash Flow Data (at period end): |
||||||||
| Cash flows from: |
||||||||
| Operating activities |
$ | (12,804 | ) | $ | (10,011 | ) | ||
| Investing activities |
$ | (107,465 | ) | $ | (38,746 | ) | ||
| Financing activities |
$ | 106,183 | $ | 23,740 | ||||
| Balance Sheet Data: |
||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 6,426 | $ | 18,470 | ||||
| Total assets |
$ | 182,853 | $ | 89,348 | ||||
| Total liabilities |
$ | 22,272 | $ | 4,667 | ||||
| Total stockholders equity (deficit) |
$ | 160,581 | $ | 84,681 | ||||
17
Table of Contents
Investing in our common stock involves risks. You should carefully consider the information in this prospectus, including the matters addressed under Cautionary Note Regarding Forward-Looking Statements, the following risks and all of the other information set forth in this prospectus before making an investment decision. The risks and uncertainties described below are not the only ones we face. Additional risks not presently known to us or that we currently deem immaterial may also impair our business operations. If any of the following risks actually occur, our business, financial condition and results of operations could be materially and adversely affected, and we may not be able to achieve our goals. We cannot assure you that any of the events discussed in the risk factors below will not occur. The trading price of our common stock could decline due to any of these risks, and you may lose all or part of your investment.
Risks Related to Our Business and Industry
Our business plan requires substantial additional capital, which we may be unable to raise on acceptable terms in the future, or at all, which may in turn limit our ability to execute on our plans.
We estimate expenses of approximately $26 million to drill and complete each of our six to 10 additional appraisal wells necessary to commercialize our natural gas assets within the Beetaloo. Our ability to raise the capital required to fund the various phases of our development plan will depend on many factors, including:
| | our success in attracting third party strategic and financial partners and investors to significantly fund our midstream and LNG terminal development goals; |
| | the scope, rate of progress and cost of our development activities; |
| | natural gas prices; |
| | our ability to produce natural gas from our properties; |
| | the terms and timing of any drilling and other production-related arrangements that we may enter into; |
| | the infrastructure available and developed near our properties; |
| | the cost and timing of governmental approvals and/or concessions; and |
| | the effects of competition by other companies operating in the oil and natural gas industry. |
We do not currently have any commitments for future external funding, and we do not expect to generate any revenue from production until 2026 at the earliest, which will depend upon successful drilling results, additional and timely capital funding, further regulatory approvals, and access to suitable infrastructure. Additional financing may not be available on favorable terms, or at all. Even if we succeed in selling additional securities to raise funds, at such time the ownership percentage of our existing stockholders would be diluted, and new investors may demand rights, preferences or privileges senior to those of existing stockholders. If we raise additional capital through debt financing, the financing may involve covenants that restrict our business activities. If we choose to farm-out interests in our property, we may lose operating control over such property.
In addition, limitations on new share issuances under Australian Securities Exchange listing rules may limit or prevent us from raising additional capital by issuing and selling shares of common stock or other securities when such additional capital is required. See Our ability to raise additional capital may be significantly limited by listing rules of the ASX that limit the amount of common stock that we are permitted to issue without stockholder approval.
18
Table of Contents
We are an early stage development company with no revenues and have a limited operating history, and our future performance is uncertain. Our ability to successfully drill and complete the wells identified for our current capital plan will depend on a variety of factors.
We are an early stage development company with no revenues or reserves currently. To date we have drilled and completed only four wells as operator. We have observed lower normalized flow rates in one well compared to other wells that we have participated in drilling in the Beetaloo. We are currently commencing a stimulation program on SS1H and will commence stimulation of A3H in the second quarter of 2024. Companies in the early stages of operations face substantial business risks and may suffer significant losses. We face challenges and uncertainties in financial planning as a result of the unavailability of historical data and uncertainties regarding the nature, scope and results of our future activities. In the event that our drilling program is delayed, our operating results will be adversely affected, and our operations will differ materially from the activities described in this prospectus.
Our business strategy includes importing and successfully utilizing U.S. drilling and completion techniques to the Northern Territory. We may not be successful in implementing that strategy or in completing the development of the infrastructure necessary to conduct our business as planned. Our ability to successfully maximize the benefits of U.S. technology and techniques depends on a variety of factors, including avoiding delays in procuring equipment and the ability to attract and train employees qualified to operate with U.S. best practices. As a result, we cannot assure you that we will achieve a rate of drilling success that is in line with, or even comparable to, expectations for natural gas development in the United States.
Our business plan contemplates delivering natural gas to the Australian East Coast as well as select markets in South and East Asia. Our ability to deliver natural gas in significant quantities to these markets depends on the construction of additional pipeline capacity. We cannot assure you that we will be able to secure sufficient take-away capacity on our timing or at all.
The anticipated production from our business plan will exceed the capacity of the existing pipeline infrastructure that services the Beetaloo. Although we have preliminary agreements with APA Group for the joint development and construction of two additional pipelines from the Beetaloo, APA Groups obligation to construct these additional pipelines is subject to the execution of mutually satisfactory definite documentation and the satisfaction of several conditions precedent. We cannot assure you that we will reach a mutually satisfactory agreement with APA Group for the construction of the required take-away capacity or the satisfaction to the conditions of any such obligation. The failure to contract for the construction of additional take-away capacity will adversely affect the ability to execute our proposed business plan. In addition, even if we are able to contract for sufficient take-away capacity, we may not be able to contract for gathering and compression services, storage facility capacity, and interconnections to the major pipelines.
We have no proved reserves at this time and areas that we decide to drill may not yield natural gas in commercial quantities or quality, or at all.
We presently have no proved reserves and have not sold any natural gas produced. Based on seismic data, we have identified locations and drilled appraisal wells that indicate the potential presence of natural gas. However, our appraisal wells may not be indicative of future results. Additionally, the areas we have drilled, or may decide to drill in the future, may not yield natural gas in commercial quantities or quality, or at all. All of our current property is undeveloped and in various stages of evaluation that will require substantial additional seismic data reprocessing and interpretation. Accordingly, we do not know if our properties will contain natural gas in sufficient quantities or quality to recover drilling and completion costs or to be economically viable. Even if natural gas is found on our property in commercial quantities, construction costs of natural gas pipelines, associated infrastructure, and transportation costs may prevent such property from being economically viable.
Additionally, the analogies drawn by us from available data from other wells may not prove valid in respect of additional wells on our property. If a significant portion of our property does not prove to be successful, our business, financial condition and results of operations will be materially adversely affected.
19
Table of Contents
We face substantial uncertainties in estimating the characteristics of our property, so you should not place undue reliance on any of our estimates.
In this prospectus we provide estimates of the characteristics of our properties, such as implied production volumes (including our 2.0 Bcf/d gross production goal, potential EUR ranges for certain wells and the normalization of initial production rates to longer lateral lengths), in the Beetaloo. These estimates may be incorrect, as the accuracy of these estimates is a function of the available data, geological interpretation and our judgment. We may not achieve our 2.0 Bcf/d gross production goal on our proposed timeline or at all, and the wells we have drilled or will drill may not achieve ultimate recoveries within the ranges we have estimated. To date, only four wells on our property have been drilled and completed with us as an operator. Any analogies drawn by us from other wells or producing fields may not prove to be accurate indicators of the success of developing reserves from our property. Furthermore, we have no way of evaluating the accuracy of the data from analog wells or properties produced by other parties that we may use. Any significant variance between actual results and our assumptions could materially affect the quantities of natural gas attributable to any particular group of properties.
Drilling wells is speculative, often involving significant costs that may be more than our estimates, and may not result in any discoveries or additions to our future production or reserves. Any material inaccuracies in drilling costs, estimates or underlying assumptions will materially affect our business.
Exploring for and developing natural gas reserves involves a high degree of operational and financial risk, which precludes definitive statements as to the time required and costs involved in reaching certain objectives. The budgeted costs of drilling, completing and operating wells are often exceeded and can increase significantly when drilling costs rise due to a tightening in the supply of various types of natural gas field equipment and related services. Drilling may be unsuccessful for many reasons, including geological conditions, weather, cost overruns, equipment shortages and mechanical difficulties. Exploratory and appraisal wells bear a much greater risk of loss than development wells. Moreover, the successful drilling of a natural gas well does not necessarily result in a profit on investment.
Following the stimulation of the A2H well in EP 98, which is the first Beetaloo well that we have drilled and completed, we observed lower normalized flow rates than other wells we have participated in the drilling of in the Beetaloo. Laboratory testing of the recovered fluid identified a zone of reduced permeability, or a skin, which created an impediment to the flow of natural gas. A variety of factors, both geological and market-related, can cause a well to become uneconomic or only marginally economic. Our initial drilling sites, and any potential additional sites that may be developed, require significant additional exploration and development, regulatory approval and commitments of resources prior to commercial development. If our actual drilling and development costs are significantly more than our estimated costs, we may not be able to continue our business operations as proposed and would be forced to modify our plan of operation.
We intend to import and implement U.S. practices and technology for use in the development of our properties in the Northern Territory. There is limited experience with these practices and technology within the workforce in the areas we operate. The ability to attract and train a qualified workforce could hamper our present operations and limit our ability to grow.
Our operations are mechanically complex and must be performed in remote geographic locations. We believe that our success depends upon our ability to employ and retain a sufficient number of technical personnel who have the ability to utilize, enhance and maintain our natural gas development equipment. Our ability to maintain and expand our operations depends in part on our ability to utilize, replace, supplement and increase our skilled labor force. The supply of skilled workers is limited in the Beetaloo, and it is not guaranteed that we will be able to access a sufficient skilled labor force. A significant increase in the wages paid by competing employers domestically and abroad could result in a reduction of our skilled labor force or cause an increase in the wage rates that we must pay or both. Employee turnover may also lead to lost productivity and decrease employee engagement which could adversely impact our business.
20
Table of Contents
Additionally, our ability to hire, train and retain qualified personnel may become more challenging as we grow and to the extent energy industry market conditions are competitive. Our ability to successfully implement U.S. practices and technology is dependent on finding, training and retaining qualified personnel within Australia for work in the Northern Territory. When general industry conditions are favorable, the competition for experienced operational and field technicians increases as other energy and manufacturing companies needs for the same personnel increases. Our ability to grow or even to continue our current level of operations could be adversely impacted if we are unable to successfully hire, train and retain these important personnel. In addition, effective succession planning for our employees and expansion planning is important to our long-term success. Failure to achieve these plans could hinder our strategic planning and execution and have a material adverse impact on our business, financial condition or results of operations.
Our inability to access appropriate equipment and infrastructure in a timely manner may hinder our access to natural gas markets and delay the phases of our business plan.
Our ability to market our natural gas will depend substantially on the availability and capacity of gathering systems, pipelines and processing facilities owned and operated by third parties not within our control. Our failure to obtain such services on acceptable terms could materially harm our business. The success of our business plan depends on importing and implementing U.S. practices and technology for use in the development of our properties in the Northern Territory. While we have contracted with H&P for H&P FlexRig® through at least August 2025, with a 10-year option to contract for up to five additional rigs, we have not yet secured importing contracts. The delivery of the further drilling rigs may be delayed or cancelled, and we may not be able to gain continued access to suitable rigs in the future. We may be required to shut in natural gas wells because of the absence of a market or because access to pipelines, gathering systems or processing facilities may be limited or unavailable. If that were to occur, then we would be unable to realize revenue from those wells until arrangements were made to deliver the production to market, which could cause significant delays to the phases of our business plan and have a material adverse effect on our results of operations and financial condition.
In the Beetaloo, as our development is in its preliminary stage, we have no binding agreements for the gathering and processing of our potential future production. As a result, our business plan is dependent on third parties to develop the infrastructure for our natural gas gathering needs. Capital constraints could limit the construction of new pipelines and gathering systems. Until this new capacity is available, we may experience delays in producing and selling our natural gas. In such event, we might have to shut in our wells while awaiting a pipeline connection or additional capacity, which would adversely affect our results of operations. Even when available, the ultimate costs of gathering and transportation systems may prevent some of our properties from being economically viable.
A portion of our natural gas production may be interrupted, or shut in, from time to time for numerous reasons, including weather conditions, accidents, loss of pipeline or gathering system access, field labor issues or strikes, or we might voluntarily curtail production in response to market conditions. If a substantial amount of our production is interrupted at the same time, it could materially adversely affect our cash flow.
Drilling, completions, workover and hydraulic fracturing operations are operationally complex activities which present certain risks that could adversely affect our business, financial condition or results of operations.
In our drilling operations, from time to time we experience certain issues and encounter risks, including, for example, mechanical and instrument or tool failures; drilling difficulties associated with drilling in swelling clay or shales and unconsolidated formation; wellbore instability and other geological hazards; loss of well control and associated hydrocarbon release and/or natural gas clouds; loss of drilling fluids circulation; surface spills of various drilling or well fluids; subsurface collision with existing wells; proximity of adjacent water wells or aquifers; inability to establish drilling fluid circulation; loss or compromise of drill pipe or casing integrity; surface pumping operations and associated pressure and hydrocarbon hazards; stuck and lost-in-hole tools, drill
21
Table of Contents
pipe or casing; large drilling equipment and machinery including electrical hazards; insufficient cementing of casing causing unwanted casing pressure or fluid migration; surface overpressure events from large machinery (horsepower), equipment or well pressure; fines and violations related to relevant laws and regulations; fires and explosions; personnel safety hazards such as working at heights, driving or equipment operation, energy isolation, excavation and trenching and more; structural damage and collapse to large equipment and machinery; major damage or malfunction to key equipment or processes; in certain instances, close proximity of operations to residences and/or communities; among other typical shale basin drilling challenges and risks.
In our hydraulic fracturing, workover and completions activities, from time to time we experience certain issues and encounter risks, including, for example, mechanical and instrument or tool failures; loss of well control and associated hydrocarbon release and/or natural gas clouds; well kick or flowback during completion or fracturing operations; lost or stuck in hole wireline, coiled tubing or workover strings and tools; loss or compromise of workover string, tubing or casing integrity; large completions, wireline, coiled tubing and workover rig equipment and machinery including electrical hazards; insufficient cementing of casing causing unwanted casing pressure or fluid migration while fracturing or thereafter; proximity of adjacent water wells or aquifers and adjacent producing wells; surface spills of various fracturing, freshwater or well fluids or chemicals; surface pumping and flowback operations and associated pressure and hydrocarbon hazards; surface overpressure events from large machinery (horsepower), equipment or well pressure; fines and violations related to relevant laws and regulations; fires and explosions; personnel safety hazards such as working at heights, driving or equipment operation, energy isolation, excavation and trenching and more; structural damage and collapse to large equipment and machinery; major damage or malfunction to key equipment or processes; in certain instances, close proximity of operations to residences and/or communities; among other typical fracturing, workover and completion challenges and risks.
Our industry requires us to navigate many uncertainties that could adversely affect our financial condition and results of operations.
Our financial condition and results of operations depend on the success of the development of our assets, which are subject to numerous risks beyond our control, including the risk that development will not result in commercially viable production or uneconomic results or that various characteristics of the drilling process or the well will cause us to abandon the well prior to fully producing commercially viable quantities.
Our actual development cost for a well could significantly exceed planned authorization for expenditure levels. Further, many factors may curtail, disrupt, delay or cancel our scheduled drilling projects and ongoing operations, including the following:
| | reductions or sustained declines in natural gas prices; and |
| | regulatory compliance, including limitations on wastewater disposal, discharge of greenhouse gases and hydraulic fracturing. |
In addition, our assets are anticipated to be developed over several years, making them susceptible to uncertainties that could materially alter the occurrence or timing of their drilling, the scope, rate of progress and cost of our exploration and production activities. Our ability to drill and develop our assets depends on a number of factors, including the availability of equipment and capital, seasonal conditions, regulatory approvals, obtaining land access agreements for regulated operations, natural gas prices, costs and drilling results. Because of these uncertainties, we do not know if our properties will be drilled within our expected timeframe or at all or if we will be able to economically produce natural gas from these or any other potential drilling locations. As such, our actual drilling activities may be materially different from our current expectations, which could adversely affect our results of operations and financial condition.
22
Table of Contents
Natural gas prices are volatile. A reduction or sustained decline in prices may adversely affect our business, financial condition or results of operations and our ability to meet our financial commitments or raise capital.
Our future growth is dependent on the continued economic importance of the natural gas development and production industry in Australia and global demand (as it relates to LNG trade). Any substantive and prolonged changes to the current economic importance of natural gas development and production industry in Australia would be likely to have an adverse effect on our business, financial condition and profits.
Prevailing natural gas prices heavily influence our potential revenue, profitability, access to capital, growth rate and value of our properties. Further, although we do not produce oil, to the extent oil prices rise considerably, the cost of services we incur may also increase. As a commodity, natural gas prices are subject to wide fluctuations in response to relatively minor changes in supply and demand. Historically, the natural gas market has been volatile. Our revenue, profitability and future growth are highly dependent on the prices we receive for our natural gas production, and the levels of our production, depend on numerous factors beyond our control. These factors include, but not limited to, the following:
| | worldwide and regional economic conditions impacting the global supply of and demand for natural gas, including economic growth expectations, inflation and hostilities in Ukraine and the Middle East; |
| | the actions of OPEC, its members and other state-controlled oil companies relating to oil price and production controls; |
| | the level of global oil and natural gas exploration and production; |
| | the level of global oil and natural gas inventories; |
| | prevailing prices on local price indexes in the areas in which we operate and expectations about future commodity prices; |
| | extent of natural gas production associated with increased oil production; |
| | the proximity, capacity, cost and availability of gathering and transportation facilities; |
| | localized and global supply and demand fundamentals and transportation availability; |
| | weather conditions across the globe; |
| | technological advances affecting energy consumption; |
| | speculative trading in natural gas markets; |
| | end-user conservation trends; |
| | petrochemical, fertilizer, ethanol, transportation supply and demand balance; |
| | the price and availability of alternative fuels; |
| | domestic, local and foreign governmental regulation and taxes; and |
| | liquefied petroleum products supply and demand balances. |
In particular, because of our higher operating costs than U.S producers, our business model is dependent on the higher natural gas prices we receive from Asian and domestic Australian markets relative to U.S prices. If commodity prices decrease or we experience widening of basis differentials, our cash flows and refinancing ability will be reduced. We may be unable to obtain needed capital or financing on commercially reasonable terms. Lower commodity prices may also reduce the amount of natural gas that we can produce economically. Additionally, a significant portion of our projects could become uneconomic and require us to abandon or postpone our planned drilling. As a result, a reduction or sustained decline in natural gas prices may materially and adversely affect our financial condition, results of operations, liquidity and our ability to finance capital expenditures.
23
Table of Contents
We may not be able to manage our future growth effectively, which could make it difficult to execute our business strategy.
Our expected future growth could create a strain on the organizational, administrative and operational infrastructure. Our ability to manage our growth effectively will require us to continue to improve our operational, financial and management controls, as well as reporting systems and procedures. Our current team is small and we will have to hire additional employees to achieve our expected future growth. Our business strategy will be difficult to execute, which may impact our ability to effectively attract employees. As we grow, any failure of our controls or interruption of our facilities or systems could have a negative impact on our business and financial operations. Our future development plan, including the potential development of pipelines, LNG export facility, and CCUS projects, will affect a broad range of business processes and functional areas. The time and resources required to implement these new extensions of our business are uncertain, and failure to complete these activities in a timely and efficient manner could adversely affect our operations. If we are unable to manage growth effectively, it may be difficult for us to execute our business strategy.
Our business plan contemplates the execution of midstream contracts with certain third parties in order to allow us to supply our own natural gas for export out of Darwin or directly to the Australian East Coast. We cannot assure you that we will be successful in obtaining the commercial contracts necessary to facilitate direct delivery of our natural gas production on commercially reasonable terms, or at all.
We cannot assure you that we will succeed in any effort to establish midstream contracts that would allow us to supply our own natural gas for export out of Darwin or directly to the Australian East Coast. Even when the physical infrastructure exists to supply our own natural gas directly to Darwin and the Australian East Coast, our ability to utilize that infrastructure depends on whether we can successfully negotiate and enter into midstream contracts on commercially reasonable terms or at all. If we fail to enter into such contracts on commercially reasonable terms or at all or are otherwise subject to capacity constraints, it could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and cash flows.
Construction of midstream projects subjects us to risks of construction delays, cost over-runs, limitations on our growth and negative effects on our financial condition, results of operations, cash flows and liquidity.
The second and third phase of our business requires the construction of midstream projects, including pipelines to access the East Coast and our proposed NTLNG terminal, some of which may take a number of years before commercial operation. These projects are complex and subject to a number of factors beyond our control, including delays from third-party landowners, the permitting process, government and regulatory approval, compliance with laws, unavailability of materials, labor disruptions, environmental hazards, financing, accidents, weather and other factors. Any delay in the completion of these projects could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition, results of operations, cash flows and ability to pay dividends on our common stock. The construction of these midstream facilities requires the expenditure of significant amounts of capital, which may exceed our estimated costs. Estimating the timing and expenditures related to these development projects is very complex and subject to variables that can significantly increase expected costs. Should the actual costs of these projects exceed our estimates, our liquidity and financial condition could be adversely affected. This level of development activity requires significant effort from our management and technical personnel and places additional requirements on our financial resources and internal financial controls. We may not have the ability to attract and/or retain the necessary number of personnel with the skills required to bring complicated projects to successful conclusions.
The construction of midstream projects also requires the support of third-party strategic partners, who may have differing goals and strategies. If our strategic partners do not cooperate in the construction of the midstream projects, we may be unable to market our future natural gas production.
24
Table of Contents
If our assessments of the Beetaloo are materially inaccurate, it will have a fundamental impact on our business.
Our assessment of our property may be inherently inexact and may be inaccurate, including the following:
| | the time it takes to bring the Beetaloo to commercial development phase; |
| | the amount of recoverable reserves; |
| | timing of development of takeaway capacity and access to other infrastructure, including LNG terminals, on an economically viable basis; |
| | geological complexity; |
| | applicable governmental rules and regulations; |
| | native title holders and traditional Aboriginal owners; |
| | estimates of operating costs; |
| | estimates of future development costs; |
| | estimates of the costs and timing of plugging and abandonment; and |
| | potential environmental and other liabilities. |
Our assessments will not reveal all existing or potential problems, nor will it permit us to become familiar enough with the breadth of the territory we hold license to in order to assess fully their capabilities and deficiencies. We plan to undertake further development of our properties through the use of cash flow from existing production. Therefore, a material deviation in our assessments of these factors could result in less cash flow being available for such purposes than we presently anticipate, which could either delay future development operations (and delay the anticipated conversion of reserves into cash), or cause us to seek alternative sources to finance development activities.
We are dependent on certain members of our management and technical team.
Investors in our common stock must rely upon the ability, expertise, judgment and discretion of our management and the success of our technical team in developing our future natural gas reserves. Our performance and success are dependent, in part, upon key members of our management and technical team, and their loss or departure could be detrimental to our future success. In making a decision to invest in our common stock, you must be willing to rely to a significant extent on our managements discretion and judgment. There can be no assurance that our senior management will remain in place. The loss of any of our management and technical team members could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations and financial condition, as well as on the market price of our common stock. See Management and Executive and Director Compensation.
We have limited control over properties and investments operated by others or through joint ventures.
Certain of our properties are operated by other companies and may involve third-party working interest owners. We have limited influence and control over the operation or future development of such properties and investments, including compliance with environmental, health and safety regulations or the amount and timing of required future capital expenditures. In addition, we conduct certain of our operations through joint ventures in which we may share control with third parties, and the other joint venture participants may have interests or goals that are inconsistent with those of the joint venture or us. These limitations and our dependence on such third parties could result in unexpected future costs or liabilities and unplanned changes in operations or future development, which could adversely affect our financial condition and results of operations.
25
Table of Contents
Our financial performance is subject to our counterparties or joint venture partners performance of their obligations under the relevant contracts, including the joint venture agreements. If one of our counterparties or joint venture partners fails to perform its contractual obligations, it may result in loss of earnings, termination of other related contracts, disputes and/or litigation that could impact our financial performance.
Currently, we are not the operator of EP 161, which is operated by Santos. As we carry out our exploration and development programs, we may enter into arrangements with respect to existing or future properties that result in a greater proportion of our properties being operated by others. As a result, we may have limited ability to exercise influence over the operations of the properties operated by our partners. Dependence on the operator could prevent us from realizing our target returns for those properties. Further, it may be difficult for us to pursue one of our key business strategies of minimizing the cycle time between discovery and initial production with respect to properties for which we do not operate. The success and timing of exploration and development activities operated by our partners will depend on a number of factors that will be largely outside of our control, including:
| | the timing and amount of capital expenditures; |
| | the operators expertise and financial resources; |
| | approval of other participants in drilling wells; |
| | selection of technology; and |
| | the rate of production of reserves, if any. |
This limited ability to exercise control over the operations of some of our properties may cause a material adverse effect on our results of operations and financial condition.
All of our assets and operations are located in the Beetaloo, making us vulnerable to risks associated with operating in one geographic area.
Our operations are geographically concentrated in the Northern Territory of Australia, and specifically the Beetaloo. As a result, we may be disproportionately exposed to the impact of regional supply and demand factors in the Beetaloo caused by significant governmental regulation, curtailment of production or interruption of the processing or transportation of natural gas produced from wells in this area. In addition, the effect of fluctuations on supply and demand may become more pronounced within a specific geographic natural gas producing area such as the Beetaloo, which may cause these conditions to occur with greater frequency or magnify the effects of these conditions. Due to the concentrated nature of our operations, we could experience any of the same conditions at the same time, resulting in a relatively greater impact on our revenue than they might have on other companies that have more geographically diverse operations.
Our business is subject to operating hazards that could result in substantial losses or liabilities for which we may not have adequate insurance coverage.
Natural gas operations are subject to many risks, including well blowouts, craterings, explosions, uncontrollable flows of natural gas or well fluids, fires, pipe, casing or cement failures, abnormal pressure, pipeline leaks, ruptures or spills, vandalism, pollution, releases of toxic gases, adverse weather conditions or natural disasters and other environmental hazards and risks. If any of these hazards occur, we could sustain substantial losses as a result of:
| | injury or loss of life; |
| | severe damage to or destruction of property, natural resources and equipment; |
| | pollution or other environmental damage; |
| | investigatory, monitoring, and cleanup responsibilities; |
26
Table of Contents
| | regulatory investigations and penalties or lawsuits; |
| | loss of, or delay in revenue; |
| | suspension or impairment of operations; and |
| | repairs to resume operations. |
We maintain insurance against some, but not all, potential losses or liabilities arising from our operations in accordance with what we believe are customary industry practices and in amounts and at costs that we believe to be prudent and commercially practicable. Our insurance includes deductibles that must be met prior to recovery, as well as sub-limits and/or self-insurance. Additionally, our insurance is subject to exclusions and limitations. Our insurance does not cover every potential risk associated with our operations, including the potential loss of significant revenues. We can provide no assurance that our coverage will adequately protect us against liability from all potential consequences, damages and losses.
We maintain insurance coverage that is considered appropriate for a company of our size operating in the gas exploration phase, subject to policy terms and conditions. This includes insurance coverage related to general and product liability, property, workers compensation, cyber, terrorism and malicious acts, operators extra expenses for control of well, seepage and pollution, cleanup and contamination, evacuation expenses and making the well safe.
We may elect not to obtain insurance if we believe that the cost of available insurance is excessive relative to the risks presented. Some forms of insurance may become unavailable in the future or unavailable on terms that we believe are economically acceptable. No assurance can be given that we will be able to maintain insurance in the future at rates that we consider reasonable, and we may elect to maintain minimal or no insurance coverage. If we incur substantial liability from a significant event and the damages are not covered by insurance or are in excess of policy limits, then we would have lower revenues and funds available to us for our operations, that could, in turn, have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Additionally, we will rely to a large extent on transportation infrastructure owned and operated by third parties and damage to, or destruction of, those third-party infrastructure will affect our ability to process, transport and sell our production.
We are subject to numerous risks inherent to the exploration and production of natural gas.
Natural gas exploration and production activities involve many risks that a combination of experience, knowledge and careful evaluation may not be able to overcome. Our future success will depend on the success of our exploration and production activities and on the future existence of the infrastructure that will allow us to take advantage of our findings. Additionally, our natural gas properties are located in an area without significant existing infrastructure, which generally increases the capital and operating costs, technical challenges and risks associated with natural gas exploration and production activities. As a result, our natural gas exploration and production activities are subject to numerous risks, including the risk that drilling will not result in commercially viable natural gas production. Our decisions to purchase, explore, develop or otherwise exploit properties will depend in part on the evaluation of seismic data through geophysical and geological analyses, production data and engineering studies, the results of which are often inconclusive or subject to varying interpretations.
Furthermore, the marketability of expected natural gas production from our property will also be affected by numerous factors. These factors include, but are not limited to, market fluctuations of prices, proximity, capacity and availability of pipelines, the availability of processing facilities, equipment availability and government regulations (including, without limitation, regulations relating to prices, taxes, royalties, allowable production, importing and exporting of natural gas, environmental protection and climate change). The effect of these factors, individually or jointly, may result in us not receiving an adequate return on invested capital.
27
Table of Contents
In the event that our drilling programs are developed and become operational, they may not produce natural gas in commercial quantities or at the costs anticipated, and our projects may cease production, in part or entirely, in certain circumstances. Drilling programs may become uneconomic as a result of an increase in operating costs to produce natural gas. Our actual operating costs may differ materially from our current estimates. Moreover, it is possible that other developments, such as increasingly strict environmental, health and safety laws and regulations and enforcement policies thereunder and claims for damages to property or persons resulting from our operations, could result in substantial costs and liabilities, delays, an inability to complete our drilling programs or the abandonment of such drilling programs, which could cause a material adverse effect on our results of operations and financial condition.
Our identified drilling locations are scheduled out over several years, making them susceptible to uncertainties that could materially alter the occurrence or timing of their drilling.
Our management team has identified and scheduled drilling locations on our acreage over a multi-year period. Our ability to drill and develop these locations depends on a number of factors, including the availability of equipment and capital, seasonal conditions, regulatory approvals, natural gas prices, costs and drilling results. The final determination on whether to drill any of these drilling locations will be dependent upon the factors described above as well as, to some degree, the results of our drilling activities with respect to our appraisal wells. Because of these uncertainties, we do not know if the drilling locations we have identified will be drilled within our expected timeframe or at all. As such, our actual drilling activities may be materially different from our current expectations, which could adversely affect our results of operations and financial condition.
The development schedule of natural gas projects, including the availability and cost of drilling rigs, equipment, supplies, personnel and natural gas field services, is subject to delays and cost overruns.
Historically, some natural gas projects have experienced delays and capital cost increases and overruns due to, among other factors, the unavailability or high cost of drilling rigs and other essential equipment, supplies, personnel and natural gas field services. The cost to develop our projects has not been fixed and remains dependent upon a number of factors, including the completion of detailed cost estimates and final engineering, contracting and procurement costs. Our construction and operation schedules may not proceed as planned and may experience delays or cost overruns. Any delays may increase the costs of the projects, requiring additional capital, and such capital may not be available in a timely and cost-effective fashion.
Part of our business strategy involves using some of the latest available horizontal drilling and completion techniques, which involve risks and uncertainties in their application.
Difficulties that we face while completing our wells include:
| | the ability to fracture stimulate the planned number of stages with the planned amount of proppant; |
| | the ability to run tools through the entire length of the wellbore during completion operations; and |
| | the ability to successfully clean out the wellbore after completion of the final fracture stimulation stage. |
In addition, certain of the new techniques we are adopting may cause irregularities or interruptions in production. If our development and production results are less than anticipated, the return on our investment for a particular well may not be as attractive as we anticipated, and its value could decline in the future.
We also may be subject to additional costs or shortages of equipment and labor because of the necessity of importing certain equipment or hiring talent from the United States. The unavailability or high cost of drilling rigs, completion crews, equipment, supplies, personnel and oilfield services could adversely affect our ability to execute our development plans within our budget and on a timely basis.
Shale gas completions require significant amounts of water which is subject to delays in regulatory approval from certain aquifers and the cost of utilization of aquifer water may increase over time.
28
Table of Contents
The demand for drilling rigs, completion crews, pipe and other equipment and supplies, including sand and other proppant used in hydraulic fracturing operations and acid used for stimulation can fluctuate significantly, often in correlation with commodity prices or drilling activity in our area of operation and in other shale basins, causing periodic shortages of supplies and needed personnel and rapid increases in costs. Increased drilling activity could materially increase the demand for and prices of these goods and services, and we could encounter rising costs and delays in or an inability to secure the personnel, equipment, power, services, resources and facilities access necessary for us to conduct our drilling and development activities, which could result in production volumes being below our forecasted volumes. In addition, any such negative effect on production volumes, or significant increases in costs could have a material adverse effect on our future cash flow and profitability.
Our recurring losses from operations, negative cash flows and substantial cumulative net losses raise substantial doubt about our ability to continue as a going concern.
In Note 1 titled Nature of the Organization and Business of our audited consolidated financial statements as of and for the year ended June 30, 2023 included elsewhere in this prospectus, we disclose that there is substantial doubt about our ability to continue as a going concern. In addition, our independent registered public accounting firm included an explanatory paragraph in its report on our consolidated financial statements as of and for the year ended June 30, 2023, which stated that there are factors that raise substantial doubt on our ability to continue as a going concern. We have negative working capital and have incurred significant operating losses and negative cash flows from operations and expect to continue incurring increasing losses for the foreseeable future as we further our development program. Further, we had accumulated losses of approximately $142.2 million as of June 30, 2023. These conditions raise substantial doubt about our ability to continue as a going concern. Our consolidated financial statements do not include any adjustments that might result from the outcome of this uncertainty.
Our ability to become a profitable operating company is dependent upon our ability to generate revenue and obtain financing adequate to fulfill our development and commercialization activities, and achieving a level of revenue adequate to support our cost structure. We have plans to obtain additional resources to fund our currently planned operations and expenditures through additional debt and equity financing however there is no guarantee we obtain financing at all or on commercially acceptable terms. Based on our managements current expectations and assumptions, we estimate that $40.6 million of capital will be necessary for us to raise to continue as a going concern through fiscal year 2024. We believe that the amount of proceeds from this offering will be sufficient to fund our current operations. Our plans are substantially dependent upon the success of commercial production at the Beetaloo, which is still in the early stages of development, and are dependent upon, among other things, the success of our drilling program and infrastructure development in the Beetaloo. If we are unable to obtain sufficient funding, our financial condition and results of operations will be materially and adversely affected and we may be unable to continue as a going concern. Future financial statements may disclose substantial doubt about our ability to continue as a going concern. If we seek additional financing to fund our business activities in the future and there remains substantial doubt about our ability to continue as a going concern, investors or other financing sources may be unwilling to provide additional funding to us on commercially reasonable terms or at all.
Our long-term business plan contemplates the development of an additional LNG export terminal on the northern coast of Australia. Our ability to develop such a facility is dependent on our ability to attract a third-party partner as well as securing the necessary permits.
We anticipate commencing construction of the NTLNG project as early as 2027 with completion occurring as early as 2030. Our ability to commence construction of the NTLNG or complete the project on schedule is dependent on a number of factors outside of our control, including the willingness of potential third-party partners to commit to the project. Although we have entered into memoranda of understanding with subsidiaries of each of bp and Shell with respect to long-term contracts for the purchase of a total of 4.4 Mtpa from NTLNG,
29
Table of Contents
these memoranda of understanding are not binding obligations of bp or Shell and either may decide not to pursue our project. We cannot assure you we will be successful in the negotiating or execution of definitive agreements. Failure to do so could cause significant delays to the phases of our business plan and have a material adverse effect on our results of operations and financial condition.
In addition, the construction of our proposed NTLNG export facility in the Middle Arm Sustainable Development (MASD) precinct relies on the award of a binding land use agreement between the Company and the Northern Territory government. The MASD acreage has been allocated to us on an exclusive basis for 12 months from June 2023 during which we are progressing a concept selection phase and plan to present our findings to the Northern Territory government. There is no guarantee that we are awarded a binding land use agreement with respect to this land.
A financial crisis or deterioration in general economic, business or industry conditions could materially adversely affect our results of operations and financial condition.
Concerns over global economic conditions, stock market volatility, energy costs, geopolitical issues, inflation and U.S. Federal Reserve interest rate increases in response, the availability and cost of credit, and slowing of economic growth in the United States and fears of a recession have contributed and may continue to contribute to economic uncertainty and diminished expectations for the global economy.
Although inflation in Australia had been relatively low for many years, inflation rose from 3.8% in June 2021 to a peak of 7.8 % in December 2022 and then moderated to 5.4% in June 2023. In addition, inflation in the United States rose from 7.0% in December 2021 to a high of 9.1% in June 2022 and fell to 3.7% in September 2023. As a result, we experienced supply chain constraints and inflationary pressure on our cost structure throughout 2022 and 2023. Some supply chain constraints and inflationary pressures could persist into 2024 but are expected to plateau. If we are unable to manage our supply chain, our ability to procure materials and equipment in a timely and cost-effective manner, if at all, may be negatively impacted, which could materially adversely impact our results of operations and financial condition.
Similarly, we cannot predict the impact that high market volatility and instability in the banking sector could have on economic activity and our business in particular. The failure of banks and financial institutions and measures taken, or not taken, by governments, businesses and other organizations in response to these events could adversely impact our business, financial conditions and results of operations.
In addition, continued hostilities between Russia and the Ukraine, the conflict between Israel and Hamas, other hostilities in the Middle East, and the occurrence or threat of terrorist attacks in Australia or other countries could adversely affect the economies of Australia and other countries. The ongoing conflict in Ukraine and Israel could continue to have repercussions globally by continuing to cause uncertainty, not only in the natural gas markets, but also in the capital markets. Such uncertainty could result in stock price volatility and supply chain disruptions, as well as higher natural gas prices which could potentially result in increased inflation worldwide and could negatively impact demand for natural gas, NGLs, oil and electricity.
Concerns about global economic growth can result in a significant adverse impact on global financial markets and commodity prices. In addition, any financial crisis may cause us to face limitations on our ability to access the debt and equity capital markets and complete asset purchases or sales.
Further, if there is a financial crisis or the economic climate in Australia or abroad deteriorates, worldwide demand for hydrocarbon-based products could materially decrease, which could impact the price at which natural gas from our properties are sold, affect the ability of vendors, suppliers and service providers associated with our properties to continue operations and ultimately materially adversely impact our results of operations, financial condition and ability to pay dividends on our common stock.
30
Table of Contents
Events outside of our control, including an epidemic or outbreak of an infectious disease, terrorism, geopolitical instability, and security threats, could have a material adverse effect on our business, liquidity, financial condition, results of operations, and/or cash flows.
We face risks related to pandemics, epidemics, outbreaks or other public health events, or the threat thereof, that are outside of our control, and could significantly disrupt our business and operational plans and adversely affect our liquidity, financial condition, results of operations, cash flows and ability to pay dividends on our common stock.
The nature, scale and scope of the above-described events, combined with the uncertain duration and extent of governmental actions, prevent us from identifying all potential risks to our business. We believe that the known and potential impacts of pandemic-related events include, but are not limited to, the following:
| | disruption in the demand for natural gas, NGLs and oil and other petroleum products; |
| | intentional project delays until commodity prices stabilize; |
| | a potential future downgrade of our credit rating and potentially higher borrowing costs in the future; |
| | a need to preserve liquidity, which could result in reductions, delays or changes in our capital expenditures; |
| | supply chain and shipping lane disruptions, resulting in shortages of, and increased pricing pressures on, among other things, equipment, services and labor; |
| | liabilities resulting from operational delays due to decreased productivity resulting from stay-at-home orders affecting our workforce or facility closures; |
| | future asset impairments, including impairment of our natural gas properties and other property and equipment; and |
| | infections and quarantining of our employees and the personnel of vendors, suppliers and other third parties. |
A terrorist attack or armed conflict targeting our systems or natural gas infrastructure generally could materially adversely impact our operations.
Growing geopolitical instability and armed conflicts (including the armed conflict between Russia and Ukraine and between Israel and Hamas as well as other hostilities in the Middle East) has resulted in energy infrastructure becoming a more prominent target of attack by terrorists and conflicting countries. Natural gas, NGLs and oil related facilities, including those operated by us or our service providers, could be direct targets of physical or cyber-attacks, and, if infrastructure integral to our operations is destroyed or damaged, we may experience a significant disruption in our operations. Any such disruption could materially adversely affect our financial condition, results of operations and cash flows. Costs for insurance and other security may increase as a result of increased threats, and certain insurance coverage may become more difficult to obtain, if available at all.
Our business could be negatively affected by security threats and disruptions, including electronic, cybersecurity or physical security threats and other disruptions.
Our business faces various security threats, including cybersecurity threats to gain unauthorized access to sensitive information or to render data or systems unusable; threats to the security of our facilities and infrastructure or third-party facilities and infrastructure, such as processing plants and pipelines; and threats from terrorist acts. The potential for such security threats has subjected our operations to increased risks that could have a material adverse effect on our business. In particular, our implementation of various procedures and controls to monitor and mitigate security threats and to increase security for our information, facilities and infrastructure may result in increased capital and operating costs. Moreover, there can be no assurance that such
31
Table of Contents
procedures and controls will be sufficient to prevent security breaches from occurring. Security breaches could lead to losses of sensitive information, critical infrastructure or capabilities essential to our operations and could have a material adverse effect on our reputation, financial position, results of operations and cash flows. Cybersecurity attacks in particular are becoming more sophisticated and include, but are not limited to, malicious software, attempts to gain unauthorized access to data and systems and other electronic security breaches that could lead to disruptions in critical systems, unauthorized release of confidential or otherwise protected information and corruption of data. These events could damage our reputation and lead to financial losses from remedial actions, loss of business or potential liability.
Loss of our information and computer systems could adversely affect our business.
We are heavily dependent on our information systems and computer-based programs, including our well operations information, seismic data, electronic data processing and accounting data. If any of such programs or systems were to fail or create erroneous information in our hardware or software network infrastructure, possible consequences include our loss of communication links, inability to find, produce, process and sell natural gas and inability to automatically process commercial transactions or engage in similar automated or computerized business activities. Any such consequence could have a material adverse effect on our business.
We may be involved in legal proceedings that could result in substantial liabilities.
Like many energy companies, in the ordinary course of our business, we are from time to time involved in various disputes and disagreements that may lead to legal and other proceedings, such as title, royalty or contractual disputes, regulatory compliance matters, land access disputes, appeals and judicial reviews of regulatory approvals, personal injury or property damage matters. Such legal proceedings are inherently uncertain and their results cannot be predicted. Regardless of the outcome, such proceedings could have an adverse impact on us because of legal costs, diversion of management and other personnel and other factors. In addition, it is possible that a resolution of one or more such proceedings could result in liability, penalties or sanctions, as well as judgments, consent decrees or orders requiring a change in our business practices, which could materially and adversely affect our business, prospects, financial condition, results of operations, cash flows and ability to pay dividends on our common stock. Accruals for such liability, penalties or sanctions may be insufficient, and judgments and estimates to determine accruals or range of losses related to legal and other proceedings could materially change from one period to the next.
We are subject to risks related to corporate social responsibility, including the risk that our expectations or estimates regarding environmental, social and governance matters may not be achieved or may be incorrect.
Our business, as well as those of other companies, faces increasing public scrutiny related to ESG activities, which are increasingly considered to contribute to the long-term sustainability of a companys performance.
We risk damage to our brand and reputation if we fail, or are perceived to fail, to act responsibly in a number of areas, such as environmental stewardship and corporate governance and transparency. Adverse incidents with respect to ESG activities could impact the value of our brand, the cost of our operations and relationships with investors, all of which could adversely affect our business and results of operations. For example, we have been in the past, and may in the future, be subject to claims of greenwashing (e.g., if our carbon footprint is alleged to be greater than what we claim, or if our ESG claims (including our claims in relation to our goals in respect of net zero equity Scope 1 and Scope 2 emissions) turn out to be false or misleading). Our expectations and estimates regarding ESG matters, including the potential environmental impact of our development and initiatives, may not be achieved or may ultimately prove to be incorrect, which may lead to additional claims or liability. The law in relation to false and misleading claims about ESG matters and statements about net zero emissions goals is evolving, and there continues to be risk that statements we have made could be deemed to be in breach of the Australian Consumer Law and other similar legislation in Australia or other jurisdictions. Breaches of these laws can result in significant financial penalties and other enforcement action.
32
Table of Contents
Some of our ESG efforts may ultimately rely on the right to claim certain emissions offsets or other environmental attributes or to package such attributes with the natural gas we produce. This may be affected by evolving approaches to these matters, complex calculations or commercial agreements, and any disputes or ambiguities regarding such environmental attributes may negatively affect perceptions of our operations and products, subject us to litigation or stakeholder activism, require us to incur additional costs to procure replacement attributes, or otherwise adversely impact our operations.
We are also subject to evolving expectations on ESG matters from various stakeholders, including regulators, investors, customers, and business partners. For more information, see our risk factor titled Increased attention to ESG matters and environmental conservation measures may adversely impact our business.
Risks Related to Environmental, Legal Compliance and Regulatory Matters
We are subject to complex federal, local and other laws and regulations that could adversely affect the cost, manner or feasibility of conducting our operations or expose us to significant liabilities.
Exploration and production activities in the oil and natural gas industry within Australia are subject to extensive local, state, federal and international laws and regulations. We may be required to make material expenditures to comply with governmental laws and regulations, particularly in respect of the following matters:
| | approvals for drilling operations and other regulated activities; |
| | land access; |
| | royalties and royalty increases; |
| | drilling and development bonds; |
| | cost recovery for regulatory approvals; |
| | securities and orphan well levies; |
| | reports concerning operations; |
| | the spacing of wells; |
| | unitization of oil accumulations; |
| | tenure, landholders, native title holders and traditional Aboriginal owners; |
| | greenhouse gas emission targets and offset requirements; |
| | water extraction and disposal; |
| | remediation or investigation activities for environmental purposes; and |
| | taxation. |
Under these and other laws and regulations, we could be liable for personal injuries, property damage and other types of damages, penalties, and costs. Accordingly, non-compliance may impact our ability to commercialize or retain its assets, which may in turn impact its operational and financial performance. Failure to comply with these laws and regulations also may result in the suspension or termination of our operations, loss of permits and subject us to administrative, civil and criminal penalties. Moreover, these laws and regulations could change in ways that could substantially increase our costs. Any such liabilities, penalties, suspensions, or terminations or regulatory changes could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations.
Our business is affected by government policy, which in turn may be influenced by international policies and laws. While we consider the Federal Governments current policy to be supportive of the investment and
33
Table of Contents
development of Australias natural gas resources, there is no guarantee that this stance will not change in the future. In particular, there is a risk that the Federal Government could shift its domestic or international policy. International policy developments have the potential to have an indirect impact on our operations, given that domestic policy makers might consider those developments in formulating and in setting the direction of local policy. For example, the International Energy Agency recently released a report in relation to its recommendations for a pathway to achieve global net zero emissions by 2050, and includes a key recommendation that no new oil and natural gas projects should be developed. It is unknown what impact the report might have, if any, on domestic policy development for natural gas. A shift in energy policy announced and adopted by the NT Government in relation to natural gas or the development of the Beetaloo would pose a similar risk. The NT Government had previously imposed a moratorium on the operations in the Beetaloo, which ended in 2018 following a scientific inquiry and certain recommendations.
Shifts in government policy could have varying degrees of impact on our operations and its profitability and could range from loss or reduction in industry incentives, preventing infrastructure development to moratoriums on future natural gas development in specific areas or across the Beetaloo.
We must comply with relevant laws and regulations in each jurisdiction in which we operate as it applies to the environment, tenure, land access, landholders, native title holders and traditional Aboriginal owners. Non-compliance with these laws and regulations and any special license conditions could result in suspension of operations, loss of permits or financial penalties. Non-compliance may impact our ability to commercialize or retain our assets, which may in turn impact our operational and financial performance. The relevant environmental, tenure, land access, landholder, native title, land rights and cultural heritage laws and regulations applicable to our operations are described in BusinessEnvironmental Matters and Regulation.
Changes to these requirements (including, for example, new requirements relating to climate change, environmental protection and energy policy, and the government of the Northern Territorys commitment to implement the recommendations from the Final Report of The Scientific Inquiry into Hydraulic Fracturing) may restrict or affect our right or ability to conduct our activities.
Our exploration of the Beetaloo is dependent upon the maintenance (including renewal) of the relevant permits. Maintenance of the permits is dependent on, among other things, meeting the permit conditions imposed by the relevant authorities including compliance with work program and expenditure requirements. No assurance can be given that such title and access rights are not subject to unregistered, undetected or other claims or interests which could be materially adverse to our interests in the Beetaloo. Further titles or access rights may be disputed, which could result in costly litigation or disruption of the Companys operations.
Our exploration and production operations are subject to various types of federal, state, territorial and local laws and regulations, and may be restricted or subject to conditions in relation to certain environmental features (such as watercourses or sites of conservation significance). Applicable law regulates the location of wells; the method of drilling, well construction, well stimulation, hydraulic fracturing and casing design; water withdrawal and procurement from designated aquifers for well stimulation purposes; well production; spill prevention plans; the use, transportation, storage and disposal of water and other fluids and materials, including solid and hazardous wastes, incidental to natural gas and oil operations; surface usage and the reclamation of properties upon which wells or other facilities have been located; the plugging and abandoning of wells; the calculation, reporting and disbursement of royalties and taxes; and the gathering of production in certain circumstances.
Our production operations are subject to the discovery of commercially exploitable petroleum and the discretion of the Minister to grant a production license. Specifically, we will only be entitled to apply for a production license once a commercially exploitable petroleum discovery is made. Further, the Minister may grant the production license subject to such conditions as the Minister determines to be appropriate at any time, the Minister may direct the holder of a production license to maintain, increase or reduce the rate of recovery of petroleum from the area. The grant of any future production license to the Company over areas that are subject to
34
Table of Contents
native title rights and interests or are Aboriginal land will require engagement with the relevant native title holders and land councils in accordance with the Native Title Act and the ALRA as relevant. Any delays or costs in engaging with the relevant native title holders in negotiating new arrangements in respect of a production license may adversely impact the Companys ability to carry out petroleum extraction activities within the affected areas.
Our operations are also subject to the Petroleum Act, which allows for the unitization of a petroleum pool that extends beyond a license area but which is desirable for efficiency and avoiding wasteful and harmful development and practices.
Environmental and occupational health and safety laws and regulations govern discharges of substances into the air, ground and water; the management and disposal of hazardous substances and wastes; the clean-up of contaminated sites; groundwater quality and availability; plant and wildlife protection; locations available for drilling; environmental impact studies and assessments required for permitting; restoration of drilling properties upon completion of drilling activities; and work practices related to employee health and safety.
To conduct our operations in compliance with these laws and regulations, we must obtain and maintain numerous permits, approvals and certificates from various federal, state and local governmental authorities. Complying with the laws, regulations and other legal requirements applicable to our business and any delays in obtaining related authorizations may affect the costs and timing of developing our natural gas resources. These requirements could also subject us to claims for personal injuries, property damage, penalties, costs and other damages. In addition, our costs of compliance may increase if existing laws and regulations are revised or reinterpreted, or if new laws and regulations become applicable to our operations. Such costs could materially adversely affect our results of operations, cash flows and financial position. Our failure to comply with the laws, regulations and other legal requirements applicable to our business, even as a result of factors beyond our control, could result in the suspension or termination of our operations and subject us to administrative, civil and criminal penalties and damages as well as corrective action costs.
We face community opposition from certain parties with respect to our development of the Beetaloo and related operations, which could result in significant costs and delays and could impede our ability to obtain the government approvals required for such operations.
We have been the target of protests and adverse publicity from certain parties due to concerns with environmental issues or Indigenous rights, and there is a risk from existing or future community opposition to our operations. For example, two pastoralists whose pastoral leases are subject, in part, to our petroleum interests refused to enter into access agreements for us to conduct certain regulated activities which require an access agreement, and we were required to make applications to the relevant tribunal to obtain access agreements for such regulated activities. Additionally, the Central Australian Frack Free Alliance has sought judicial review of the Ministers decision to approve one of our environment management plans to conduct certain petroleum exploration activities. The matter is yet to be determined by the courts, but the courts decisions could result in a redetermination of the subject environment management plan.
Disapproval from local communities or other interested parties may lead to direct action that could impede our ability to carry out our operations, resulting in project delay, reputational damage and increased costs, and thus impact our financial performance. Such community opposition may include undertaking legal proceedings (including challenges to required governmental approvals), media campaigns and protests, which could result in significant legal costs and delays. If such community members were successful in their campaigns, we may not be able to obtain the permits and approvals we will need to carry out our commercial operations.
35
Table of Contents
The exploration and development of natural gas in the Beetaloo can pose native title and heritage risks, potentially leading to legal disputes, operational disruptions, and reputational damage.
We are required to comply with the Native Title Act 1993 (Cth) and we operate on areas in which native title has been judicially determined to exist. Consultation and negotiations have occurred, leading to exploration agreements. Further agreements will be required for any production phase, but the exploration agreements anticipate production and provide the parameters for those negotiations and outcomes. We will also be required to comply with the Aboriginal Land Rights (Northern Territory) Act 1976 (Cth) (ALRA) for tenement applications over Aboriginal land (i.e., freehold land held by an Aboriginal Land Trust under the ALRA, or land subject to a deed of grant held in escrow by an Aboriginal Land Council under the ALRA). Compliance with either legislative regime and their respective requirements for negotiation and agreement can significantly delay the grant of exploration and production tenements, and substantial compensation may be payable as part of any agreement reached. Applications for exploration tenements over Aboriginal land can also be placed into moratorium for 5 years at a time under the ALRA (unless the Governor-General of Australia declares by proclamation that the Australian national interest requires that the license be granted). These legislative regimes may impact our existing or future activities, ability to develop projects and operational and financial performance.
In addition, we will also need to comply with the Northern Territory Aboriginal Sacred Sites Act 1989 (NT) (SSA), the Heritage Act 2011 (NT), the Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Heritage Protection Act 1984 (Cth) and the ALRA in relation to sacred sites and certain Aboriginal cultural heritage. Sacred sites and Aboriginal cultural heritage have been identified within areas covered by the tenements in which we have an interest, and other such sites may exist. It is an offense under Part IV of the SSA to enter onto or remain on, carry out work on or use, or desecrate a sacred site without authority. All Sacred Sites are protected under the SSA, regardless of whether or not they are included on the register maintained under the SSA. Destruction, disturbance or harming protected sites and artifacts may result in us incurring significant civil and/or criminal penalties, which may adversely impact or delay our activities. In addition, in the event of damage to sacred sites and Aboriginal cultural heritage, remediation costs may be substantive. Compliance with these laws requires significant expenditure and non-compliance may potentially result in fines and requests for improvement action from the regulator all of which may result in limitations on actions and project delays or cost overruns.
Upon commencement of commercial production, we are required by the Australian government to produce natural gas in the Beetaloo on a Scope 1 net zero basis. We also have set an internal goal of producing natural gas with net zero equity Scope 1 and 2 emissions. Meeting these requirements and goals may increase our costs of production, and we may be unable to meet these requirements and goals.
Australian law requires that, upon commencement of commercial production and reaching the relevant threshold of 100,000 t-CO2-e emissions per financial year, we produce natural gas in the Beetaloo on a Scope 1 net zero basis. We also have set an internal goal of producing natural gas with net zero equity Scope 1 and 2 emissions. To achieve this, we intend to utilize renewables to supply our upstream operation power needs and integrate carbon capture and sequestration with our upstream production activities as well as purchase carbon credits as required, however there is no guarantee we will achieve such plans. If we are unable to utilize renewables to supply our upstream operation power needs and integrate carbon capture and sequestration with our upstream production activities to the extent we currently expect, if the price of carbon credits increases or if we have otherwise underestimated the amount of Scope 1 or Scope 2 emissions that we will need offset, then our costs of production will increase further which could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations.
We may not achieve, and there are potential risks associated with, our growth strategy and vision to become a net zero equity emissions producer for our equity share of Scope 1 and Scope 2 emissions. Achievement of our vision of becoming a net zero equity emissions producer of gas is presently uncertain and depends on us being able to economically manage our carbon emissions, which could, for example, be impacted by availability of future revenues to fund various carbon initiatives, market pricing of carbon offsets, technological developments
36
Table of Contents
affecting operations and costs of implementing sustainable practices. Failure, or perceived failure, to meet these or other goals or commitments regarding the ESG characteristics of our offerings may subject us to litigation or stakeholder activism (which may be costly) or otherwise adversely impact our business. For more information, see our risk factor titled We are subject to risks related to corporate social responsibility, including the risk that our expectations or estimates regarding environmental, social and governance matters may not be achieved or may be incorrect.
Increased attention to ESG matters and environmental conservation measures may adversely impact our business.
Increasing investor and societal attention to climate change and ESG, rising expectations for companies to address climate change and develop voluntary ESG initiatives, and growing consumer demand for alternative forms of energy may result in increased costs (including but not limited to increased costs related to compliance, stakeholder engagement, contracting and insurance), reduced demand for our products, reduced profits, increased investigations and litigation and negative impacts on our access to capital markets. Increasing attention to climate change, environmental justice and environmental conservation, for example, may result in demand shifts for natural gas products and additional governmental investigations and private litigation against us. To the extent that societal, political, or other factors are involved, including factors associated with geopolitical considerations, it is possible that we could be subject to changing market conditions, liability, or loss of certain assets without regard to our ultimate role in the causation of or contribution to the asserted events or damages, or to other mitigating factors.
Opposition toward natural gas drilling and development activity has been growing globally. Companies in the natural gas industry are often the target of activist efforts from both individuals and non-governmental organizations regarding safety, environmental compliance and business practices. Anti-development activists are working to, among other things, reduce access to federal and state government lands and delay or cancel certain projects such as the development of natural gas shale plays.
While we have in the past engaged in, and expect in the future to continue to engage in, voluntary initiatives (such as voluntary disclosures, certifications, or goals, among others) to improve the ESG profile of our company and/or products or to respond to stakeholder expectations, such initiatives may be costly and may not have the desired effect. For example, we may ultimately be unable to complete certain initiatives or targets, either on the timelines initially announced or at all, due to technological or legal cost, or other constraints, which may be within or outside of our control. In some cases, our statements or actions are based on hypothetical expectations and assumptions that may or may not be representative of current or actual risks or events or forecasts of expected risks or events, including the costs associated therewith. Such expectations and assumptions are necessarily uncertain and may be prone to error or subject to misinterpretation given the long timelines involved and the lack of an established single approach to identifying, measuring and reporting on many ESG matters. Such disclosures may also be at least partially reliant on third-party information that we have not verified, or cannot verify, independently.
Our actions or statements based on expectations, assumptions or third-party information may subsequently be determined to be erroneous, unreasonable, or otherwise inappropriate. If we fail to, or are perceived to fail to, comply with or advance certain ESG initiatives (including the timeline and manner in which we complete such initiatives), we may be subject to various adverse impacts, including reputational damage and potential stakeholder engagement and/or litigation, even if such initiatives are currently voluntary. For example, there have been increasing allegations of greenwashing against companies making significant ESG claims due to a variety of perceived deficiencies in performance, including as stakeholder perceptions of sustainability continue to evolve.
In addition, we expect there will likely be increasing levels of regulation, disclosure-related and otherwise, with respect to ESG matters. For example, various policymakers, such as the SEC and the Australian Treasury,
37
Table of Contents
have adopted, or are considering adopting, rules to require companies to provide significantly expanded climate-related disclosures in their periodic reporting, which may require us to incur significant additional costs to comply, including the implementation of significant additional internal controls, processes and procedures regarding matters that have not been subject to such controls in the past, and impose increased oversight obligations on our management and board of directors. Simultaneously, there are efforts by some stakeholders to reduce companies efforts on certain ESG-related matters. Both advocates and opponents to certain ESG matters are increasingly resorting to a range of activism forms, including media campaigns and litigation, to advance their perspectives. To the extent we are subject to such activism, it may require us to incur costs or otherwise adversely impact our business. In addition, we note that standards and expectations regarding carbon accounting and the processes for measuring and counting GHG emissions and GHG emission reductions are evolving, and it is possible that our approach to measuring both our emissions and our approaches to reduce emissions may be, either currently or in the future, considered inconsistent with common or best practices with respect to measuring and accounting for such matters, reducing overall emissions and/or achieving net zero. If our approaches to such matters fall out of step with common or best practice, we may be subject to additional scrutiny, criticism, regulatory and investor engagement or litigation, any of which may adversely impact our business, financial condition or results of operations. This and other stakeholder expectations will likely lead to increased compliance costs as well as scrutiny that could heighten all of the risks identified in this risk factor.
Organizations that provide information to investors on corporate governance and related matters have developed ratings processes for evaluating companies on their approach to ESG matters. Such ratings are used by some investors to inform their investment and voting decisions. Unfavorable ESG ratings and recent activism directed at shifting funding away from companies with fossil fuel-related assets could lead to increased negative investor sentiment toward us and our industry and to the diversion of investment to other industries, which could have a negative impact on our access to and costs of capital. Also, institutional lenders may decide not to provide funding for fossil fuel energy companies based on climate change and natural capital related concerns, which could affect our access to capital for potential growth projects. Moreover, to the extent ESG matters negatively impact our reputation, we may not be able to compete as effectively to recruit or retain employees, customers, or business partners. Such ESG matters may also impact our suppliers or service providers, which may adversely impact our business, financial condition, or results of operations.
Federal and local legislative and regulatory initiatives relating to hydraulic fracturing as well as governmental reviews of such activities could result in increased costs and additional operating restrictions or delays in the completion of natural gas wells and adversely affect our production.
Public debate exists regarding the potential sub surface and surface impact of unconventional drilling, including concern about the impacts of unconventional drilling water. In addition, there are many regulatory requirements for us to adhere to including, but not limited to, those specified in the Petroleum Act, Petroleum Regulations (NT), Petroleum (Environment) Regulations 2016 (NT), Water Act (NT), Environment Protection Act 2019 (NT), Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999 (Cth) and the Work Health and Safety (National Uniform Legislation) Act (NT) and Work Health and Safety (National Uniform Legislation) Regulations (NT). Unconventional drilling requires large volumes of water (the availability and regulation of which may change over time) and there are costs associated with water disposal that may be required should we produce water in our wells. As more impacts of unconventional drilling are fully understood, it may be subject to additional regulations or restrictions from local, state, or federal governmental authorities, resulting in increased compliance costs. Any modification to the current requirements may adversely impact the value of our assets and future financial performance.
For example, on April 17, 2018, the NT Government announced that it accepted all 135 of the recommendations set out in the The Scientific Inquiry into Hydraulic Fracturing in the Northern Territory (Fracking Inquiry Report). The implementation of the recommendations has resulted in a more rigorous regulatory regime by placing additional obligations on oil and natural gas companies including the introduction of a stricter code of practice for decommissioning onshore shale gas wells, requiring tenement holders to provide
38
Table of Contents
a non-refundable levy prior to granting any further production approvals and introducing no go zones where a person cannot explore or drill for petroleum resources.
A number of the recommendations may affect the Companys tenements. In particular, some key recommendations include but are not limited to: (a) decommissioning wells to implement a stricter code of practice setting out the minimum requirements for the decommissioning of onshore shale natural gas wells in respect of cement integrity tests, the repair of defects prior to abandonment, and cement plugs to be placed to isolate critical formations; (b) objections to allow for any person to object to the proposed grant of an EP; (c) compensation to landowners, a land access agreement must be negotiated and signed by the pastoral lessee and the natural gas company; (d) accountable industry practice to allow for the NT Government to develop and implement a financial assurance framework for the onshore shale natural gas industry prior to the grant of any further production approvals; (e) non-refundable levy for appropriate monitoring and remediation activities; (f) merits review to allow for a range of third parties to have standing to seek merits review in relation to decisions under the petroleum statue and regulations prior to the granting of production approvals; and (g) reserved blocks or no go zones, where certain areas must be declared reserved blocks (areas where a person cannot explore or drill for petroleum resources), each with an appropriate buffer zone.
Our operations are subject to risks relating to climate change that could increase compliance or operating costs, limit natural gas exploration and production areas, and reduce demand for the natural gas we produce.
Climate change continues to attract considerable public and scientific attention. As a result, numerous proposals have been adopted, been considered for adoption, and are likely to continue to be made at the international, national, regional and state levels of government to monitor and limit emissions of carbon dioxide, methane and other GHGs. These efforts have included consideration of cap-and-trade programs, carbon taxes, GHG reporting and tracking programs and regulations that directly limit GHG emissions from certain sources. As a natural gas development company, we are exposed to both transition risks and physical risks associated with climate change. Transitioning to a lower-carbon economy may entail extensive policy, legal, technology and market changes and, if demand for gas declines, we will find it difficult to commercialize any resources we discover.
The transition and physical risks associated with climate change (including also regulatory responses to such issues and associated costs) may significantly affect our operating and financial performance. For example, the Australian government announced its policy to target net zero carbon emissions economy-wide by 2050. In connection with that announcement, the Australian government designated that shale natural gas facilities in the Beetaloo that exceed the relevant threshold of 100,000 gross tonnes of CO2e emissions per financial year will be given a Zero GHG baseline. Accordingly, once a natural gas producer has exceeded the 100,000 gross t-CO2e Scope 1 threshold, the Company must demonstrate that it has achieved Scope 1 net zero emissions, either through operational measures (such as carbon capture and storage) or by purchasing carbon offsets. Various policymakers have also adopted, or are considering adopting, rules to require companies to provide significantly expanded climate-related disclosures. For more information, see our risk factor titled Increased attention to ESG matters and environmental conservation measures may adversely impact our business. In addition, the increased frequency or severity of natural disasters and weather events due to climate change could delay or prevent our ability to conduct our activities, which could negatively impact our financial performance.
Increasing attention to global climate change has resulted in increased risk of public and private litigation, which could increase our costs or otherwise adversely affect our business. A number of parties have sought to bring suit against oil and natural gas companies in state or federal court, alleging, among other things, that such companies contributed to climate impacts by producing, handling or marketing fossil fuels, or violate citizens rights by contributing to climate change, or alleging that companies have been aware of the adverse effects of climate change for some time but failed to adequately disclose those impacts. In some jurisdictions, litigation has also been brought to establish legal mandates for particular entities to take certain climate-related actions, such as pursuing aggressive emissions reductions for their Scope 3 emissions reductions, regardless of whether entities
39
Table of Contents
have established any such goals already. The ultimate outcome and impact to us of any such litigation cannot be predicted with certainty, and we could incur substantial legal costs associated with defending these and similar lawsuits in the future. Shareholder activism related to climate change has also recently been increasing in our industry, and shareholders may attempt to effect changes to our business or governance, whether by stockholder proposals, public campaigns, proxy solicitations or otherwise. Any of these risks could result in unexpected costs, negative sentiments about us, disruptions in our operations, increases to our operating expenses and reduced demand for our products, which in turn could have an adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
There are also increasing financial risks for fossil fuel producers as various capital providers may elect in the future to shift some or all of their investments into non-fossil fuel energy related sectors. Many capital providers have also incorporated more substantial assessment of climate-related matters into their funding considerations, including how such funding may impact such capital providers own Scope 3 emissions, and may elect not to provide, or to continue not to provide, funding to fossil fuel energy companies. For example, at COP26, the Glasgow Financial Alliance for Net Zero (GFANZ) announced that commitments from over 650 firms across over 50 countries had capital committed to net zero goals. The various sub-alliances of GFANZ generally require participants to set short-term, sector-specific targets to transition their financing, investing, and/or underwriting activities to net zero emissions by 2050. There is also a risk that financial institutions will be required to adopt policies that have the effect of reducing the funding provided to the fossil fuel sector. Limitation of investments in and financings for fossil fuel energy companies could result in the restriction, delay or cancellation of drilling programs or development or production activities.
Significant physical effects of climatic change have the potential to damage our facilities, disrupt our production activities and cause us to incur significant costs in preparing for or responding to those effects. Climate change could have an effect on the frequency or severity of weather events (including hurricanes, wildfires, droughts and floods), sea levels, the arability of farmland, changes in temperature and other meteorological patterns, and water availability and quality. If such effects were to occur, our development and production operations have the potential to be adversely affected. Potential adverse effects could include damages to our facilities from powerful winds or rising waters in low lying areas, disruption of our production activities either because of climate related damages to our facilities or in our costs of operation potentially arising from such climatic effects, less efficient or non-routine operating practices necessitated by climate effects or increased costs (or decreased availability) for insurance coverage in the aftermath of such effects. Additionally, in response to changing climatic conditions, certain policymakers have proposed increased restrictions on the withdrawal and use of water for fossil fuel production or other industrial uses, which may either delay or prohibit our access to certain bodies of water; to the extent we do not have sufficient local water sources available, we may be required to incur substantial costs or curtail operations, which may become more significant in periods of drought or other water scarcity. Significant physical effects of climate change could also have an indirect effect on our financing and operations by disrupting the transportation or process-related services provided by midstream companies, service companies or suppliers with whom we have a business relationship. We may not be able to recover through insurance some or any of the damages, losses or costs that may result from potential physical effects of climate change. While we may take various actions to mitigate our business risks associated with climate change, this may require us to incur substantial costs and may not be successful, due to, among other things, the uncertainty associated with the longer-term projections associated with managing climate risks.
Our ability to pursue our business strategies may be adversely affected if we incur costs and liabilities due to a failure to comply with environmental, health and safety laws or regulations or a release into the environment.
Despite efforts to conduct activities in an environmentally responsible manner and in accordance with applicable laws, there is a risk that gas activities may cause harm to the environment which could impact production or delay future development timetables.
We are subject to laws and regulations to minimize the environmental impact of our operations and rehabilitation of any areas affected by our operations. Changes to environmental laws may result in the cessation
40
Table of Contents
or reduction of our activities, materially increase development or production costs or otherwise adversely impact our operations, financial performance or prospects. Penalties for failure to adhere to requirements and, in the event of environmental damage, remediation costs can be substantial and may not, in their entirety, be insurable. Compliance with these laws requires significant expenditure and non-compliance may potentially result in fines or requests for improvement action from the regulator.
In addition, if we were to be held responsible for environmental damage, in addition to remediation costs, we may suffer reputational damage, possible suspension or cessation of operations, revocation of permits or financial penalties.
We may incur significant costs and liabilities as a result of environmental, health and safety laws and regulations applicable to the operation of our wells, gathering systems and other facilities including, for example, the following laws, as amended from time to time. Further details of these legislative instruments are described in the section entitled BusinessEnvironmental Matters and Regulation:
| | Petroleum Act 1984 (NT); |
| | Petroleum Regulations 2020 (NT); |
| | Petroleum (Environment) Regulations 2016 (NT); |
| | Water Act 1992 (NT); |
| | Environment Protection Act 2019 (NT); |
| | Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999 (Cth); |
| | Northern Territory Aboriginal Sacred Sites Act 1989 (NT); |
| | Heritage Act 2011 (NT); |
| | Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Heritage Protection Act 1984 (Cth); |
| | Native Title Act 1993 (Cth); |
| | Aboriginal Land Rights (Northern Territory) Act 1976 (NT); |
| | The National Greenhouse and Energy Reporting Act 2007 (Cth); and |
| | Work Health and Safety (National Uniform Legislation) Act 2011 (NT). |
These laws and their implementing regulations, as well as state counterparts, generally restrict the level of pollutants emitted to ambient air, discharges to surface water and disposals or other releases or threats of release to surface, soils and groundwater. Failure to comply with these laws and regulations may result in the assessment of sanctions, including administrative, civil and criminal penalties, the imposition of investigatory, remedial and corrective action obligations, the incurrence of capital expenditures, the occurrence of delays in the permitting, development or expansion of projects and the issuance of orders enjoining some or all of our future operations in a particular area. Certain environmental laws impose strict joint and several liability, without regard to fault or legality of conduct, for costs required to clean up and restore sites where hazardous substances or other wastes have been disposed of or otherwise released. Moreover, it is not uncommon for neighboring landowners and other third parties to file claims for personal injury and property damage allegedly caused by the release of hazardous substances, wastes or other materials into the environment. In addition, these laws and regulations may restrict the rate of natural gas production or underground injection, disposal, and sequestration of carbon dioxide. Historically, our environmental compliance costs have not had a material adverse effect on our results of operations; however, there can be no assurance that such costs will not be material in the future or that such future compliance will not have a material adverse effect on our business and operating results.
In addition, as a result of these environmental, health and safety laws and regulations, and their impact on our operations, we rely on specialized contracted companies to perform the majority of the specialized services
41
Table of Contents
inherent in the oil and natural gas industry. As such, we rely on the ability of these contractors to provide trained labor and properly designed and maintained equipment unique to their services. With the cyclical nature of the oil and natural gas business, the personnel used by these specialized contractors to perform these services may differ significantly in experience levels. From time to time, these specialized contractors may use new personnel that are still in training or may further sub-contract these services to other companies or personnel. There is a risk that these sub-contractors are unqualified or under-trained or that their equipment is not properly designed or maintained, which could result in work being performed inadequately or unsafely.
Moreover, public interest in the protection of the environment has increased dramatically in recent years. The trend of more expansive and stringent environmental legislation and regulations applied to the oil and natural gas industry could continue, resulting in increased costs of doing business and consequently affecting profitability. To the extent laws are enacted or other governmental action is taken that restricts drilling or production or imposes more stringent and costly operating, waste handling, disposal and cleanup requirements, our business, prospects, financial condition or results of operations could be materially adversely affected.
Our future gathering systems and processing, treating and fractionation facilities will be subject to regulation by the Northern Territory that could have a material adverse effect on our operations and cash flows.
NT Government regulation of gathering systems and processing, treating and fractionation facilities includes safety and environmental requirements. In addition, several of our future gas gathering systems will be subject to non-discriminatory take requirements and complaint-based regulation with respect to our rates and terms and conditions of service. Northern Territory regulation may cause us to incur additional costs or limit our operations, any or all of which could have a material adverse effect on our operations and revenue.
We may face unanticipated water and other waste disposal costs as a result of increased water-related regulations.
We may be subject to regulation that restricts our ability to discharge water produced as part of our natural gas production operations. Productive zones frequently contain water that must be removed for the natural gas to produce, and our ability to remove and dispose of sufficient quantities of water from the various zones will determine whether we can produce natural gas in commercial quantities. The produced water must be transported from the leasehold and/or injected into disposal wells. The availability of disposal wells with sufficient capacity to receive all of the water produced from our wells may affect our ability to produce our wells. Also, the cost to transport and dispose of that water, including the cost of complying with regulations concerning water disposal, may reduce our profitability. Where water produced from our projects fails to meet the quality requirements of applicable regulatory agencies, our wells produce water in excess of the applicable volumetric permit limits, the disposal wells fail to meet the requirements of applicable regulatory agencies, or we are unable to secure access to disposal wells with sufficient capacity to accept all of the produced water, we may have to shut in wells, reduce drilling activities, or upgrade facilities for water handling or treatment. The costs to dispose of this produced water may increase if any of the following occur:
| | we cannot obtain future permits from applicable regulatory agencies; water of lesser quality or requiring additional treatment is produced; |
| | our wells produce excess water; |
| | new laws and regulations require water to be disposed in a different manner; or |
| | costs to transport the produced water to the disposal wells increase. |
Restrictions on drilling, completion, production or related activities intended to protect certain species of wildlife may adversely affect our ability to conduct drilling activities in some of the areas where we operate.
Natural gas operations in our operating areas can be adversely affected by seasonal or permanent restrictions on drilling activities designed to protect various wildlife, such as those restrictions imposed under the
42
Table of Contents
Environment Protection Act 2019 (NT) or Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999 (Cth) (the EPBC Act). Seasonal restrictions may limit our ability to operate in certain protected areas and can intensify competition for drilling rigs, oilfield equipment, services, supplies and qualified personnel, which may lead to periodic shortages when drilling is allowed. These constraints and the resulting shortages or high costs could delay our operations and materially increase our operating and capital costs. Permanent restrictions imposed to protect endangered species could prohibit drilling in certain areas or require the implementation of expensive mitigation measures. The designation of previously unprotected species in areas where we operate as threatened or endangered could cause us to incur increased costs arising from species protection measures or could result in limitations on our exploration, development and production activities that could have an adverse impact on our ability to develop and produce our reserves. To the extent species are listed or re-designated under the EPBC Act, or previously unprotected species are designated as threatened or endangered in areas where our properties are located, operations on those properties could incur increased costs arising from species protection measures and face delays or limitations with respect to production activities thereon. There is also increasing interest in nature-related matters beyond protected species, such as general biodiversity, which may similarly require us to incur costs or take other measures which may materially impact our business or operations.
Our business is subject to complex and evolving laws and regulations regarding privacy and data protection.
The regulatory environment surrounding data privacy and protection is constantly evolving and can be subject to significant change. New laws and regulations governing data privacy and the unauthorized disclosure of personal or confidential information pose increasingly complex compliance challenges and could potentially elevate our costs. Any failure to comply with these laws and regulations could result in significant penalties and legal liability. We continue to monitor and assess the impact of these laws, which in addition to penalties and legal liability, could impose significant costs for investigations and compliance, require us to change our business practices and carry significant potential liability for our business should we fail to comply with any such applicable laws.
Risks Related to our Corporate Structure
We are a holding company. Our sole material asset is our equity interest in Tamboran Resources Limited and we will be accordingly dependent upon distributions from Tamboran Resources Limited to pay taxes and cover our corporate and other overhead expenses.
We are a holding company and have no material assets other than our equity interest in Tamboran Resources Limited. See Corporate Reorganization. We have no independent means of generating revenues. To the extent Tamboran Resources Limited has available cash, we intend to cause Tamboran Resources Limited to make distributions to us, in an amount at least sufficient to allow us to pay our taxes and reimburse us for our corporate and other overhead expenses. We may be limited, however, in our ability to cause Tamboran Resources Limited and its subsidiaries to make these and other distributions or payments to us due to certain limitations, including the cash requirements and financial condition of Tamboran Resources Limited and restrictions in any relevant debt instruments entered into by Tamboran Resources Limited or its subsidiaries and/other entities in which it directly or indirectly holds an equity interest. To the extent that we need funds and Tamboran Resources Limited or its subsidiaries are restricted from making such distributions or payments under applicable laws or regulations or under the terms of any future financing arrangements, or are otherwise unable to provide such funds, our liquidity and financial condition could be materially adversely affected.
The unaudited pro forma financial information included in this prospectus is preliminary and the actual financial condition and results of operations may differ materially.
The unaudited pro forma financial information included in this prospectus is presented for illustrative purposes only and is not necessarily indicative of what our actual financial position or results of operations would be. The preparation of the pro forma financial information is based upon available information and certain
43
Table of Contents
assumptions and estimates that we believe are reasonable. The unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial information does not consider any impacts of integration costs, potential revenue enhancements, anticipated cost savings and expense efficiencies, or other synergies that may or may not result from the corporate reorganization or any strategies that management may consider in order to continue to efficiently manage our Predecessors operations. Accordingly, the final accounting adjustments may differ materially from the pro forma adjustments reflected in this prospectus. See Selected Historical Consolidated Financial Data for more information.
We may be unable to achieve some or all of the benefits that we expect to achieve from the corporate reorganization, which could materially adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
We may not be able to achieve the full strategic and financial benefits expected to result from the corporate reorganization, or such benefits may be delayed or not occur at all. We may not achieve these and other anticipated benefits for a variety of reasons, including, among others, because we may experience unanticipated competitive developments, including changes in the conditions of industry and the markets in which we operate, including fluctuations in the prices of natural gas that could negate some or all of the expected benefits from the corporate reorganization.
If we do not realize some or all of the benefits expected to result from the corporate reorganization, or if such benefits are delayed, our business, expected future financial and operating results and our prospects could be adversely affected.
Risks Related to the Offering, our Common Stock and our CDIs
The requirements of being a public company, including compliance with the reporting requirements of the ASX listing rules and the Exchange Act, and the requirements of the SOX, may strain our resources, increase our costs and distract management, and we may be unable to comply with these requirements in a timely or cost-effective manner.
As our CDIs and common stock are publicly traded in both Australia and the United States, we will need to comply with new laws, regulations and requirements, certain corporate governance provisions of SOX, related regulations of the SEC and the requirements of the ASX and NYSE, with which we were not required to comply as an unlisted or private company. Complying with these statutes, regulations and requirements will occupy a significant amount of our time and will significantly increase our costs and expenses. We will need to:
| | institute a more comprehensive compliance function to test and conclude on the sufficiency of our internal controls around financial reporting |
| | comply with rules promulgated by the ASX and the NYSE; |
| | prepare and distribute periodic public reports; |
| | establish new internal policies, such as those relating to insider trading; and |
| | involve and retain to a greater degree outside professionals in the above activities. |
Furthermore, while we generally must comply with Section 404 of the SOX, we are not required to have our independent registered public accounting firm attest to the effectiveness of our internal controls until our first annual report subsequent to our ceasing to be an emerging growth company. We may not be required to have our independent registered public accounting firm attest to the effectiveness of our internal controls until as late as our annual report for the year ending . At any time, we may conclude that our internal controls, once tested, are not operating as designed or that the system of internal controls does not address all relevant financial statement risks. Once required to attest to control effectiveness, our independent registered public accounting firm may issue a report that concludes it does not believe our internal controls over financial reporting are effective. Compliance with SOX requirements may strain our resources, increase our costs and distract management; and we may be unable to comply with these requirements in a timely or cost-effective manner.
44
Table of Contents
If, however, we do not follow those procedures and policies, or they are not sufficient to prevent non-compliance, we could be subject to liability, fines and lawsuits. These laws, regulations and standards are subject to varying interpretations and, as a result, their application in practice may evolve over time as new guidance is provided by regulatory and governing bodies. We intend to invest resources to comply with evolving laws, regulations and standards, and this investment may result in increased general and administrative expenses and a diversion of managements time and attention from revenue generating activities to compliance activities. If, notwithstanding our efforts to comply with new laws, regulations and standards, we fail to comply, regulatory authorities may initiate legal proceedings against us and our business may be harmed.
The initial public offering price of our common stock in the United States may not be indicative of the market price of our common stock after this offering on the NYSE. In addition, an active, liquid and orderly trading market for our CDIs on the ASX and common stock on the NYSE may not develop or be maintained, and our stock price may be volatile.
Prior to this offering, our common stock was not traded on the NYSE or any other U.S. market (only on the ASX in the form of CDIs since December 13, 2023 and before that ordinary shares of our Predecessor were traded on the ASX). An active, liquid and orderly trading market for our common stock may not develop or be maintained after this offering. Active, liquid and orderly trading markets usually result in less price volatility and more efficiency in carrying out investors purchase and sale orders. The market price of our CDIs and common stock could vary significantly as a result of a number of factors, some of which are beyond our control. In the event of a drop in the market price of our CDIs and common stock, you could lose a substantial part or all of your investment in our CDIs or common stock. The initial public offering price will be negotiated between us and representatives of the underwriters, based on numerous factors which we discuss in Underwriting, and may not be indicative of the market price of our CDIs or common stock after this offering. Consequently, you may not be able to sell shares of our common stock at prices equal to or greater than the price paid by you in this offering.
The following factors could affect our stock price:
| | our operating and financial performance and drilling locations, including reserve estimates; |
| | quarterly variations in the rate of growth of our financial indicators, such as net income per share, net income and revenues; |
| | the public reaction to our press releases, our other public announcements and our filings with the ASX and the SEC; |
| | strategic actions by our competitors; |
| | changes in revenue or earnings estimates, or changes in recommendations or withdrawal of research coverage, by equity research analysts; |
| | speculation in the press or investment community; |
| | the failure of research analysts to cover our CDIs or common stock; |
| | sales of our CDIs or common stock by us or our stockholders, or the perception that such sales may occur; |
| | changes in accounting principles, policies, guidance, interpretations or standards; |
| | additions or departures of key management personnel; |
| | actions by our stockholders; |
| | announcements or events that impact our assets, competitors or markets; |
| | general market conditions, including fluctuations in commodity prices; |
| | domestic and international economic, legal and regulatory factors unrelated to our performance; and |
| | the realization of any risks described under this Risk Factors section. |
45
Table of Contents
The stock markets in general have experienced extreme volatility that has often been unrelated to the operating performance of particular companies. These broad market fluctuations may adversely affect the trading price of our CDIs and common stock. Securities class action litigation has often been instituted against companies following periods of volatility in the overall market and in the market price of a companys securities. Such litigation, if instituted against us, could result in very substantial costs, divert our managements attention and resources and harm our business, operating results and financial condition.
Changes in foreign currency exchange rates could materially adversely affect our business, results of operations or financial condition.
In our operations, there are transactions and balances denominated in currencies other than the U.S. dollar (which is the currency used to report our results of operations and financial condition in our financial statements), consisting primarily of the Australian dollar. To the extent our assets and liabilities denominated in Australian dollars as of June 30, 2023 are not hedged, we estimate that a 10% change in the exchange rate versus the U.S. dollar would expose us to foreign currency gains or losses of approximately US$16.9 million for the Australian dollar.
In addition, all of our facilities are located in Australia, a majority of our officers and employees are residents in Australia and substantially all of our expenses are payable in Australian dollars. In the event that the U.S. dollar weakens compared with the Australian dollar, our results of operations or financial condition may be adversely affected, perhaps substantially.
We have engaged in transactions with our affiliates and expect to do so in the future. The terms of such transactions and the resolution of any conflicts that may arise may not always be in our or our stockholders best interests.
We have engaged in transactions and expect to continue to engage in transactions with affiliated companies. Related party transactions can create the possibility of conflicts of interest with regard to our management. Such a conflict could cause an individual in our management to seek to advance his or her economic interests above ours. Further, the appearance of conflicts of interest created by related party transactions could impair the confidence of our investors. Once established, our Audit and Risk Management Committee will review related party transactions in accordance with our related party transaction policy; however, review of related party transactions by our Audit and Risk Management Committee does not mean such transactions will have the expected benefits and, as such, could have an adverse impact on our financial condition or results of operations.
Certain of our affiliates are participants in joint ventures or may have other rights with respect to properties in which we have interests. For instance, Daly Waters, which is controlled by Bryan Sheffield, is an equal owner of the TB2 Joint Venture that owns our interests in EPs 76, 98 and 117. Certain actions, such as a sale of property or incurrence of indebtedness, will require the approval of Daly Waters or its representatives on the board of the TB2 Joint Venture. In addition, we have granted Daly Waters Royalty, which is controlled by Bryan Sheffield, and certain of our directors ORRIs in certain of the permits we have interests in. See Certain Relationships and Related Party Transactions and BusinessOur Assets within the Beetaloo.
Our certificate of incorporation and bylaws, as well as Delaware law, will contain provisions that could discourage acquisition bids or merger proposals, which may adversely affect the market price of our CDIs and common stock.
Our certificate of incorporation will authorize our board of directors to issue preferred stock without stockholder approval. If our board of directors elects to issue preferred stock, it could be more difficult for a third-party to acquire us. In addition, some provisions of our certificate of incorporation and bylaws could make
46
Table of Contents
it more difficult for a third-party to acquire control of us, even if the change of control would be beneficial to our stockholders, including:
| | limitations on the removal of directors; |
| | our classified board of directors with directors serving staggered three-year terms; |
| | limitations on the ability of our stockholders to call special meetings; |
| | establishing advance notice provisions for stockholder proposals and nominations for elections to the board of directors to be acted upon at meetings of stockholders; |
| | the requirement that the affirmative vote of the holders of at least 662⁄3% in voting power of all the then-outstanding shares of our stock be obtained to amend and restate our existing bylaws or to remove directors; |
| | the requirement that the affirmative vote of the holders of at least 662⁄3% in voting power of all the then-outstanding shares of our stock be obtained to amend our certificate of incorporation; |
| | providing that the board of directors is expressly authorized to adopt, or to alter or repeal our bylaws; and |
| | establishing advance notice and certain information requirements for nominations for election to our board of directors or for proposing matters that can be acted upon by stockholders at stockholder meetings. |
Our certificate of incorporation will designate the Court of Chancery of the State of Delaware as the sole and exclusive forum for certain types of actions and proceedings that may be initiated by our stockholders, which could limit our stockholders ability to obtain a favorable judicial forum for disputes with us or our directors, officers, employees or agents.
Our certificate of incorporation will provide that, unless we consent in writing to the selection of an alternative forum, the Court of Chancery of the State of Delaware will, to the fullest extent permitted by applicable law, be the sole and exclusive forum for (i) any derivative action or proceeding brought on our behalf, (ii) any action asserting a claim of breach of a fiduciary duty owed by any of our directors, officers, employees or agents to us or our stockholders, (iii) any action asserting a claim against us or any director or officer or other employee of ours arising pursuant to any provision of the Delaware General Corporation Law (the DGCL), our certificate of incorporation or our bylaws, or (iv) any action asserting a claim against us or any director or officer or other employee of ours that is governed by the internal affairs doctrine, in each such case subject to such Court of Chancery having personal jurisdiction over the indispensable parties named as defendants therein. Any person or entity purchasing or otherwise acquiring any interest in shares of our capital stock will be deemed to have notice of, and consented to, the provisions of our certificate of incorporation described in the preceding sentence. This choice of forum provision may limit a stockholders ability to bring a claim in a judicial forum that it finds favorable for disputes with us or our directors, officers, employees or agents, which may discourage such lawsuits against us and such persons. Alternatively, if a court were to find these provisions of our certificate of incorporation inapplicable to, or unenforceable in respect of, one or more of the specified types of actions or proceedings, we may incur additional costs associated with resolving such matters in other jurisdictions, which could adversely affect our business, financial condition or results of operations.
Our certificate of incorporation will provide that the exclusive forum provision will be applicable to the fullest extent permitted by applicable law. Section 27 of the Exchange Act creates exclusive federal jurisdiction over all suits brought to enforce any duty or liability created by the Exchange Act or the rules and regulations thereunder. Accordingly, our certificate of incorporation will provide that the exclusive forum provision will not apply to suits brought to enforce any liability or duty created by the Exchange Act or any other claim for which the federal courts have exclusive jurisdiction.
47
Table of Contents
If securities or industry analysts do not publish research reports or publish unfavorable research about our business, the price and trading volume of our CDIs and common stock could decline.
The trading market for our CDIs and common stock depends in part on the research reports that securities or industry analysts publish about us or our business. We do not currently have and may never obtain research coverage by securities and industry analysts. If no securities or industry analysts commence coverage of us, the trading price for our CDIs and common stock and other securities would be negatively affected. In the event we obtain securities or industry analyst coverage, if one or more of the analysts who covers us downgrades our securities, the price of our securities would likely decline. We do not have any control over these analysts. If one or more of these analysts cease to cover us or fail to publish regular reports on us, interest in the purchase of our securities could decrease, which could cause the price of our CDIs and common stock and other securities and their trading volume to decline.
Investors in this offering will experience immediate and substantial dilution of $ per share.
Based on an assumed initial public offering price of $ per share (the midpoint of the range set forth on the cover of this prospectus), purchasers of our common stock in this offering will experience an immediate and substantial dilution of $ per share in the as adjusted net tangible book value per share of common stock from the initial public offering price, and our as adjusted net tangible book value as of June 30, 2023 after giving effect to this offering would be $ per share. This dilution is due in large part to earlier investors having paid substantially less than the initial public offering price when they purchased their shares. See Dilution.
We may invest or spend the proceeds of this offering in ways with which you may not agree or in ways which may not yield a return.
The net proceeds from this offering are expected to be used for working capital and other general corporate purposes and to fund our growth strategies discussed in this prospectus. Our management will have considerable discretion in the application of the net proceeds, and you will not have the opportunity, as part of your investment decision, to assess whether the proceeds are being used appropriately. The net proceeds may be used for corporate purposes that do not increase our operating results or market value. Until the net proceeds are used, they may be placed in investments that do not produce significant income or that may lose value.
We do not intend to pay dividends on our CDIs or common stock in the foreseeable future and, consequently, the ability of CDI holders and common stockholders to achieve a return on investment will depend on appreciation in the trading price of our CDIs and common stock.
We have never declared or paid any cash dividends on our capital stock or on our Predecessors ordinary shares. We intend to retain any earnings to finance the operation and expansion of our business, and we do not anticipate paying any cash dividends in the foreseeable future. We anticipate that we will retain all of our future earnings for use in the operation of our business and for general corporate purposes. Any determination to pay dividends in the future will be at the sole discretion of our board of directors. Accordingly, investors must rely on sales of their CDIs or common stock after price appreciation, which may never occur, as the only way to realize any future gains on their investments.
Future sales of our CDIs and common stock in the public market, or the perception that such sales may occur, could reduce our stock price, and any additional capital raised by us through the sale of equity or convertible securities may dilute your ownership in us.
We may issue additional CDIs or shares of common stock or securities convertible into our CDIs or common stock in subsequent public offerings. After the completion of this offering, we will have outstanding shares of common stock. This number includes shares of common stock that we are
48
Table of Contents
selling in this offering and the shares of common stock that we may sell in this offering if the underwriters option to purchase additional shares is fully exercised, which may be resold immediately in the public market. Following the completion of this offering, our Predecessors former shareholders will hold an economic interest equivalent to % of the Companys outstanding common stock. A portion of such shares are restricted from immediate resale under the federal securities laws and are subject to the lock-up agreements between such parties and the underwriters described in Underwriting, but may be sold into the market in the future. We expect that certain of the former shareholders of our Predecessor will be party to an agreement with us that will require us to effect the registration of their shares in certain circumstances no earlier than the expiration of the lock-up period contained in the underwriting agreement entered into in connection with this offering. Officers and directors will be subject to certain restrictions on the sale of their shares for 180 days after the date of this prospectus; however, after such period, and subject to compliance with the Securities Act or exemptions therefrom, these individuals may sell such shares into the public market. See Shares Eligible for Future Sale.
In connection with this offering, we intend to file a registration statement with the SEC on Form S-8 providing for the registration of shares of our common stock issued or reserved for issuance under our equity incentive plan. Subject to the satisfaction of vesting conditions and the expiration of lock-up agreements, shares registered under the registration statement on Form S-8 will be available for resale immediately in the public market without restriction.
We cannot predict the size of future issuances of our CDIs, common stock or securities convertible into common stock or the effect, if any, that future issuances and sales of CDIs or shares of our common stock will have on the market price of our CDIs or common stock. Sales of substantial amounts of our CDIs or common stock (including shares issued in connection with an acquisition), or the perception that such sales could occur, may adversely affect prevailing market prices of our CDIs or common stock.
The representatives of the underwriters of this offering may waive or release parties to the lock-up agreements entered into in connection with this offering, which could adversely affect the price of our common stock.
Our directors and executive officers have entered into lock-up agreements with respect to their common stock, pursuant to which they are subject to certain resale restrictions for a period of 180 days following the effectiveness date of the registration statement of which this prospectus forms a part. The representatives of the underwriters at any time and without notice, may release all or any portion of the common stock subject to the foregoing lock-up agreements. If the restrictions under the lock-up agreements are waived, then common stock will be available for sale into the public markets, which could cause the market price of our common stock to decline and impair our ability to raise capital.
We may issue preferred stock whose terms could adversely affect the voting power or value of our CDIs and common stock.
Our certificate of incorporation will authorize us to issue, without the approval of our stockholders, one or more classes or series of preferred stock having such designations, preferences, limitations and relative rights, including preferences over our common stock respecting dividends and distributions, as our board of directors may determine. The terms of one or more classes or series of preferred stock could adversely impact the voting power or value of our common stock. For example, we might grant holders of preferred stock the right to elect some number of our directors in all events or on the happening of specified events or the right to veto specified transactions. Similarly, the repurchase or redemption rights or liquidation preferences we might assign to holders of preferred stock could affect the residual value of our common stock.
We will incur increased costs as a result of being a publicly traded company in the United States.
We have no history of operating as a publicly traded company in the United States (only in Australia on the ASX). As a publicly traded company in the United States, we will incur significant legal, accounting and other
49
Table of Contents
expenses that we did not incur prior to this offering. In addition, the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, as well as rules implemented by the ASX, SEC and the NYSE, requires publicly traded entities to adopt various corporate governance practices that will further increase our costs.
Prior to this offering, we have not filed reports with the SEC. Following this offering, we will become subject to the public reporting requirements of the Exchange Act. We expect these rules and regulations to increase certain of our legal and financial compliance costs and to make activities more time-consuming and costly. For example, as a result of becoming a publicly traded company, we are required to adopt policies regarding internal controls and disclosure controls and procedures, including the preparation of reports on internal controls over financial reporting. In addition, we will incur additional costs associated with our SEC reporting requirements.
We also expect to incur significant expense to obtain director and officer liability insurance. Because of the limitations in coverage for directors, it may be more difficult for us to attract and retain qualified persons to serve on our board of directors or as executive officers.
We estimate that we will incur incremental costs associated with being a publicly traded company.
We have identified a material weakness in our internal control over financial reporting. Any material weakness may cause us to fail to timely and accurately report our financial results or result in a material misstatement of our financial statements.
Subject to applicable reporting requirement exemptions we take advantage of as an emerging growth company, we are required to comply with the SEC rules implementing Sections 302 and 404 of the SOX, which require management to certify financial and other information in our quarterly and annual reports and provide an annual management report on the effectiveness of controls over financial reporting. Effective internal control over financial reporting is necessary for us to provide reliable and timely financial reports and, together with adequate disclosure controls and procedures, are designed to reasonably detect and prevent fraud. We are also required to report any material weaknesses in such internal control. A material weakness is a deficiency, or a combination of deficiencies, in internal control over financial reporting such that there is a reasonable possibility that a material misstatement of our financial statements will not be prevented or detected on a timely basis.
In connection with the audit of our financial statements for the fiscal years ended June 30, 2023 and 2022, we identified deficiencies in our internal control over financial reporting, which in the aggregate, constituted a material weakness. We determined in both years that we had deficiencies relating to insufficiently designed and operating internal controls over financial reporting, including: i) lack of sufficient evidence retained of the performance of internal controls, ii) insufficient resources in key accounting and finance roles leading to inadequate segregation of duties and iii) lack of manage access and manage change IT general controls over the cloud-based enterprise resource planning system, which in the aggregate constitute a material weakness.
As part of our plan to address this material weakness, we are performing a full review of our processes and internal controls. We have implemented, and plan to continue to implement, new controls and processes. We will also provide training to control owners in support of an effective internal control framework, including how to sufficiently document and evidence the operation of internal controls. Finally, we are also evaluating our current enterprise resource planning system and considering options for replacing it with a new system to better support our financial reporting, including any related internal controls. While we have begun implementing a plan to remediate this material weakness, we cannot predict the success of such plan or the outcome of our assessment of this plan at this time. If our steps are insufficient to successfully remediate the material weakness and otherwise establish and maintain an effective system of internal control over financial reporting, the reliability of our financial reporting, investor confidence in us, and the value of our common stock could be materially and adversely affected. We can give no assurance that this implementation will remediate this deficiency in internal control or that additional material weaknesses in our internal control over financial reporting will not be identified in the future. Our failure to implement and maintain effective internal control over financial reporting
50
Table of Contents
could result in errors in our financial statements that could result in a restatement of our financial statements, or cause us to fail to meet our periodic reporting obligations. For as long as we are an emerging growth company under the JOBS Act, our independent registered public accounting firm will not be required to attest to the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting pursuant to Section 404.
Once we no longer qualify as an emerging growth company, we will be required to have our independent registered public accounting firm provide an attestation report on the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting. An independent assessment of the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting could detect problems that our managements assessment might not. Undetected material weaknesses in our internal control over financial reporting could lead to financial statement restatements and require us to incur the expense of remediation. An adverse report may be issued if our independent registered public accounting firm is not satisfied with the level at which our controls are documented, designed or operating.
We cannot be certain that our efforts to develop and maintain our internal controls will be successful, that we will be able to maintain adequate controls over our financial processes and reporting in the future or that we will be able to comply with our obligations under Section 404 of the SOX. Any failure to develop or maintain effective internal controls, or difficulties encountered in implementing or improving our internal controls, could harm our operating results or cause us to fail to meet our reporting obligations. Ineffective internal controls could also cause investors to lose confidence in our reported financial information, which would likely have a negative effect on the trading price of our CDIs and common stock.
For as long as we are an emerging growth company, we will not be required to comply with certain reporting requirements, including those relating to accounting standards and disclosure about our executive compensation, that apply to other public companies.
We are classified as an emerging growth company under the JOBS Act. For as long as we are an emerging growth company, which may be up to five full fiscal years, unlike other public companies, we will not be required to, among other things, (i) provide an auditors attestation report on managements assessment of the effectiveness of our system of internal control over financial reporting pursuant to Section 404(b) of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, (ii) comply with any new requirements adopted by the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board requiring mandatory audit firm rotation or a supplement to the auditors report in which the auditor would be required to provide additional information about the audit and the financial statements of the issuer, (iii) provide certain disclosure regarding executive compensation required of larger public companies or (iv) hold nonbinding advisory votes on executive compensation. We will remain an emerging growth company for up to five years, although we will lose that status sooner if we have more than $1.235 billion of revenues in a fiscal year, have more than $700.0 million in market value of our common stock held by non-affiliates or issue more than $1.0 billion of non-convertible debt over a three-year period.
To the extent that we rely on any of the exemptions available to emerging growth companies, you will receive less information about our executive compensation and internal control over financial reporting than issuers that are not emerging growth companies. If some investors find our common stock to be less attractive as a result, there may be a less active trading market for our common stock and our stock price may be more volatile.
Because we have elected to take advantage of the extended transition period pursuant to Section 107 of the JOBS Act, our financial statements may not be comparable to those of other public companies.
Section 107 of the JOBS Act provides that an emerging growth company can use the extended transition period provided in Section 7(a)(2)(B) of the Securities Act for complying with new or revised accounting standards. This permits an emerging growth company to delay the adoption of certain accounting standards until those standards would otherwise apply to private companies. We are choosing to take advantage of this extended transition period and, as a result, we will comply with new or revised accounting standards on the relevant dates on which adoption of such standards is required for private companies. Accordingly, our financial statements
51
Table of Contents
may not be comparable to companies that comply with public company effective dates, and our stockholders and potential investors may have difficulty in analyzing our operating results by comparing us to such companies.
Investors purchasing shares of our common stock in this offering will not be able to freely sell those shares, or CDIs representing those shares, in Australia during the 12 months after the issue date of those shares in this offering and therefore will not be able to take advantage of any liquidity that may be available for CDIs traded on the ASX during that period.
Although we expect that our shares of common stock will be listed on the NYSE, the shares sold in this offering will not be freely tradable in Australia during the 12 months after their issue date in this offering. In general, shares purchased in this offering may be resold in Australia during that period only to certain sophisticated investors and professional investors (as defined in the Australian Corporations Act) and certain persons associated with us under Section 708(12) of the Australian Corporations Act, and any subsequent resale of those shares will also be subject to the same restrictions during the 12 months after their issue date in this offering. See Underwriting Notice to Prospective Investors in Australia. So long as those restrictions are in effect, to the extent that investors who purchase shares in this offering are able to resell those shares in Australia, the price they receive may be different than the market price of our common stock. Likewise, while investors purchasing shares in this offering will be entitled to exchange those shares for CDIs, which are listed on the ASX, sales of those CDIs in Australia will be subject to the same restrictions that are applicable to the underlying shares of common stock as described above. As a result, any sale of those CDIs in Australia while those restrictions are in effect is also likely to be at a substantial discount to their market price. Although we expect that the majority of the shares of common stock outstanding immediately after this offering will be represented by CDIs that are traded on the ASX, investors purchasing shares in this offering will not be able to freely sell those shares, or CDIs representing those shares, in Australia during the 12 months after the issue date of those shares in this offering and therefore will not be able to take advantage of any liquidity which may be available for CDIs traded on the ASX during that period, and any amounts received upon the resale by investors purchasing in this offering while those restrictions are in effect will likely be at a substantial discount to the market price. We intend to apply to the Australian Securities and Investments Commission for waivers from the application of these resale restrictions; however, there is no certainty that all or any of the requested waivers will be granted or, if granted, that such waivers will provide relief from all of these resale restrictions.
Our CDIs will be listed on the ASX and will be freely tradable in the public markets in Australia. Trading in our CDIs may have a material adverse effect on the trading price of our common stock on the NYSE.
Our common stock will be traded on the NYSE and our CDIs will be traded on ASX. The CDIs are, in general, the economic equivalent of shares of our common stock and, as a result, the trading price of the CDIs on the ASX will likely affect the trading price of our common stock on the NYSE, and vice versa. The trading price of the CDIs may be influenced by factors different from those that affect the trading price of our common stock on the NYSE and, as discussed below in these risk factors, may be influenced by arbitrage activities. In addition, holders of shares of our common stock, including shares sold in this offering, may deliver those shares to the depositary for the CDIs in exchange for CDIs. If a significant number of the shares of our common stock that are sold in the offering are exchanged for CDIs, it may have an adverse effect, which could be material, on the liquidity and trading price of our common stock on the NYSE.
Trading in our securities on these markets will take place in different currencies (U.S. dollars on NYSE and Australian dollars on the ASX), and at different times (resulting from different time zones, trading days and public holidays in the United States and Australia). The trading prices of our securities on these two markets may differ due to these and other factors, including the fact that ASX and NYSE have different criteria for trading halts as well as different listing rules and disclosure requirements. Any decrease in the price of our CDIs on the ASX could cause a decrease in the trading price of our common stock on the NYSE.
52
Table of Contents
All of the shares of our common stock and the CDIs representing those shares to be outstanding following this offering will be freely tradable in the public markets and a substantial majority of the shares of our common stock distributed in the corporate reorganization and the CDIs representing those shares will not be subject to lock-up agreements.
Upon completion of this offering, we will have outstanding an aggregate of approximately shares of common stock and CDIs. Of these outstanding shares and CDIs, all of such shares or CDIs will be freely tradeable without restriction or further registration under the Securities Act, unless such shares or CDIs are held by our directors, executive officers or any of our affiliates, as that term is defined in Rule 144 under the Securities Act.
In connection with this offering, our directors, executive officers, and certain of our shareholders have each agreed to enter into lock-up agreements with the underwriters and thereby are subject to a lock-up period, meaning that they and their permitted transferees will not be permitted to sell any shares of common stock for 180 days after the date of this prospectus, subject to certain customary exceptions, without the prior consent of the representatives of the underwriters. Although we have been advised that there is no present intention to do so, the representatives may, in their sole discretion, release all or any portion of the shares from the restrictions in any of the lock-up agreements described above. See the section entitled Underwriting for more information. Possible sales of these shares in the market following the waiver or expiration of such agreements could exert significant downward pressure on our share price.
Also, in the future, we may issue our securities in connection with investments or acquisitions. The amount of common stock issued in connection with an investment or acquisition could constitute a material portion of our then outstanding common stock.
The different characteristics of the capital markets in Australia and the United States may negatively affect the trading prices of our CDIs and common stock, and may limit our ability to take certain actions typically performed by a U.S. company.
We are subject to ASX listing and associated Australian regulatory requirements, and intend to concurrently list our shares on the NYSE as well, which has its own listing and regulatory requirements. Such exchanges have different trading hours, trading characteristics (including trading volume and liquidity), trading and listing rules, and investor bases (including different levels of retail and institutional participation). As a result of these differences, the trading prices of our CDIs and our common stock may not be the same, even allowing for currency differences. Fluctuations in the price of our common stock due to circumstances peculiar to the U.S. capital markets could materially and adversely affect the price of the CDIs, or vice versa. Certain events having significant negative impact specifically on the Australian capital markets may result in a decline in the trading price of our CDIs notwithstanding that such event may not impact the trading prices of securities listed in Australia generally or to the same extent, or vice versa.
Our ability to list our common stock on the NYSE is subject to us meeting applicable initial listing criteria.
In the event we are unable to list our common stock on the NYSE, our common stock will continue to trade on the ASX (as CDIs). Our failure to list our common stock on the NYSE could make it more difficult for U.S. persons to trade our common stock, could prevent our common stock trading on a frequent and liquid basis in the U.S., and could result in the value of our common stock being less than it would be if we were able to list our common stock on the NYSE.
Our ability to raise additional capital may be significantly limited by listing rules of the ASX that limit the amount of common stock that we are permitted to issue without stockholder approval.
Limitations on new share issuances under ASX listing rules may significantly limit or prevent us from raising additional capital by issuing and selling shares of our common stock or other securities when such
53
Table of Contents
additional capital is required. In particular, the ASX listing rules will prohibit us from issuing, during any 12-month period, shares of our common stock in an amount greater than 15% of the total number of shares of our common stock then outstanding without the affirmative vote of the holders of a majority of the outstanding shares of our common stock. We have received the approval of our shareholders to permit us to issue up to 25% of the total number of shares of our common stock then outstanding during the 12-month period commencing on the date we are admitted to the official list of the ASX; however, this increase is only effective for that 12-month period and may still limit or prevent us from raising additional capital when such additional capital is required. As discussed elsewhere in this prospectus, we will require substantial additional financing to develop and commercialize our resources and execute our strategy and, because we do not have any revenues from natural gas sales and would likely be unable to raise capital by borrowing funds, we will be dependent primarily upon issuing and selling additional shares of common stock to obtain such financing. The foregoing listing rule of the ASX is substantially more restrictive than the comparable NYSE rule and, even with the approval of our shareholders to permit us to issue up to 25% of the total number of shares of our common stock then outstanding during the 12-month period commencing on the date we are admitted to the official list of the ASX, this rule may significantly limit or prevent us from raising funds by issuing and selling shares of our common stock, which may have a material adverse effect on our results of operations, financial condition and the development of our business. Moreover, seeking shareholder approval to issue common stock is likely to take considerable time and expense and there can be no assurance that any such approval will be given in the future.
An investor may have limited ability to bring an action against us or against our directors and officers, or to enforce a judgment against us or them, because we conduct a majority of our operations in Australia, and many of our directors and officers reside outside the United States.
We conduct substantially all of our operations in Australia. Many of our directors and officers and certain other persons named in this prospectus are citizens and residents of countries other than the United States and a portion of the assets of the directors and officers and certain other persons named in this prospectus and substantially all of our assets are located outside of the United States. As a result, it may not be possible or practicable for you to effect service of process within the United States upon such persons or to enforce against them or against us judgments obtained in U.S. courts predicated upon the civil liability provisions of the federal securities laws of the United States. Even if you are successful in bringing such an action, there is doubt as to whether Australian courts would enforce certain civil liabilities under U.S. securities laws in original actions or judgments of U.S. courts based upon these civil liability provisions. In addition, awards of punitive damages in actions brought in the United States or elsewhere may be unenforceable in Australia or elsewhere outside the United States. An award for monetary damages under U.S. securities laws would be considered punitive if it does not seek to compensate the claimant for loss or damage suffered and is intended to punish the defendant. The enforceability of any judgment in Australia will depend on the particular facts of the case as well as the laws and treaties in effect at the time. The United States and Australia do not currently have a treaty or statute providing for recognition and enforcement of the judgments of the other country (other than arbitration awards) in civil and commercial matters. As a result, our holders of our common stock may have more difficulty in protecting their interests through actions against us, our management or our directors than would shareholders of a corporation operating within the United States.
As a result of listing CDIs on the ASX, we will be subject to the listing rules of the ASX, which may strain our resources, divert managements attention and affect our ability to manage our business or raise additional capital.
As a result of listing CDIs on the ASX, we will be subject to the listing rules of the ASX, which may strain our resources, divert managements attention and affect our ability to manage our business or raise additional capital. The listing rules of the ASX differ from, and in some cases are more restrictive than, the rules and requirements of the NYSE, including restrictions that:
| | limit non-executive director compensation to a maximum amount approved by shareholders at a general meeting; |
54
Table of Contents
| | require that the terms of every class of our securities, including any preferred stock, be approved by the ASX; |
| | prohibit us from removing or changing the voting rights or dividend rights (if any) of our securities, except in certain circumstances; |
| | specify certain terms and conditions of options and rights plans; |
| | prohibit issuing equity securities without shareholder approval in the three months after we receive any notice in writing that a person proposes to make a takeover bid; |
| | limit the issuance of restricted (escrowed) securities; and |
| | prohibit golden parachutes or other termination benefits for officers upon a change in ownership or control of us. |
These listing rules may, in some cases, limit our ability to take certain actions that would otherwise be permitted by NYSE rules and may affect our ability to manage our business and to attract and retain key management and scientific personnel. In addition, the listing rules of the ASX include approval and reporting requirements that differ from the requirements under the NYSE rules, such as requirements to:
| | comply with required timetables for issuance of equity securities; |
| | deliver notice to the ASX prior to the release of restricted (escrowed) securities; |
| | file quarterly, half-yearly and annual periodic reports that include specific disclosure required by the listing rules of the ASX; |
| | obtain stockholder approval for certain related-party transactions and for securities issuances to directors; |
| | deliver drafts to the ASX of charter documents, debt and convertible securities documents, certain meeting notices and documents sent to certain holders of securities; and |
| | prior to release to any other person, release announcements through the ASX as the central collection point for market sensitive information. |
Compliance with these additional rules will increase our legal and financial compliance costs, make some activities or transactions more difficult, time-consuming or costly, may limit or prevent us from raising additional capital by issuing and selling shares of our common stock or other securities and increase demand on our systems and resources. We applied to the ASX for, and received, certain waivers from the application of some of its listing rules; however, such waivers will not afford us relief from all of the increased restrictions and requirements imposed by such listing rules. Increases in our costs and expenses associated with compliance with the ASX listing rules will adversely impact our results of operations and financial condition. In addition, limitations on new share issuances under ASX listing rules may limit or prevent us from raising additional capital by issuing and selling shares of our common stock or other securities when such additional capital is required, which may have a material adverse effect on our results of operations, financial condition and the development of our business. See Our ability to raise additional capital may be significantly limited by listing rules of the Australian Securities Exchange that limit the amount of common stock that we are permitted to issue without stockholder approval.
The market price of our common stock may be adversely affected by arbitrage activities.
Investors may seek to profit by exploiting the difference, if any, in the price of our shares of common stock as reflected by the trading price of our CDIs, which will represent shares of our common stock, on the ASX and the trading price of our shares of common stock on the NYSE. Such arbitrage activities could cause the price of our common stock or the CDIs representing our common stock, as the case may be, in the market with the higher
55
Table of Contents
value to decrease to the price set by the market with the lower value or could otherwise adversely affect the market price of our common stock. These arbitrage risks may be increased by the fact that our common stock will be quoted in U.S. dollars on the NYSE while our CDIs will be quoted in Australian dollars on the ASX, which may also give investors the opportunity to exploit the impact of fluctuations in currency exchange rates on the market price of our common stock and the CDIs.
Changes in accounting standards issued by the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) or other standard-setting bodies may adversely affect our financial statements.
Our financial statements are prepared in accordance with GAAP as defined in the Accounting Standards Codification (ASC) of the FASB. From time to time, we are required to adopt new or revised accounting standards or guidance that are incorporated into the ASC. It is possible that future accounting standards we are required to adopt could change the current accounting treatment that we apply to our combined and consolidated financial statements and that such changes could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations.
In addition, the FASB is working on several projects with the International Accounting Standards Board, which could result in significant changes as GAAP converges with International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS), including how our financial statements are presented. Furthermore, the SEC is considering whether and how to incorporate IFRS into the U.S. financial reporting system. The accounting changes being proposed by the FASB will be a complete change to how we account for and report significant areas of our business. The effective dates and transition methods are not known; however, issuers may be required to or may choose to adopt the new standards retrospectively. In this case, issuers would report results under the new accounting method as of the effective date, as well as for all periods presented. Any such changes to GAAP or conversion to IFRS would impose special demands on issuers in the areas of governance, employee training, internal controls and disclosure and would likely affect how we manage our business.
56
Table of Contents
CAUTIONARY STATEMENT REGARDING FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
This prospectus contains certain forward-looking statements within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. All statements, other than statements of historical fact included in this prospectus, regarding our strategy, future operations, financial position, estimated revenue and losses, projected costs, prospects, plans and objectives of management and dividend policy are forward-looking statements. When used in this prospectus, words such as expect, project, estimate, believe, anticipate, intend, budget, plan, seek, envision, forecast, target, predict, may, should, would, could, will, the negative of these term and similar expressions are intended to identify forward-looking statements, although not all forward-looking statements contain such identifying words. These forward-looking statements are based on our current expectations and assumptions about future events and are based on currently available information as to the outcome and timing of future events. When considering forward-looking statements, you should keep in mind the risk factors and other cautionary statements described under Risk Factors. These forward-looking statements are based on managements current belief, based on currently available information, as to the outcome and timing of future events.
Forward-looking statements may include statements about, among other things:
| | our business strategy and the successful implementation of our business strategy; |
| | our future reserves; |
| | our financial strategy, liquidity and capital required for our development programs; |
| | estimated natural gas prices; |
| | our dividend policy; |
| | the timing and amount of future production of natural gas; |
| | our drilling and production plans; |
| | competition and government regulation; |
| | our ability to obtain and retain permits and governmental approvals; |
| | legal, regulatory or environmental matters; |
| | marketing of natural gas; |
| | business or leasehold acquisitions and integration of acquired businesses; |
| | our ability to develop our properties; |
| | the availability and cost of developing appropriate infrastructure around and transportation from our properties to market; |
| | the availability and cost of drilling rigs, production equipment, supplies, personnel and oilfield services; |
| | costs of developing our properties and of conducting our operations; |
| | our ability to reach FID and execute and complete our planned pipeline or planned LNG export projects; |
| | our anticipated Scope 1 and Scope 2 emissions from our businesses and our plans to offset our Scope 1 and Scope 2 emissions from our business; |
| | our ESG strategy and initiatives, including those relating to the generation and marketing of environmental attributes or new products seeking to benefit from ESG-related activities; |
| | general economic conditions, including cost inflation; |
57
Table of Contents
| | credit markets and the ability to obtain future financing on commercially acceptable terms; |
| | our ability to expand our business, including through the recruitment and retention of skilled personnel; |
| | our dependence on our key management personnel; |
| | our future operating results; and |
| | our plans, objectives, expectations and intentions. |
The forward-looking statements included in this prospectus are based on current expectations and involve numerous risks and uncertainties, most of which are difficult or impossible to predict and many of which are beyond our control, incident to the exploration for and development, production and sale of natural gas. Assumptions relating to these forward-looking statements involve judgments, risks and uncertainties with respect to, among other things, market factors (including competition and inflation), market prices (including geographic basis differentials) of natural gas, results of future drilling and marketing activity, future production and costs (including availability of drilling and production equipment and services), legislative and regulatory initiatives, electronic, cyber or physical security breaches, drilling and other operating risks, environmental risks (including climate change and weather-related events), future business decisions, the uncertainty inherent in estimating natural gas reserves and the other risks described under Risk Factors.
Reserve engineering is a process of estimating underground accumulations of natural gas that cannot be measured in an exact way. The accuracy of any reserve estimate depends on the quality of available data, the interpretation of such data and price and cost assumptions made by reserve engineers. In addition, the results of drilling, testing and production activities may justify revisions of estimates that were made previously. If significant, such revisions would change the schedule of any further production and development drilling. Accordingly, reserve estimates may differ significantly from the quantities of natural gas that are ultimately recovered.
Although we believe that the assumptions underlying these forward-looking statements are reasonable, should one or more of the risks or uncertainties described in this prospectus occur, or should underlying assumptions prove incorrect, actual outcomes and our results and financial condition may differ materially from those indicated in any forward-looking statements. In light of the significant uncertainties inherent in these forward-looking statements, the inclusion of such information should not be regarded as a representation by us or any other person that our objectives and plans will be achieved.
All forward-looking statements, expressed or implied, included in this prospectus are expressly qualified in their entirety by this cautionary statement. This cautionary statement should also be considered in connection with any subsequent written or oral forward-looking statements that we or persons acting on our behalf may issue.
All forward-looking statements, expressed or implied, in this prospectus are based only on information currently available to us and speak only as of the date on which they are made. Except as otherwise required by applicable law, we disclaim any duty to publicly update any forward-looking statement, each of which is expressly qualified by the statements in this section, to reflect events or circumstances after the date of this prospectus.
Additionally, our discussion of ESG assessments, goals and relevant issues herein, including the mitigation of the risks associated with climate change and the energy transition, are informed by various ESG standards and frameworks (including standards for the measurement of underlying data) and the interests of various stakeholders. Any references to materiality in the context of such discussions and any related assessment of ESG materiality may differ from the definition of materiality under the federal securities laws for SEC
58
Table of Contents
reporting purposes. Similarly, we cannot guarantee strict adherence to standard recommendations, and our disclosures based on any standards may change due to revisions in framework or legal requirements, availability of information, changes in our business or applicable government policies, or other factors, some of which may be beyond our control. Separately, the standards and performance metrics used, and the expectations and assumptions they are based on, should not be assumed, unless otherwise expressly specified, to have been verified by us or any third party.
59
Table of Contents
We estimate the net proceeds to us from the sale of our common stock in this offering, after deducting underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses payable by us, will be approximately $ million (or approximately $ million if the underwriters exercise in full their option to purchase additional shares), based on an assumed initial public offering price of $ per share (the midpoint of the price range set forth on the cover page of this prospectus).
Each $1.00 increase (decrease) in the assumed initial public offering price of $ per share (the midpoint of the price range set forth on the cover page of this prospectus) would increase (decrease) the net proceeds to us from this offering by $ million, assuming that the number of shares offered by us, as set forth on the cover page of this prospectus, remains the same and after deducting underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses payable by us. We may also increase or decrease the number of shares we are offering. Each increase (decrease) of 1.0 million shares in the number of shares we are offering would increase (decrease) the net proceeds to us from this offering by $ million, assuming that the assumed initial public offering price of $ per share (the midpoint of the price range set forth on the cover page of this prospectus) remains the same, and after deducting underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses payable by us.
We intend to use all the net proceeds of this offering to fund our development plan and for working capital and other general corporate purposes.
The expected use of net proceeds from this offering represents our intentions based upon our present plans and business conditions. We cannot specify with certainty the particular uses of the net proceeds that we will receive from this offering or the amounts we actually spend on the uses set forth above. The timing and amount of our actual expenditures will be based on many factors, including the anticipated growth of our business. Pending the use of proceeds from this offering as described above, we plan to invest a portion of the net proceeds that we receive in this offering in short-term and intermediate-term interest-bearing obligations, investment-grade investments, certificates of deposit, or direct or guaranteed obligations of the U.S. government. Our management will have broad discretion in the application of the net proceeds from this offering and investors will be relying on the judgment of our management regarding the application of the proceeds.
60
Table of Contents
We have not declared or paid to date a cash dividend to holders of ordinary shares of our Predecessor or holders of our common stock. We currently intend to retain any future earnings, if any, to fund the development and expansion of our business and do not expect to pay any dividends in the foreseeable future. Any future dividends will be subject to the sole discretion of our board of directors and the considerations discussed below.
Any future determination to declare and pay a regular or special dividend, as well as the amount of any such dividends, will depend on our board of directors consideration of general economic and business conditions, our financial condition and results of operations, capital requirements, restrictions under our indebtedness, potential acquisition opportunities and other current and anticipated cash needs and any other factors our board of directors deems relevant.
Our dividend policy may change from time to time, and there can be no assurance that we will declare any regular or special cash dividends at all or in any particular amounts.
61
Table of Contents
The following table shows our capitalization as of June 30, 2023:
| | on an actual basis; and |
| | on an as adjusted basis, after giving effect to the sale of shares of our common stock in this offering (which assumes that the underwriters do not exercise their option to purchase additional shares), at an assumed initial public offering price of $ per share (the midpoint of the price range set forth on the cover page of this prospectus), the corporate reorganization, our receipt of the estimated net proceeds of this offering and after deducting underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses payable by us and the application of such net proceeds as described under Use of Proceeds. |
The as adjusted information set forth in the table below is illustrative only and will adjust based on the actual initial public offering price and other terms of this offering determined when the initial public offering price is determined. You should read the following table together with Selected Historical Consolidated Financial Data, Managements Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations, and our historical and pro forma consolidated and combined financial statements and the related notes thereto included elsewhere in this prospectus.
| As of June 30, 2023 | ||||||||
| Actual | As Adjusted | |||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents |
||||||||
| Debt: |
||||||||
| Convertible notes |
||||||||
| Total debt |
||||||||
| Stockholders equity: |
||||||||
| Common stock, par value $0.001 per share; authorized shares; shares issued and outstanding, actual; and shares issued and outstanding, as adjusted |
||||||||
| Additional paid-in capital |
||||||||
| Total stockholders equity |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total capitalization |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
62
Table of Contents
Purchasers of the common stock in this offering will experience immediate and substantial dilution in the net tangible book value per share of the common stock for accounting purposes. Our net tangible book value as of June 30, 2023 was $ million, or $ per share. Net tangible book value per share is determined by dividing our tangible net worth (tangible assets less total liabilities) by the total number of shares of common stock that were outstanding as of June 30, 2023. After giving effect to the sale of the shares in this offering and the distribution of CDIs in the corporate reorganization and further assuming the receipt of the estimated net proceeds (after deducting estimated underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses), our as adjusted net tangible book value as of June 30, 2023 would have been approximately $ million, or $ per share. This represents an immediate increase in the net tangible book value of $ per share to our existing stockholders and an immediate dilution (i.e., the difference between the initial public offering price per share of our common stock and the as adjusted net tangible book value per share of our common stock after this offering) to new investors purchasing shares of common stock in this offering of $ per share.
The following table illustrates the per share dilution to new investors purchasing shares of common stock in this offering:
| Assumed initial public offering price per share |
$ | |||
| Net tangible book value per share as of June 30, 2023 |
$ | |||
| Increase in net tangible book value per share attributable to new investors in this offering |
||||
| Less: As adjusted net tangible book value per share of common stock after giving effect to this offering |
||||
| Dilution in as adjusted net tangible book value per share to new investors from this offering |
$ |
A $1.00 increase (decrease) in the assumed initial public offering price of $ per share (the midpoint of the price range set forth on the cover page of this prospectus), would increase (decrease) the as adjusted net tangible book value per share after this offering by $ per share and increase (decrease) the dilution in net tangible book value per share to new investors in this offering by $ per share, in each case assuming the number of shares of common stock offered by us, as set forth on the cover page of this prospectus, remains the same and less estimated underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses payable by us (and if the underwriters exercise in full their option to purchase additional shares, the as adjusted net tangible book value per share would be $ per share, and the dilution in net tangible book value per share to new investors in this offering would be $ per share).
The following table summarizes, as of June 30, 2023, the differences between the number of shares issued as a result of this offering, the total amount paid by existing shareholders and the average price per share to be paid by investors in this offering, based upon an assumed initial public offering price of $ per share (the midpoint of the price range set forth on the cover page of this prospectus).
| Shares | Total Consideration | Average Price per Share |
||||||||||||||||||
| Number | Percent | Amount | Percent | |||||||||||||||||
| Existing CDI holders |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Existing common stock stockholders |
% | % | $ | |||||||||||||||||
| New investors |
% | % | $ | |||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Total |
100 | % | 100 | % | $ | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
63
Table of Contents
The above tables and related discussion are based on the number of shares of our common stock to be outstanding as of the closing of this offering and the corporate reorganization. If the underwriters option to purchase additional shares is exercised in full, the number of shares held by new investors will be increased to , or approximately % of the total number of shares of common stock.
64
Table of Contents
MANAGEMENTS DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
The following discussion and analysis of our financial condition and results of operations should be read in conjunction with our historical consolidated financial statements and related notes included elsewhere in this prospectus. The following discussion contains forward-looking statements that reflect our future plans, estimates, beliefs and expectations. Cautionary Statement Regarding Forward-Looking Statements, Risk Factors and the historical and pro forma consolidated and combined financial statements and the related notes thereto (included elsewhere in this prospectus) contain important information you should reference. We disclaim any duty to publicly update any forward-looking statements except as otherwise required by applicable law.
Unless the context otherwise requires, the terms we, us and our refer to (i) Tamboran Resources Limited, an Australian public company formed in 2009, and its subsidiaries (our Predecessor), our predecessor entity before the completion of our corporate reorganization described in this prospectus and (ii) Tamboran Resources Corporation, a Delaware corporation formed in 2023, and its subsidiaries (Tamboran), the issuer of the notes and successor entity resulting from our corporate reorganization described in this prospectus. For more information on our organizational structure, see the section entitled Corporate Reorganization and Note 1 General Information to our historical consolidated financial statements included elsewhere in this prospectus.
Corporate Reorganization
On December 13, 2023, we acquired all of the issued and outstanding ordinary shares of our Predecessor and former parent company pursuant to a scheme of arrangement under Australian law (the corporate reorganization). As part of the corporate reorganization, we issued to the shareholders of our Predecessor one CDI (representing an interest in 1/200th of a share of our common stock) in exchange for one ordinary share of our Predecessor then issued and outstanding. Prior to the corporate reorganization, we had no business or operations, and following the corporate reorganization, our business and operations consist solely of the business and operations of our Predecessor and its subsidiaries.
Our Predecessor was established in 2009 and is headquartered in Sydney, Australia. Our Predecessor completed its initial public offering in Australia in July 2021 and was publicly listed on the Australian Securities Exchange under the ticker TBN. Our Predecessor was removed from the ASX following the corporate reorganization, at which time CDIs representing shares of common stock of Tamboran Resources Corporation were listed on the ASX under the same ticker TBN. Tamboran Resources Corporation was incorporated in the State of Delaware on October 3, 2023 for the purposes of effecting the corporate reorganization.
The historical results of operations discussed in this Managements Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations includes the results of our Predecessor and its consolidated subsidiaries prior to the corporate reorganization.
Overview
We are an early stage, growth-driven independent natural gas production company focused on an integrated approach to the commercial development of the natural gas resources in the Beetaloo located within the Northern Territory of Australia. We and our working interest partners have EPs to approximately 4.7 million gross (1.9 million net to Tamboran) contiguous prospective acres, and are currently the largest acreage holder in the Beetaloo.
We are focused on developing early stage, unconventional gas resources within our portfolio. Our key assets are (i) a 25% non-operated working interest in EP 161, (ii) a 38.75% working interest in EPs 76, 98 and 117, where we are the operator, and (iii) a 100% working interest in EPs 136, 143 and EP(A) 197, where we are the operator, all of which are located in the Beetaloo.
65
Table of Contents
Recent Developments
Origin B2 Asset Acquisition
On November 9, 2022, the TB2 Joint Venture, an entity 50/50 owned by Tamboran (West) Pty Ltd (our wholly owned subsidiary), and Daly Waters and governed by a joint venture and shareholders agreement, completed the purchase of a 77.5% interest in EPs 76, 98 and 117 covering approximately four million gross prospective acres (1.5 million net prospective acres). Consideration for the purchase included A$60 million in cash and a 2.3% ORRI on petroleum production from the assigned permits to Daly Waters Royalty LP.
Capital Raising
On October 31, 2022, we successfully completed a private placement of ordinary shares of our Predecessor for approximately $88.7 million in gross proceeds. The sale of ordinary shares included an issuance of $66.2 million in shares to strategic partners and U.S. cornerstone investors, supported by investments of $20 million by Bryan Sheffield and $15 million by H&P. In June 2023, we received commitments for the institutional placement component of a $36.3 million (before costs) capital raise with proceeds to be used to fund our ongoing drilling program, including the SS1H and A3H wells. The placement was supported by a $10.0 million investment from our largest shareholder, Bryan Sheffield.
On July 6, 2023, we agreed to issue up to $9 million of five-year unsecured convertible notes (the Convertible Notes) from time to time to H&P for purposes of funding reimbursement of H&Ps mobilization and related reimbursable costs for Rig 469 as well as other working capital requirements. The Convertible Notes may be converted into a maximum of shares of the Companys common stock. The Convertible Notes accrue interest at 5.5% per annum on the amount drawn and outstanding. As of the date of this prospectus, we have not borrowed any amount under the Convertible Notes. See Liquidity and Capital ResourcesConvertible Notes.
On December 14, 2023, we successfully completed a private placement of our CDIs for approximately A$40.8 million in gross proceeds, supported by a A$15.3 million strategic placement from Liberty Energy and a A$7.6 placement from Mr. Sheffield.
In connection with the private placement, Tamboran made an offer to retail holders of existing CDIs to purchase CDIs at the same price as the purchasers in the December 14, 2023 private placement. The retail offer was completed on January 14, 2024 and raised approximately A$14.2 million. The funds from the capital raises will support our Beetaloo development activities to the sanctioning of the proposed 40 MMcf/d Shenandoah South raw gas processing plant.
SS1H Well Drilling
In early July 2023, H&Ps FlexRig® was successfully mobilized to the SS1H well location targeting the deeper Mid-Velkerri B Shale in EP 117. We successfully commenced drilling of the SS1H well in early August 2023 and intersected a 295-foot interval of Mid-Velkerri B Shale, the thickest recorded section in the Beetaloo depocenter to date. We anticipate flow test results from SS1H will be available during the first quarter of 2024.
Market Outlook
We believe natural gas can play a key role in supporting the emissions reduction targets of many regional markets through the transition of coal-to-gas fired power plants. To date the increasing global demand for LNG, as well as under-investment in new supply, has led to projected LNG supply shortages by 2030. By 2030, the global LNG market is expected to be 30 Mtpa short of supply.
66
Table of Contents
We have the potential, subject to achieving commercial viability in the Beetaloo, to supply natural gas to both Australian domestic and international LNG markets, which would support countries in the region in achieving their GHG emission reduction targets and help reduce global GHG emissions if LNG is adopted as an alternative to coal fired power. We are in the initial phase of development of our operations. Successful commercialization of the Beetaloo will require the development of the infrastructure necessary to conduct our business as planned on commercially acceptable terms. In addition, success of our business will rely on the Australian East Coast and the Asian LNG markets maintaining elevated prices relative to North America to offset the higher costs associated with developing infrastructure in the Beetaloo.
The natural gas industry is cyclical and commodity prices are highly volatile. During the period from 2021 through 2023, the natural gas continuous futures price on JKM reached a high of $69.96 per MMBtu on August 25, 2022 and a low of $5.81 per MMBtu on February 25, 2021.
We expect the natural gas markets will continue to be volatile in the future. Our future revenue, profitability and future growth are highly dependent on the prices we will receive for natural gas production. See Risk FactorsNatural gas prices are volatile. A reduction or sustained decline in prices may adversely affect our business, financial condition or results of operations and our ability to meet our financial commitments.
Although inflation globally had been relatively low for many years, there was a significant increase in inflation beginning in the second half of calendar year 2022, which continued through calendar year 2023, due to a substantial increase in the money supply by central banks (including the US Federal Reserve, and the Reserve Bank of Australia), a stimulation focused global fiscal policy, a significant rebound in consumer demand as COVID-19 restrictions were relaxed, the Russia-Ukraine war and worldwide supply chain disruptions resulting from the economic contraction caused by COVID-19 and lockdowns followed by a rapid recovery. Inflation rose in the United States from 6.1% in 2022 to 6.6% in 2023 and in Australia from 4.1% in 2022 to 8.0% in 2023. Global, industry-wide supply chain disruptions have resulted in widespread shortages of labor, materials and services. Such shortages have resulted in our facing significant cost increases for labor, materials and services. We do not expect these shortages and cost increases to reverse in the short term. Typically, as the price for natural gas increases, so do associated costs. Conversely, in a period of declining prices, associated cost declines are likely to lag and may not adjust downward in proportion to prices. We cannot predict the future inflation rate but to the extent inflation remains elevated, we may experience cost increases in our operations, including costs for drill rigs, workover rigs, hydraulic fracturing fleets, tubulars and other well equipment, as well as increased labor costs. If we are unable to recover higher costs through higher commodity prices, our future revenue stream, would be significantly impacted. We are monitoring the situation and assessing its impact on our business, including to our partners. We expect to continue to achieve our business strategy by remaining vigilant in maintaining a disciplined financial strategy and in optimizing the value of our core business.
Factors that Affect Comparability of Future Results
Our historical financial condition and results of operations for the periods presented and future periods may not be comparable, either from period to period or going forward primarily for the following reasons:
Recent events and formation transactions
The Company was incorporated as a Delaware corporation on October 3, 2023 and does not have historical financial operating results. As a result, our accounting predecessor for all periods presented herein is the Predecessor, an Australian public company. The historical results of our operations are based on the financial statements of our accounting Predecessor prior to our corporate reorganization as described in Corporate Reorganization.
67
Table of Contents
Success in our development of our natural gas properties
Because we have no operating history in the production of natural gas, our future results of operations and financial condition will be directly affected by our ability to develop and commercialize our assets through our drilling programs and future sales and marketing.
Natural gas revenue
We have not generated any revenue from natural gas production since inception due to the current stage of our operations, which is exploration drilling of the Tamboran Assets to test their commercial viability. If and when we do commence natural gas production, we expect to generate revenue from such production. No revenue from natural gas production is reflected in our historical financial statements.
Operating costs and expenses
We have not yet commenced natural gas production. If and when we do commence production, we will incur additional operating costs and expenses, which may include lease operating expense, workover costs, taxes and royalty fees. Our operating costs and expenses consisted of the following during the years ended June 30, 2022 and 2023: salaries, share based compensation, and related taxes and benefits of personnel employed by us, professional fees for consultants, auditors, tax advisors and legal services, depreciation and amortization of natural gas properties, impairment of our natural gas properties, the loss on sale of assets due to the sale of rigs in fiscal year 2023, exploration expenses, and general and administrative expenses.
Acquisitions
We may continue to grow our operations and financial results through strategic acquisition opportunities that may arise relevant to our Beetaloo strategy. Additionally, we may from time to time effect divestitures of certain of our non-core assets.
Supply, demand, market risk and the impact on natural gas prices
As discussed above in Market Outlook, the natural gas industry historically has been cyclical with highly volatile commodity prices. Natural gas prices are subject to large fluctuations in response to relatively minor changes in the demand for natural gas. Prices are affected by current and expected supply and demand dynamics, including the market disruptions resulting from the Russian-Ukraine war, the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic and related erosion of demand for natural gas, supply growth driven by advances in drilling and completion technologies, resulting in increased supply in the global market. Other factors impacting supply and demand include weather conditions (including severe weather events), pipeline capacity constraints, inventory storage levels, basis differentials, export capacity, supply chain quality and availability, as well as other factors, the majority of which are outside of our control. These commodity prices are likely to remain volatile in the future. Sustained periods of low natural gas prices could materially and adversely affect our financial condition, our results of operations, the quantities of natural gas that we can economically produce and our ability to access capital. Since we have not generated revenues, these key factors will only affect us when we produce and sell natural gas.
U.S. reporting company expenses
Prior to our corporate reorganization, the ordinary shares of our Predecessor were listed on the ASX. Concurrently with the closing of this offering, our common stock is expected to be listed on NYSE and we will be subject to the periodic reporting requirements of the Exchange Act. Although we have been listed on the ASX and have been required to file financial information and make certain other filings with the ASX, our status as a U.S. reporting company under the Exchange Act will cause us to incur additional legal, accounting and other
68
Table of Contents
expenses that we have not previously incurred, including costs related to compliance with the requirements of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act. These incremental legal and financial compliance expenses are not included in our historical results of operations; therefore, our results of operations for future periods may not be comparable to our results of operations for the periods under review.
Results of Operations
Our functional currency is the Australian dollar and our reporting currency is the U.S. dollar. For revenues and expenses reported in any period, we use the average currency exchange rate between U.S. dollars and Australian dollars for the period. For assets and liabilities, we use the current currency exchange rate as at the end of the period, based on the same source. Given the fluctuations in currency exchange rates, we may experience changes in reported amounts from period to period that occur primarily as a result of these fluctuations and that are not reflective of actual changes in our business or operations.
Currently, we are exposed to foreign exchange risk, particularly with the U.S. dollar and Australian dollar, as a result of revenue and expenses that are denominated in each currency. It is our policy to limit the use of financial derivatives and seek risk mitigation through natural hedges. These natural hedges include the maintenance of U.S. dollar and Australian bank accounts and deposits. Because our functional currency is the Australian dollar, our reported financial results are subject to fluctuation resulting from changes in the U.S. dollar to Australian dollar exchange rate.
The following tables present selected financial information for the periods presented:
| Year ended June 30, |
||||||||
| 2023 | 2022 | |||||||
|
(in thousands, except per share data) |
||||||||
| Revenue and other operating income / Revenues |
$ | | $ | | ||||
| Operating costs and expenses: |
||||||||
| Compensation and benefits, excluding stock based compensation |
(5,432 | ) | (2,627 | ) | ||||
| Stock based compensation |
(909 | ) | (1,057 | ) | ||||
| Consultancy, legal and professional fees |
(6,818 | ) | (2,708 | ) | ||||
| Depreciation and amortization |
(118 | ) | (128 | ) | ||||
| Loss on assets classified as held for sale |
(12,585 | ) | | |||||
| Accretion of asset retirement obligations |
(601 | ) | (79 | ) | ||||
| Exploration expense |
(2,793 | ) | (1,707 | ) | ||||
| General and administrative |
(2,763 | ) | (1,637 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total operating costs and expenses |
(32,019 | ) | (9,943 | ) | ||||
| Other income: |
||||||||
| Interest expense, net |
31 | (6 | ) | |||||
| Foreign exchange gain, net |
130 | 471 | ||||||
| Other expenses |
(337 | ) | (144 | ) | ||||
| Total other (expense)/income |
(176 | ) | 321 | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Net loss |
(32,196 | ) | (9,622 | ) | ||||
| Foreign currency translation |
1,633 | (7,278 | ) | |||||
| Total comprehensive loss |
(30,455 | ) | (16,890 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Comparison of the Years Ended June 30, 2022 and June 30, 2023
Revenue and other operating income. We have not yet commenced natural gas production. Therefore, we did not realize any revenue and other operating income during the years ended June 30, 2022 and June 30, 2023, respectively.
69
Table of Contents
Compensation and benefits, excluding stock based compensation. Compensation and benefits, excluding stock based compensation, increased by $2.8 million during the year ended June 30, 2023, as compared to the year ended June 30, 2022 due to increased headcount, higher salaries for skilled workers, and short term incentive payments made to personnel.
Consultancy, legal and professional fees. Consultancy, legal and professional fees increased by $4.1 million during the year ended June 30, 2023, as compared to the year ended June 30, 2022 due to preparation for a U.S. initial public offering including expenses related to corporate restructuring, and legal and professional expenses associated with capital raises in addition to consulting costs related to government and community relations and midstream activities.
Loss on assets classified has held for sale. We recognized a $12.6 million loss during the year ended June 30, 2023 due to the write down of two rigs held for sale to be the lower of carrying amount and fair value less costs. We bought the two rigs for $15.9 million and incurred $2 million in additional capitalizable expenses, while the fair value less costs to sell was $8.8 million. The two rigs remain unsold as of June 30, 2023. The remaining difference relates to the foreign exchange impact of consolidation.
Accretion of asset retirement obligations expense. For the year ended June 30, 2023, an expense for accretion of asset retirement obligations of $601 thousand was recognized. The recognition of such an expense was due to the initial recognition of an asset retirement obligation in relation to all EPs, inclusive of EPs 76, 98, 117, 136 and 161 on December 31, 2022.
Exploration expense. Exploration expense increased by $1.1 million during the year ended June 30, 2023, as compared to the year ended June 30, 2022 due to expenses associated with drilling our SSIH and A3H wells. Our exploration expense consisted of costs related to topographical, geographical and geophysical studies during the years ended June 30, 2022 and 2023.
General and administrative. General and administrative costs increased by $1.1 million during the year ended June 30, 2023, as compared to the year ended June 30, 2022 due to increased travel subsequent to the easing of COVID-19 restrictions and an increase in insurance premiums. Our general and administrative expense consisted of the following during the years ended June 30, 2022 and 2023: expenses related to travel, insurance, and office and administrative fees.
Foreign currency translation. Foreign currency transactions are translated into our functional currency using the exchange rates prevailing at the dates of the transactions. Foreign exchange gains and losses resulting from the settlement of such transactions and from the translation at financial year-end exchange rates of monetary assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currencies are recognized on our income statement. We recognized a gain of $1.6 million during the year ended June 30, 2023, as compared to a loss of $7.3 million during the year ended June 30, 2022 due primarily to the large acquisition of permits at a period during the year when the Australian Dollar had strengthened in comparison to end position as of June 30, 2023.
Income Tax Expense. We have no income tax expense due to operating losses incurred for the year ended June 30, 2022 and June 30, 2023. We have provided a full valuation allowance on our net deferred tax asset because management has determined that it is more-likely-than-not that the we will not earn income sufficient to realize the deferred tax assets during a future period.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
We are a development stage enterprise and will continue to be so until commencement of substantial production from our natural gas properties. We do not expect to generate any revenue from production until 2026 at the earliest, which will depend upon successful drilling results, additional and timely capital funding, and access to suitable infrastructure. Until then our primary sources of liquidity are expected to be cash on hand at the
70
Table of Contents
time of this offering, net proceeds from this offering and funds from future private and public equity placements, debt funding and asset sales.
We expect to incur substantial expenses and generate significant operating losses as we continue to develop our natural gas prospects and as we:
| | complete our current appraisal drilling and testing program; |
| | develop and commercialize our assets, including development of pipelines, the proposed NTLNG facility and other infrastructure; |
| | opportunistically invest in additional natural gas assets adjacent to our current positions; |
| | incur expenses related to operating as a public company and compliance with regulatory requirements. |
Our future financial condition and liquidity will be impacted by, among other factors, the success of our exploration and appraisal drilling program, the number of commercially viable natural gas discoveries made, the quantities of natural gas discovered, the speed with which we can bring such discoveries to production, and the actual cost of exploration, appraisal and development of our prospects.
We estimate that we will need to invest approximately $57 million for the fiscal year ending June 30, 2024 in order to progress our development plans. We expect the proceeds of this offering, together with our existing cash on hand, to be sufficient to fund our planned appraisal drilling and testing program at least through the end of fiscal year 2025. However, we may require significant additional funds earlier than we currently expect in order to execute our strategy as planned. We may seek additional funding through asset sales or public or private financings. Additional funding may not be available to us on acceptable terms or at all. In addition, the terms of any financing may adversely affect the holdings or the rights of our stockholders. For example, if we raise additional funds by issuing additional equity securities, further dilution to our existing stockholders will result. If we are unable to obtain funding on a timely basis, we may be required to significantly curtail one or more of our planned activities. We also could be required to seek funds through arrangements with collaborators or others that may require us to relinquish rights to some of our assets which we would otherwise develop on our own, or with a majority working interest.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
The following table summarizes our key measures of liquidity for the periods indicated (all dollars amounts are presented in thousands).
| Year Ended June 30, | ||||||||||||
| 2023 | 2022 | Change | ||||||||||
| Balance Sheet Statistics: |
||||||||||||
| Cash & cash equivalents |
$ | 6,426 | $ | 18,470 | (12,044 | ) | ||||||
As of June 30, 2023, we had $6.4 million of cash and cash equivalents. This period balance represents a decrease of $12 million from the same date in fiscal year 2022. The reason for this decrease is primarily due to costs associated with our operations, particularly drilling our appraisal wells.
Convertible Notes
On July 6, 2023, we agreed to issue up to $9 million of our five-year Convertible Notes from time to time to H&P for purposes of funding reimbursement of H&Ps mobilization and related reimbursable costs for Rig 469 as well as other working capital requirements. The Convertible Notes may be converted into a maximum of shares of the Companys common stock. The Convertible Notes accrue interest at 5.5% per annum on the amount drawn and outstanding. As of the date of this prospectus, we have not borrowed any amount under the Convertible Notes.
71
Table of Contents
Capital Commitments
We had following capital commitments as of the years ended June 30, 2023 and 2022 which are not recognized as liabilities or payable in the consolidated statement of financial position (all dollar amounts are presented in thousands):
| Year Ended June 30, | ||||||||||||
| 2023 | 2022 | Change | ||||||||||
| Capital commitments: |
||||||||||||
| Sweetpea |
$ | 42,465 | $ | 32,103 | 10,362 | |||||||
| McArthur Joint Venture |
2,652 | 1,653 | 999 | |||||||||
| Beetaloo Joint Venture |
54,209 | | 54,209 | |||||||||
Sweetpea Commitments
In EP 143, we have committed to spending a minimum of $0.3 million due in April 2024 on work requirements including subsurface studies, environmental assessments, design and planning of 2D seismic survey and progress of land access negotiations with pastoralist for regulated activities.
In EP 136, we initially planned to spend at least $18.9 million due on December 31, 2023 for the 5 year work requirements, including the re-entry of a vertical well, side track to drill a horizontal well, stimulation and testing of one exploration well plus the assessment of petroleum resources potential. As of December 31, 2023 this work had not been completed, however, an application to vary the minimum work commitments by removing this requirement to drill the horizontal well was submitted to the Department of Industry, Tourism and Trade (DITT) on September 1, 2023. If approved, the minimum expenditure will decrease to $4.1 million to reflect spending on the permit to date. A renewal application for EP136 was submitted to DITT on September 28, 2023 with a proposed expected work program commitment of $14.0 million for the next exploration term (five years). This remains under review.
McArthur Joint Venture
For the McArthur Joint Venture, we are obligated to contribute our share of expenses to uphold our stake in EP 161. Our commitment through March 2026 is approximately $2.7 million based on the minimum work requirements.
Beetaloo Joint Venture
The terms of the Beetaloo Joint Venture necessitate specific work obligations through May 2028. These commitments include an expected spend of $54.2 million related to drilling and multi-stage hydraulic fracturing of five wells across the permits as well as subsurface studies.
Cash Flows
The following table summarizes our cash flows for the periods indicated (in thousands):
| Year Ended June 30, | ||||||||||||
| 2023 | 2022 | Change | ||||||||||
| Statement of Cash Flows: |
||||||||||||
| Net cash used in operating activities |
$ | (12,804 | ) | $ | (10,011 | ) | 2,793 | |||||
| Net cash used in investing activities |
$ | (107,465 | ) | $ | (38,746 | ) | (68,719 | ) | ||||
| Net cash from financing activities |
$ | 106,183 | $ | 23,740 | 82,443 | |||||||
72
Table of Contents
Net Cash Used in Operating Activities
Net cash used in operating activities for the year ended June 30, 2023, totaled approximately $12.8 million during which we incurred a net loss of $32.2 million. The net loss included the non-cash impacts of depreciation and amortization, loss on assets classified as held for sale, share based payments, and foreign exchange differences. The cash flows for operating activities also reflected the decrease in working capital compared to the prior year period.
Net Cash Used in Investing Activities
For the year ended June 30, 2023, net cash used in investing activities was $107.5 million compared to $38.7 million for the year ended June 30, 2022 due to increased spend on exploration and evaluation activities, the completion of the purchase of US based rigs, and other investments offset by proceeds from the sale of one rig and government grants.
Net Cash Used in Financing Activities
For the year ended June 30, 2023, net cash received in financing activities was $106.2 million compared to $23.7 million received for the year ended June 30, 2022, due to significant proceeds attained from the Companys capital raises in fiscal year 2023.
Internal Controls and Procedures
As an emerging growth company, we are not currently required to comply with the SECs rules implementing Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, and therefore are not required to make a formal assessment of the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting for that purpose. Upon becoming a public company, we will be required to comply with the SECs rules implementing Section 302 of the SOX, which will require our management to certify financial and other information in our quarterly and annual reports and provide an annual management report on the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting. Though we will be required to disclose material changes made to our internal controls and procedures on a quarterly basis, we will not be required to make our first annual assessment of our internal control over financial reporting pursuant to Section 404 of the SOX until the year following our first annual report required to be filed with the SEC. We will not be required to have our independent registered public accounting firm attest to the effectiveness of our internal controls over financial reporting until our first annual report subsequent to our ceasing to be an emerging growth company within the meaning of Section 2(a)(19) of the Securities Act. See Prospectus Summary Emerging Growth Company Status.
In connection with the audit of our financial statements for the fiscal years ended June 30, 2023 and 2022, we identified deficiencies in our internal control over financial reporting, which in the aggregate, constituted a material weakness. We determined in both years that we had deficiencies relating to insufficiently designed and operating internal controls over financial reporting, including: i) lack of sufficient evidence retained of the performance of internal controls, ii) insufficient resources in key accounting and finance roles leading to inadequate segregation of duties and iii) lack of manage access and manage change IT general controls over the cloud-based enterprise resource planning system, which in the aggregate constitute a material weakness.
As part of our plan to address this material weakness, we are performing a full review of our processes and internal controls. We have implemented, and plan to continue to implement, new controls and processes. We will also provide training to control owners in support of an effective internal control framework, including how to sufficiently document and evidence the operation of internal controls. Finally, we are also evaluating our current enterprise resource planning system and considering options for replacing it with a new system to better support our financial reporting, including any related internal controls. While we have begun implementing a plan to remediate this material weakness, we cannot predict the success of such plan or the outcome of our assessment of this plan at this time. If our steps are insufficient to successfully remediate the material weakness and otherwise establish and maintain an effective system of internal control over financial reporting, the reliability of our
73
Table of Contents
financial reporting, investor confidence in us, and the value of our common stock could be materially and adversely affected. We can give no assurance that this implementation will remediate this deficiency in internal control or that additional material weaknesses in our internal control over financial reporting will not be identified in the future. Our failure to implement and maintain effective internal control over financial reporting could result in errors in our financial statements that could result in a restatement of our financial statements, or cause us to fail to meet our periodic reporting obligations. For as long as we are an emerging growth company under the JOBS Act, our independent registered public accounting firm will not be required to attest to the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting pursuant to Section 404.
Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates
Managements discussion and analysis of our financial condition and results of operations are based upon our historical consolidated financial statements, which have been prepared in accordance with GAAP. The preparation of our financial statements in conformity with GAAP requires us to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of certain assets, liabilities and related disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. The following critical accounting policies relate to the more significant estimates and assumptions used in preparing the historical consolidated financial statements.
Accounting for Natural Gas Properties
We are in the exploration stage and have not yet realized any revenues from our operations. We group our EPs into areas of interest according to geographical and geological attributes. We use the successful efforts method of accounting for expenditure incurred in each area of interest. Under this method, all general exploration and evaluation costs such as geological and geophysical costs are expensed as incurred. The direct costs of acquiring the rights to explore, drilling exploratory wells and evaluating the results of drilling are capitalized as exploration and evaluation assets (as a part of unproved properties) pending the determination of the success of the well. If a well does not result in a successful discovery, the previously capitalized costs are immediately expensed.
Impairment of Natural Gas Properties
Where an indicator of impairment exists for an unproved property and it is determined that future appraisal drilling or development activities are unlikely to occur, an impairment expense is recorded. Upon approval of the commercial development of a project, the exploration and evaluation asset is classified as a development asset. Once production commences, development assets are transferred to property, plant and equipment and are depleted using the unit-of-production method based upon estimates of proved developed reserves.
Joint Interest Activities
Some of the Companys exploration, development and production activities are conducted jointly with other entities whereby each party holds an undivided interest in each asset and is proportionately liable for each liability in the scope of such arrangement. The Company has recognized its proportionate share of assets, liabilities, revenues and expenses in respect of such arrangements. These have been incorporated in the consolidated financial statements under the appropriate classifications.
Asset Retirement Obligations
Our asset retirement obligations (AROs) consist primarily of estimated future costs associated with the plugging, dismantling, removal, site reclamation and similar activities of natural gas properties in accordance with the requirements of respective EPs and with applicable local, state and federal laws. The discounted fair value of an ARO liability is required to be recognized in the period in which it is incurred, with the associated asset retirement cost capitalized as part of the carrying cost of the related long-lived asset. The recognition of an ARO requires numerous assumptions to be made by management regarding such factors as the estimated
74
Table of Contents
probabilities, amounts and timing of settlements; the credit-adjusted risk-free rate to be used; inflation rates; and future advances in technology. In periods subsequent to the initial measurement of the ARO, we recognize period-to-period changes in the liability resulting from the passage of time and revisions to either the timing or the amount of the original estimate of undiscounted cash flows. Increases in the ARO liability due to passage of time impact net income as accretion expense. The related capitalized cost, including revisions thereto, is charged to expense through depreciation and amortization over the life of the related asset.
Litigation and Environmental Contingencies
In the ordinary course of business, we may at times be subject to claims and legal actions. Management does not believe the impact of such matters will have a material adverse effect on our financial position or results of operations. We are subject to extensive federal, state, and local environmental laws and regulations, which may materially affect our operations. These laws, which are constantly changing, regulate the discharge of materials into the environment and may require us to remove or mitigate the environmental effects of the disposal or release of petroleum or chemical substances at various sites.
In our acquisition of existing assets, we may not be aware of what environmental safeguards were taken during the time such assets were operated or the environmental liabilities associated with such assets.
We maintain comprehensive insurance coverage that we believe is adequate to mitigate the risk of any adverse financial effects associated with these risks. However, should it be determined that a liability exists with respect to any environmental cleanup, remediation, or restoration, the liability to cure such a violation could still fall upon us. No claim has been made, nor are we aware of any liability which we may have, as it relates to any material environmental cleanup, remediation, restoration, or the material violation of any rules or regulations relating thereto.
Environmental expenditures are expensed or capitalized depending on their future economic benefit. Those related to an existing condition caused by past operations and that have no future economic benefits are expensed as incurred. Liabilities for expenditures of a noncapital nature are recorded when environmental assessment and/or remediation is probable, and the cost can be reasonably estimated.
Income Taxes
Income taxes are accounted for under the asset-and-liability method. Deferred tax assets and liabilities occur when differences between the financial statement carrying amounts of existing assets and liabilities and their respective tax bases and operating loss and tax credit carryforwards exist and are recognized for future tax consequences. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured using enacted tax rates expected to apply to taxable income in the years in which those temporary differences and carryforwards are expected to be recovered or settled. The effect on deferred tax assets and liabilities of a change in tax rates is recognized in income in the period that includes the enactment date. Current income tax recognized in the profit or loss is the tax payable or receivable on taxable income calculated using applicable income tax rates enacted as at reporting date. Current tax liabilities or assets are measured at the amounts expected to be paid or recovered from the relevant tax authority.
In assessing the probability that a deferred tax asset will be realized management considers whether it is more likely than not that all or some portion of the deferred tax assets will not be realized. We provide valuation allowances against deferred tax assets that are not considered more likely than not to be realized. The valuation of the deferred tax asset is dependent on, among other things, our ability to generate a sufficient level of future taxable income, in estimating future taxable income, we consider both positive and negative evidence in our assessment. If our estimate of future taxable income or tax strategies changes at any time in the future, we would record an adjustment to our valuation allowance. Recording such an adjustment could have a material effect on our financial condition or results of operations.
75
Table of Contents
Deferred income tax relating to timing difference and unused tax losses are only recognized to the extent that it is probable that future tax profit will be available against which the benefits of the deferred tax asset can be utilized.
Stock-Based Compensation
We measure and recognize compensation expense related to our share-based compensation based on the estimated fair value of the awards. The fair value of the award is measured at the grant date and is recognized as an expense over the course of the awards vesting period. The fair value of the stock options granted is estimated using either the Black-Scholes (for awards that vest based on service conditions) or the Monte-Carlo option-pricing model (for awards that vest based on market conditions). Each of these models include the share price at grant date, exercise price, the term of the right, expected price volatility of the underlying share, the expected dividend yield and the risk-free interest rate for the term of the right. The Monte Carlo model also incorporates a probability-based value impact of the market condition.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
See Note 2Summary of Significant Accounting Policies to our historical consolidated financial statements included elsewhere in this prospectus for more information about recent accounting pronouncements, the timing of their adoption, and our assessment, to the extent we have made one, of their potential impact on our financial condition and our results of operations.
Emerging Growth Company Status
Section 107 of the JOBS Act provides that an emerging growth company can take advantage of the extended transition period provided in Section 7(a)(2)(B) of the Securities Act of 1933 for complying with new or revised accounting standards. In other words, an emerging growth company can delay the adoption of certain accounting standards until those standards would otherwise apply to private companies. We intend to take advantage of all of the reduced reporting requirements and exemptions, including the longer phase-in periods for the adoption of new or revised financial accounting standards under Section 107 of the JOBS Act until we are no longer an emerging growth company. Our election to use the phase-in periods permitted by this election may make it difficult to compare our financial statements to those of non-emerging growth companies and other emerging growth companies that have opted out of the longer phase-in periods under Section 107 of the JOBS Act and who will comply with new or revised financial accounting standards. If we were to subsequently elect instead to comply with these public company effective dates, such election would be irrevocable pursuant to Section 107 of the JOBS Act.
Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosure About Market Risk
Commodity Price Risk
If and when we commence production, we will have market risk exposure in the price we receive for our natural gas production. Pricing is primarily driven by spot market prices applicable to Australia and East and South Asia. Pricing for natural gas and NGLs has historically been volatile and unpredictable, and we expect this volatility to continue in the future. The prices we will receive for our production depend on many factors outside of our control, including volatility in the differences between product prices at sales points and the applicable index price.
Due to the historical volatility of commodity prices, we may in the future enter into various derivative instruments to manage our exposure to volatility of commodity market prices. We may use options (including floors and collars) and fixed price swaps to mitigate the impact of downward swings in commodity prices to our cash flow. All contracts will be settled with cash and would not require the delivery of physical volumes to
76
Table of Contents
satisfy settlement. While in times of higher commodity prices this strategy may result in our having lower net cash inflows than we would otherwise have if we had not utilized these instruments, management believes the risk reduction benefits of such a strategy would outweigh the potential costs.
Foreign Currency Risk
Our financial results are reported in U.S. dollars. As our functional currency is the Australian dollar, we are exposed to foreign exchange risk, mainly with the U.S. dollar, which is the currency in which we receive much of our revenue and incur many of our expenses. As of June 30, 2023, 90% of our $7.1 million cash and cash equivalents were denominated in currencies other than the U.S. dollar. We have not historically used financial derivatives and we endeavor to achieve risk mitigation through natural hedges. These natural hedges may include the maintenance of a U.S. dollar bank account and bank accounts in any other currency to which we may have significant exposure in the future to facilitate the settlement of invoices in these currencies.
Interest Rate Risk
There are no material interest rate risk exposures as of the date of this prospectus. We may borrow under fixed rate and variable rate debt instruments that give rise to interest rate risk. Our objective in borrowing under fixed or variable rate debt is to satisfy capital requirements while minimizing our costs of capital.
Counterparty and Customer Credit Risk
If and when we commence production, we will sell our natural gas to a limited group of customers. If any significant customer of ours should have credit or financial problems resulting in an inability to purchase natural gas, it could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and cash flows. Additionally, if any significant vendor, joint venture partner or strategic partner of ours should have financial problems or operational delays, it could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and cash flows.
77
Table of Contents
The production of oil, natural gas and natural gas liquids plays a vital role in Australias present-day economy. Australia is a net exporter of energy, exporting approximately three-quarters of its domestic gas production. Australias geographic proximity to the large growing economies of South and East Asia, especially India and China, provide a logistical advantage and often higher commodity prices versus other commodity exporting nations like the United States. Australias status as a developed OECD economy also enables the participants in the oil and gas sector to attract capital investment, skilled labor and technology. This dual attraction of political and economic stability and economic security built on the export of natural resources creates an attractive jurisdiction for investment. According to the Australian Government Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade, in 2022, natural gas was the third largest export product of Australia valued at over A$90 billion during calendar year 2022.
Australian Natural Gas and Natural Gas Liquids Reserves
Australias hydrocarbon reserves are weighted towards natural gas. According to Geoscience Australia, Australia had ~19,439 MMboe of proved and probable natural gas reserves as of December 2021, of which 74% was conventional and 26% unconventional and, it is the seventh largest gas producer in the world by volume.
Below is a map of the primary oil and natural gas basins in Australia as well as the key LNG projects:
Source: Australia: a Review of Gas Transfer Pricing Arrangements Global LNG Hub (2023).
According to Geoscience Australia, about 93% of conventional gas resources are located on the North West Shelf with gas produced from the Northern Carnarvon, Browse and Bonaparte basins providing feedstock to seven LNG projects (Gorgon, Wheatstone, North West Shelf, Pluto, Prelude, Ichthys and Darwin) as well as the domestic market. These figures reflect only conventional reserves and offshore discoveries and do not include the Beetaloo. The Beetaloo is an unconventional gas basin and while the results to date have been promising, the Beetaloo has yet to book any meaningful reserves.
78
Table of Contents
The following diagram illustrates the sources of Australias total natural gas production in petajoules and how it was consumed during the 2021-22 financial year.
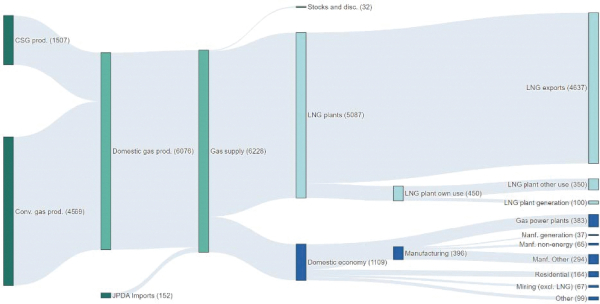
Note: Components may not sum due to rounding. Natural gas power plants include some generation by other economic sectors.
Source: DCCEEW (2023) Australian Energy Statistics.
The Australian Domestic Natural Gas Market
Historically, the Australian domestic natural gas market has consisted of three separate regional markets, separated on the basis of productive natural gas basins and pipelines that supply them, which include:
| | East Coast Domestic Gas Market: The East Coast domestic market consists of Australias eastern and southern states and territories (including Queensland, New South Wales, Victoria, South Australia, Tasmania and the Australian Capital Territory), which are connected by a single natural gas grid. The East Coast accounted for approximately 51.3% of domestic natural gas consumption in 2022. The natural gas basins that currently supply this market approximately contain around one-third of Australias natural gas reserves. |
| | The Northern Territory Domestic Market: The Northern Territory market is Australias smallest domestic market and accounted for 6.9% of domestic natural gas consumption in 2022. The Northern Territory natural gas market was connected to the East Coast market in 2019 when the Northern Gas Pipeline was opened between Tennant Creek in the Northern Territory and Mt. Isa in Queensland. Prior to this, there was no interconnectivity between these markets. The majority of natural gas used in the Northern Territory is supplied from the offshore Blacktip gas field and onshore Mereenie gas/condensate field. Recently, production from Blacktip, which is the largest supplier to the Territory, has declined and been unable to recover to historic levels following a 2023 appraisal program. This provides Tamboran with an immediate domestic opportunity. |
| | West Coast Domestic Gas Market: The West Coast domestic market accounted for 41.8% of domestic natural gas consumption in 2022. Demand in the West Coast market is predominantly driven by industrial users such as mining operations. |
The growth in LNG exports has resulted in higher natural gas prices and concerns of domestic natural gas shortfalls, particularly on the East Coast of Australia.
79
Table of Contents
East Coast Gas Market Overview
The competitive landscape for domestic natural gas supply in the East Coast natural gas market has been significantly impacted by the development of three LNG export terminals in Gladstone, Queensland over the past decade (GLNG, APLNG, and QCLNG). Prior to these facilities coming online, domestic producers had drilled a significant number of coal seam gas wells in Queensland to meet anticipated demand, lowering the prevailing market price for domestic consumers to approximately A$3 per Mcf. However, after the facilities came online and began exporting gas, domestic consumers saw a price increase of 3-5x and the risk of shortages became prevalent.
The following chart illustrates the Australian Electricity Market Operators (AEMO) natural gas consumption forecast, broken down by consumer type for all Australian states (except Western Australia), which demonstrates the vast majority of domestic natural gas production throughout the forecasted 2042 period being exported as LNG, resulting in potential supply shortages on the East Coast. These supply shortages may be exacerbated by potential increases in natural gas-powered electricity generation.
Actual and forecast total annual natural gas consumption, all sectors, Orchestrated Step Change (1.8°C)
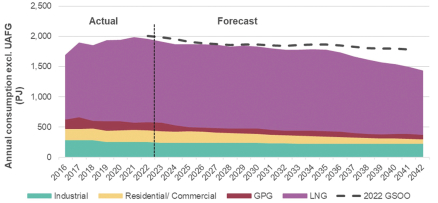
Note: The 2022 GSOO did not include the Northern Territory as a participating GSOO jurisdiction. The Northern Territory is included in actual natural gas consumption from 2020 onwards and in the 2023 forecasts. Source: Actual and forecast total annual natural gas consumption, all sectors, Orchestrated Step Change scenario (1.8°C), 2016-42 (PJ), AEMO, Gas Statement of Opportunities, March 2023.
East Coast Gas Market Pricing
Natural gas prices have remained high in Australia relative to other OECD countries. Most domestic natural gas is typically sold under contracts with fixed pricing indexed to inflation. Spot natural gas prices reflect the balance between demand and supply of natural gas at a particular delivery point supplying the market at a particular time. Because the volumes available for spot sales are typically small, wholesale prices can be volatile and can be an unreliable indicator of underlying natural gas supply and demand fundamentals.
Since the commencement of LNG exports from Queensland in 2015, East Coast wholesale domestic natural gas prices have been broadly consistent with the LNG netback price, which is defined as the price an LNG seller receives minus the costs of liquefying and transporting the natural gas to the buyer (Wallumbilla is the principal natural gas supply hub in Queensland). The East Coast LNG facilities have excess capacity, so any oversupply of natural gas in the East Coast market has potential access to the Asian LNG market via spot LNG sales, helping to stabilize prices.
80
Table of Contents
The following chart illustrates the domestic gas price between producers and retailers in the Australian East Coast for the years 2022 and 2023:
Gas commodity prices (2024$/GJ) in the east coast gas market
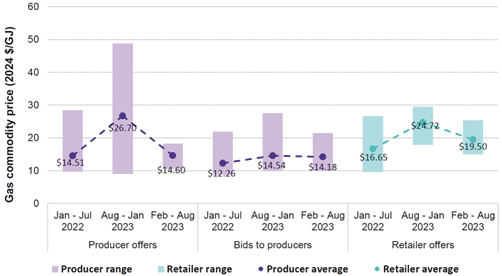
Source: ACCC Gas Inquiry 2017-2040 Interim update on east coast gas market December 2023
The following chart illustrates the LNG netback and Wallumbilla prices from January 2016 to October 2023:
LNG Netback and Wallumbilla Prices (A$/GJ)
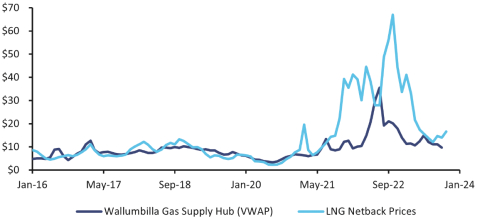
Source: LNG netback price data from ACCC Gas Inquiry 2017-2030, LNG netback price series (October 2023); Wallumbilla price data from Australian Energy Regulator, Wallumbilla Gas Supply Hub trade volume and VWA prices by pipeline.
East Coast Gas Market Supply / Demand Deficit
These market fundamentals indicate a shortage of identifiable natural gas available to both fully utilize existing LNG capacity and to meet projected domestic energy needs.
81
Table of Contents
As highlighted in the AEMOs 2023 GSOO, new supply options are forecast to be required to meet demand from 2027 through the end of the projected period, with a forecasted supply gap in 2027 to be between 0 MMboe and 1.96 MMboe, depending on weather conditions. In AEMOs assessment, to maintain adequate domestic supply, natural gas supply that would otherwise be contracted for LNG export would be required to be diverted to domestic consumers from 2027, which in turn would cause LNG supply shortages that would necessitate development of new supply options.
The below chart illustrates this fundamental supply gap, including the assumption that natural gas is diverted from LNG export to the East Coast.
Projected annual adequacy in southern regions Orchestrated Step Change (1.8°C) scenario, with existing, committed and anticipated developments, 2023-42 (PJ)
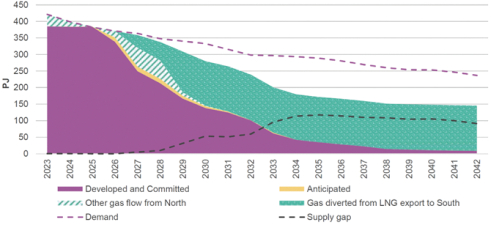
Source: AEMO, 2023 Gas Statement of Opportunities.
Potential additional domestic sources of natural gas that would supply the eastern Australian natural gas market over the next ten to fifteen years, outside of LNG diversions, include additional coal seam gas (CSG) from Queensland, CSG from New South Wales, the Beetaloo/McArthur shales of the Northern Territory/Queensland and South Nicholson shales. In addition, several domestic energy suppliers have proposed LNG regasification terminals on the East Coast, which would enable additional supply to be sourced from LNG cargoes either from the Northern Australia exporters or overseas. Notably, contracts for these volumes into the East Coast market are not subject to the Federal Government price cap (see the section entitled BusinessEnvironmental Matters and Regulation), which supports the viability of these projects. Albeit, to date all LNG regasification terminal projects have been delayed by availability of equipment and regulatory approvals.
82
Table of Contents
East Coast Gas Market Infrastructure
The following chart illustrates Australias East Coast natural gas market infrastructure:
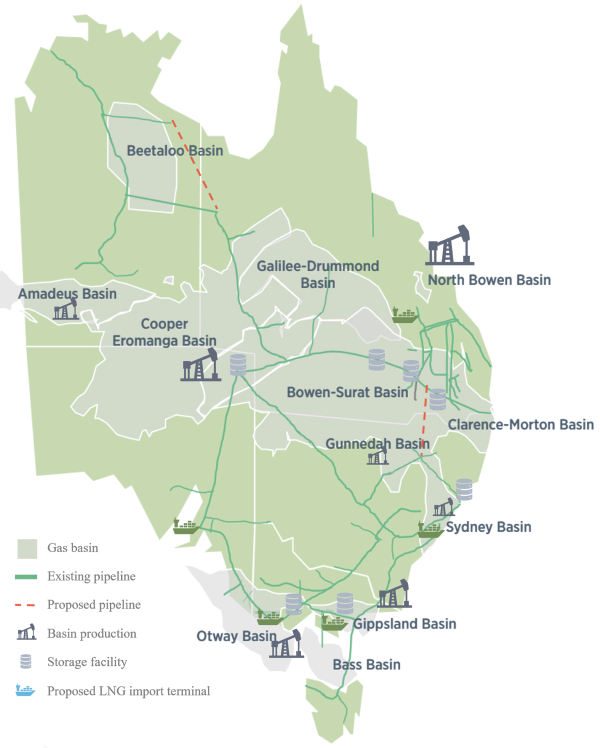
Source: ACCC analysis of data obtained from gas producers as of August 2023 and August 2022 (Beetaloo Basin only) and public information on the Hunter Gas Pipeline Project Background and Status Fact Sheet (Santos, 2022). DISR National Gas Infrastructure Plan Interim Report 2021.
83
Table of Contents
The East Coast transmission pipeline system is an interconnected grid covering Queensland, New South Wales, Victoria, South Australia, Tasmania and the Australian Capital Territory. In recent years, most transmission pipelines in the East Coast grid have been made bi-directional which means that gas produced in Queensland can be used in Tasmania and gas produced in the south of Australia can be sent to Gladstone for export. This interconnectedness has enabled more flexible arrangements for trading in gas, resulting in gas being supplied where needed.
The Northern Territory has the AGP which takes gas from fields in the Amadeus Basin near Alice Springs to Darwin. The Northern Gas Pipeline in the Northern Territory connects its gas fields to the East Coast network, linking the AGP to the Carpentaria pipeline near Mount Isa in Queensland.
The Liquefied Natural Gas Industry
LNG involves natural gas being cooled to lower than -260° Fahrenheit (-161.5 Celsius) and converted to a liquid that is 1/600th of its original size to enable it to be transported efficiently by ship to an import destination, where it is regasified for use. Historically, the largest customers for LNG have been the large north Asian economies such as China, Japan, South Korea and Taiwan, which use natural gas for both electricity generation and in various industrial processes, but have limited domestic natural gas supplies.
Since the Russian invasion of Ukraine, LNG has assumed new significance to Europe as an alternative source of natural gas originating from Russia that has historically been transported to Europe via pipeline. The Russian invasion of Ukraine and other recent geopolitical developments have highlighted the importance to energy-importing nations of securing reliable energy supplies, and LNG imports from reliable exporters can be a key contributor to energy security.
According to EIA and CEDIGAZ, global trade in LNG set a record high in 2022, averaging 388 Mtpa, a 5% increase compared with 2021. The International Energy Agency (IEA) forecasts global LNG trade to grow at an average annual rate of just under 4% between 2021 and 2025 to 437 Mtpa. The IEA forecasts that LNG imports into Europe will grow by 51% (or 39 Mtpa) over this period as European nations attempt to reduce their dependence on Russian gas, while Asian imports will grow 11% (or 29 Mtpa) over the same period.
Australias Liquefied Natural Gas Industry
Australia was the worlds largest volume exporter of LNG in 2022, overtaking Qatar. Given Australias relative geographic proximity to major Asian markets, Asian energy demand continues to be the main driver of Australias LNG industry. In the financial year ended June 30, 2023, Japan was the top export destination, by value, for Australian LNG (37% of Australian liquid natural gas export value), followed by China (22%) and Korea (20%).
84
Table of Contents
The following chart illustrates the worlds largest LNG producers in 2022:
2022 LNG exports and market share by export market (million tons)
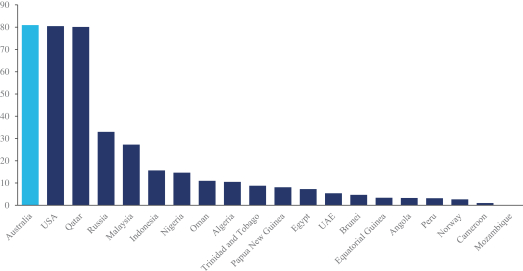
Source: International Gas Union 2023 World LNG Report
Today, Australia has three geographically separate hubs for LNG exports Gladstone, Darwin and the North West Shelf. The North West Shelf and Darwin LNG export terminals have historically been supplied by offshore conventional gas fields while the three LNG export terminals in Gladstone have been supplied with both conventional and unconventional sources (i.e., coal seam gas).
The relative geographic proximity of the existing and planned LNG export terminals in northern Australia to Asian markets provides Northern Territory operators with competitive advantages over current LNG suppliers from the Middle East and the United States. For example, LNG can be delivered from Darwin to Singapore in less than four days, and to China and Japan within six days. Shipments from the Middle East must travel through the Red Sea, while shipments from United States must travel around the southern cape of Africa or through the Panama Canal, all of which often result in delays or higher costs. The cost to ship LNG from Darwin to Japan is approximately 40% lower than the cost to ship LNG from Qatar. Additionally, spot prices in certain South and East Asian regional markets have historically been significantly higher than spot prices at Henry Hub. For example, during the calendar year ended 2023, spot prices for natural gas delivered to Henry Hub averaged $2.54 per MMBtu while over that same period the Japan Korea Marker (JKM) continuous futures price for LNG averaged $14.45 per MMBtu.
Recent Policy Updates
Temporary Pause on Certain Authorizations to Export LNG from the United States
In January 2024, the Biden Administration announced a temporary pause on the U.S. Department of Energys (DOE) review of pending applications for authorization to export LNG to countries that have not entered into free trade agreements (FTAs) with the United States (so-called non-FTA countries). The temporary pause will last until the DOE can update its underlying analyses for authorizations using more current data to account for considerations like potential energy cost increases for consumers and manufacturers or the latest assessment of the impact of GHG. The temporary pause is not expected to affect LNG exports that have already been authorized but may have a material impact on the operations of U.S.-based LNG exporters.
85
Table of Contents
Australian Domestic Gas Security Mechanism
In 2017, in response to a serious risk of a natural gas supply shortfall in the domestic market, the Commonwealth Government established the Australian Domestic Gas Security Mechanism (ADGSM). The ADGSM allows Australias Minister for Resources to restrict LNG exports if the Minister has reasonable grounds to believe that there will not be a sufficient supply of natural gas for Australian consumers during the year unless exports are controlled and that exports of LNG would contribute to that lack of supply. In April 2023, a number of reforms to the ADGSM were introduced, including that the Commonwealth Government can now consider whether to activate the ADGSM quarterly, rather than annually. As of today, the ADGSM has not been activated.
Price Cap / Mandatory Code of Conduct
In response to a period of high domestic natural gas prices, largely driven by unusually high demand from electricity generators due to the underperformance of coal fired generation, in December 2022, the Federal Government imposed a price cap of A$12.00 per GJ of natural gas for new wholesale natural gas supply agreements between East Coast and Northern Territory natural gas producers and commercial and industrial users for a period of 12 months. In July 2023, the government introduced a mandatory code of conduct for natural gas producers, which, among other things, extends the price cap until at least July 2025, subject to a number of exemptions that are designed to incentivize additional supply to the domestic market on reasonable terms. The government has provided several exemptions to industry producers and the operators of new gas projects like Tamboran. Tamboran has applied and been granted an exemption from the gas price cap.
Carbon Safeguard Mechanism
With effect from July 1, 2023, the Federal Government has reformed Australias National Greenhouse and Energy Reporting (Safeguard Mechanism) Rule 2015 (Cth) (the Safeguard Mechanism), which sets emissions limits (known as baselines) on facilities emitting greater than 100,000 tons of CO2-e annually. The reforms include a requirement that all emissions from the Beetaloo be offset once the 100,000 tons CO2-e trigger is exceeded. For more information see BusinessEnvironmental Matters and Regulation.
86
Table of Contents
Overview
We are an early stage, growth-driven independent natural gas production company focused on an integrated approach to the commercial development of the natural gas resources in the Beetaloo located within the Northern Territory of Australia. We and our working interest partners have EPs to approximately 4.7 million gross (1.9 million net to Tamboran) contiguous prospective acres, and are currently the largest acreage holder in the Beetaloo. We believe natural gas will play a significant role in the transition to cleaner energy and are committed to supporting the global energy transition by developing commercial production of natural gas in the Beetaloo with net zero equity Scope 1 and 2 emissions.
Corporate History and Corporate Reorganization
Our Predecessor was founded in 2009 and is headquartered in Sydney, Australia. Previously, we held interests in EPs and applications in the Northern Territory, South Australia, Western Australia, Northern Ireland, Republic of Ireland and Botswana. Joel Riddle become the Managing Director and CEO during 2013, and the Company chose to focus on the Northern Territory and relinquished or divested its rights to explore in other jurisdictions. Tamboran Resources Limited subsequently admitted its ordinary shares for official quotation on the ASX in July 2021.
We were incorporated in the State of Delaware on October 3, 2023 for the purposes of effecting the corporate reorganization. We received all the issued and outstanding shares of Tamboran Resources Limited pursuant to a statutory scheme of arrangement under Part 5.1 of the Australian Corporations Act. The scheme of arrangement was approved by the shareholders of Tamboran Resources Limited at a general meeting of shareholders held on December 1, 2023. Following shareholder approval, the scheme of arrangement was approved by the Federal Court of Australia on December 6, 2023.
Pursuant to the corporate reorganization, we issued to the shareholders of Tamboran Resources Limited one CHESS Depositary Interest for each ordinary share of Tamboran Resources Limited. Additionally, we amended the terms of each of the outstanding options to acquire ordinary shares of Tamboran Resources Limited so that the entitlements of option holders to be issued ordinary shares in Tamboran Resources Limited instead became entitlements to be issued CDIs in the Company. We maintain an ASX listing for our CDIs, with each CDI representing beneficial ownership in 1/200th of a share of our common stock. Holders of CDIs are able to trade their CDIs on the ASX. Following completion of the corporate reorganization, Tamboran Resources Limited became a wholly owned subsidiary of the Company.
87
Table of Contents
The Beetaloo
The Beetaloo, an area of approximately 10,800 square miles (or approximately 7 million acres), is believed to contain significant quantities of unconventional natural gas and has geological properties believed to be comparable to that found in the Marcellus Shale of the Appalachian Basin in the northeastern United States. The Beetaloo is a structural component of the Greater McArthur Basin in the Northern Territory and is located approximately 300 miles southeast of Darwin, Northern Territory. The following image illustrates the location of the Beetaloo:
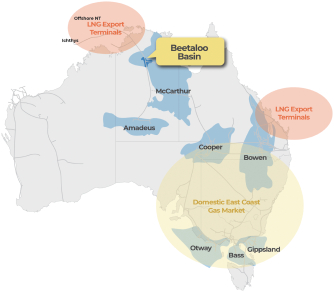
Located in the southern part of the Greater McArthur Basin, the Beetaloo is structurally subdivided into three geographical areas and two major structural highs. The north-south trending, structurally complex Daly Waters Arch (west) and the structurally benign Arnold Arch (east) divide the area into three major depocenters, referred to here as the Sever Sub-Basin, the Core area, and the OT Downs Sub-Basin from west to east, respectively.
The Northern Territory owns all petroleum resources, both onshore and in coastal waters in that jurisdiction. The Northern Territory Department of Industry, Tourism and Trade administers and regulates petroleum permit tenures and activities in these areas, including natural gas resource exploration and development permitting as well as permits for the construction and operation of oil and gas facilities and transmission pipelines.
Historical E&P Activity in the Beetaloo
In 1984, CRA Exploration, a subsidiary of Pacific Oil and Gas (POG), acquired acreage north of the core of the Beetaloo on the basis of the identification of live oil in stratigraphic wells and geological mapping that proved the existence of at least one working petroleum system. POG subsequently picked up permits farther south over the core of the Beetaloo, and, from 1987 to 1993, drilled 12 wells close to the core of the Beetaloo, providing multiple penetrations of the primary source rock in the Proterozoic Roper Group, the Velkerri Formation (Velkerri), and organic rich shales within the Velkerri. POG also completed 2D seismic surveys over a number of areas during this period.
Early drilling targeting conventional structures met limited success, but these early wells did confirm the extent of the organic rich rocks in the Velkerri (subsequently named the Amungee Member). Eventually POG withdrew from all permits and interest in the Beetaloo waned among operators for the remainder of the 1990s.
88
Table of Contents
Sweetpea Corporation (Sweetpea) believed the Beetaloo remained an economically viable drilling location, and, accordingly, applied for EPs in many of the same areas previously covered by POGs permits. In the 2000s, Sweetpea was granted permits over the vast majority of the prospective core. Sweetpeas strategy included a combination of conventional oil and gas plays, and tight gas and basin-centered gas plays (prior to the widespread recognition of the potential of shale gas that Mitchell Energy demonstrated in the Barnett Shale in Texas).
Sweetpea, later acquired by Tamboran in July 2020, collected over 400 miles of 2D seismic data before drilling an initial well, Shenandoah 1 in 2007, to a depth of approximately 5,000 feet, which was ultimately suspended. Falcon eventually became operator of four of the Sweetpea exploration permits (EPs 76, 98, 99, and 117) in 2009. Falcon re-entered and deepened Shenandoah 1 (deepened well re-named Shenandoah 1A) to approximately 8,900 feet in 2009 and completed the first hydraulic fracture stimulation of a shale gas target in Australia in 2011, and successfully flow-tested two zones within the Amungee Member of the Velkerri and one zone in the Kyalla.
In 2011, Falcon partnered with Hess Corporation (Hess) as a farminee for works on EPs 76, 99, 98 and 117. The Hess-Falcon joint venture proceeded to collect over 2,000 miles of 2D seismic data in 2011 and 2012, before terminating their participation agreement in mid-2013. This termination eventually led to the creation of the Beetaloo Joint Venture in 2014 with Origin B2 (now known as Tamboran B2) and Sasol, with Origin B2 as operator.
The Beetaloo Joint Venture drilled four key wells in 2015 and 2016; three vertical wells (Kalala S-1, Amungee NW-1 (A1V), and Beetaloo W-1) and one horizontal well (Amungee NW-1H (A1H)), from the A1V vertical appraisal well. The vertical wells all penetrated the complete prospective interval of the Amungee Member. The Amungee Member was informally divided into three intervals, A Shale, B Shale and C Shale; terms to describe the three laterally continuous but stratigraphically distinct organic rich intervals from oldest and deepest (A Shale) to youngest and shallowest (C Shale).
The Beetaloo W-1 well was drilled around 60 miles south of previous key intersections of the full Amungee Member but showed a remarkable consistency in geology of the source rock intervals. The Beetaloo Joint Venture drilled, completed and tested the A1H well during 2015 and 2016, providing evidence of a material volume of moveable gas lay within that portion of the Beetaloo and made the Amungee area a target for further appraisal.
From 2014 to 2015, Pangaea Resources also acquired 2D seismic data and drilled a number of wells in the western most extents of the Beetaloo. The well drilled by Pangaea Resources in this area demonstrated continuity of the Amungee Member to the west of the core, although substantially shallower than at Tanumbirini-#1 (T1V).
Around the same time, Tamboran farmed-out 75% of EP 161 to Santos to create the McArthur Joint Venture. In 2014, the McArthur Joint Venture drilled the T1V well to a depth of almost 13,000 feet in one of the deepest parts of the Beetaloo, informally known as the OT Downs Sub-basin. The T1V well provided a new eastern stratigraphic control point and demonstrated continuity of the source rock properties of the Amungee Member of the Velkerri.
On September 14, 2016 the NT Government announced a moratorium on hydraulic fracturing of onshore unconventional reservoirs including the use of hydraulic fracturing for exploration, extraction, and production. As a result, between 2016 and 2020, minimal activity was undertaken in the Beetaloo as the independent Scientific Inquiry into Hydraulic Fracturing of Onshore Unconventional Reservoirs in the Northern Territory was undertaken. However, since 2020, the McArthur Joint Venture and Beetaloo Joint Venture have undertaken further activity and drilled key wells that have provided further evidence of the potential for the Velkerri to be commercialized.
89
Table of Contents
Our Assets Within the Beetaloo
We currently hold interests in seven EPs and one EP(A), all of which are contiguous to one another and located in the Beetaloo in the Northern Territory in Australia. Our key assets are (i) a 25% non-operated working interest in EP 161, (ii) a 38.75% working interest in EPs 76, 98 and 117, where we are the operator, and (iii) a 100% working interest in EPs 136, 143 and EP(A) 197, where we are the operator, all of which are located in the Beetaloo. We have an undivided 50% interest in EPs covering 4.7 million gross (1.9 million net) acres through the TB2 Joint Venture with Daly Waters. The deepest portions of the Beetaloo, and our strategic near-term focus are those areas covered by EPs 76, 98, 117, 136, 143 and 161. We also hold interests in EP 318 and EP(A) 197.
Our assets are depicted by the colored areas in the map of the Beetaloo below, with the deepest core regions of the Beetaloo (the darker blues) in the west being the focus of our development:
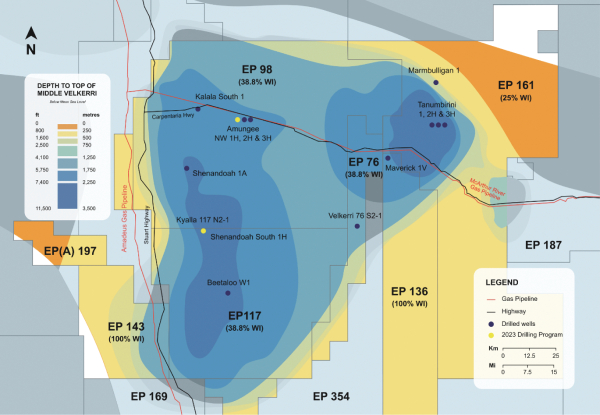
We have participated in six appraisal wells over the last 18 months, four of which we drilled as the operator:
| Well Name |
Operator | Non-Operator(s) | Exploration Permit |
Date Drilled | Tamboran Working Interest |
|||||||||
| Tanumbirini #2 (T2H) |
Santos | Tamboran | 161 | 2021 | 25 | % | ||||||||
| Tanumbirini #3 (T3H) |
Santos | Tamboran | 161 | 2021 | 25 | % | ||||||||
| Maverick 1V (M1V) |
Tamboran | N/A | 136 | August 2022 | 100 | % | ||||||||
| Amungee NW-2H (A2H) |
Tamboran | DWE & FOG | 98 | November 2022 | 38.75 | % | ||||||||
| Shenandoah South 1H (SS1H) |
Tamboran | DWE & FOG | 117 | August 2023 | 38.75 | % | ||||||||
| Amungee NW 3H (A3H) |
Tamboran | DWE & FOG | 98 | September 2023 | 38.75 | % | ||||||||
90
Table of Contents
Exploration Permits 76, 98 and 117
On November 9, 2022, the TB2 Joint Venture, an entity 50/50 owned by Tamboran (West) Pty Ltd (our wholly owned subsidiary), and Daly Waters and governed by a joint venture and shareholders agreement, completed the purchase of a 77.5% working interest in EPs 76, 98 and 117 for upfront cash consideration of A$60 million plus a future production royalty, providing us an undivided 50% (i.e., 38.75% working interest) in each these EPs. Falcon Oil and Gas Australia Ltd holds the remaining 22.5% non-operating working interest. The operation and management of the TB2 Joint Venture is governed by a joint venture and shareholders agreement. See EPs 76, 96, and 117 Joint Venture and Shareholders Agreement for a description of the material terms of the agreement governing the TB2 Joint Venture.
Following completion of the acquisition, we successfully drilled and cased the A2H well in the EP 98 permit. The well reached a total depth of approximately 12,700 feet in 38 days (spud to total depth). The well included an approximately 4,200 foot horizontal section within the target formation of the Mid-Velkerri B Shale. The A2H well intersected the formation at approximately 8,000 feet (vertical depth) and encountered significant natural gas shows within the formation, in line with pre-drill expectations.
The A2H well is the first well in the Beetaloo targeting the Mid-Velkerri B Shale to have been drilled and cased with 5-1⁄2 inch casing. We believe this is the optimal casing size to place a high intensity stimulation and is comparable to modern U.S. unconventional drilling designs. We successfully completed a stimulation program in March 2023. A total of 25 stages were successfully stimulated across an approximately 3,350-foot horizontal section within the Mid-Velkerri B Shale.
In March 2023, we contracted Silver City Drilling to undertake completion operations at the A2H well, including the installation of production tubing. Operations to install production tubing were completed in late-April 2023 and the well was re-opened in preparation to commence flow testing.
In June 2023, we announced interim results from A2H. Modelling and independent third-party analysis of fluids recovered from the well identified a potential zone of reduced permeability, or a skin inhibiting natural gas and water flow resulting from water contamination. In late June 2023, the well was flowing at 0.83 MMcf/d and averaged 0.97 MMcf/d over the first 50 days. The well was shut-in during July 2023 in preparation for potential remediation activities, subject to joint venture approval.
In early July 2023, Helmerich & Paynes (NYSE: HP) FlexRig® was successfully mobilized to the SS1H well location targeting the deeper Mid-Velkerri B Shale in EP 117. We commenced drilling of the SS1H well in early August 2023 and intersected a 295-foot interval of Mid-Velkerri B Shale. This represents the thickest section of Mid-Velkerri B Shale seen in the Beetaloo depocenter to date. Logging of the well also showed high quality Mid-Velkerri B Shale with strong dry gas shows. Logging of the Mid-Velkerri B Shale formation also indicated higher porosity and gas saturation relative to offset wells, consistent with the Marcellus Shale of the Appalachian Basin in the U.S. A 3,500-foot horizontal section was completed within the target shale zone ahead of a stimulation program planned for the fourth quarter of 2023.
During the drilling activities at SS1H, the Company completed its capital commitments under the Farmin Agreement with Falcon to earn title to a 77.5% working interest (38.75% each) and operatorship of the EP 76, 98 and 117 permits. Falcon elected to fund their 22.5% share of ongoing costs in the SS1H and A3H drilling activities.
In September 2023, we commenced drilling of the A3H well from the same well pad as the A2H well to follow up earlier drilling results. The well was successfully drilled in less than 18 days, the fastest well drilled with a horizontal section in the Beetaloo to date. The activities were completed 20 days faster than the shallower A2H well and approximately 30% lower cost, demonstrating the increased drilling efficiency of the H&P rig.
Daly Waters Royalty holds an ORRI of 2.3% of the petroleum produced from the land over which the EP 76, 98 and 117 was originally granted.
91
Table of Contents
EP 76 will remain in effect until at least May 30, 2028; EP 98 will remain in effect until at least May 30, 2028; and EP 117 will remain in effect until May 30, 2028.
Exploration Permit 161
EP 161 is a polygonal shaped tract that spans north-south with varying widths having a total area of approximately 4,000 square miles. Recent NSAI estimates based on the current work program include a prospective fairway acreage in EP 161, which is located on the eastern portion of the Beetaloo, of approximately 800 square miles. We hold a non-operated 25% working interest in EP 161 with Santos QNT Pty Ltd (Santos QNT) holding the remaining 75% working interest as operator. Pursuant to our joint operating agreement with Santos QNT, we are required to contribute our proportionate share of expenditures in order to maintain our interest in EP 161.
In the fourth quarter of 2019, the T1V vertical well was successfully fracture stimulated and flow tested. A Declaration of Discovery was submitted to the NT Government on December 19, 2019 and accepted by the NT Government in April 2020. In 2020, a 130-day flow test conducted for EP 161 exceeded 1.2 MMcf/d and settled at .4 MMcf/d with minimal decline. The flow test was ended prematurely due to the shelter-in-place orders in the Northern Territory during the COVID-19 pandemic. After being shut in for over 160 days, the well was reopened in the last quarter of 2020 and initially flowed 10 MMcf/d ultimately achieving an average flow rate of 2.3 MMcf/d during the first 90 hours of testing.
In 2021, Santos successfully drilled and fracture stimulated the T2H and T3H short lateral wells into the Mid-Velkerri B shale. The T2H well delivered an average IP30 flow rate of 2.1 MMcf/d over a 2,200 foot completed horizontal section (normalized at 9.5 MMcf/d over 10,000-foot lateral lengths). The T2H well had already produced 0.27 Bcf prior to the installation of production tubing.
In December 2022, Santos completed IP90 testing of the T2H and T3H wells following the installation of production tubing. Each reached IP90 of 1.6 and 2.1 MMcf/d, respectively (normalized at 7.4 and 10.7 MMcf/d, respectively, over 10,000-foot lateral lengths). Operations were subsequently suspended following the completion of the on-site activities.
In July 2023, we completed analysis of two Tanumbirini flow tests, including modelling of the production curves by independent third-party subsurface experts, Subsurface Dynamics, Inc. Results of the analysis demonstrated a 20-year EUR of approximately 16.8 18.5 Bcf for a proposed approximate 10,000-foot development scale well. The productivity of the wells, which flow tested the Mid-Velkerri B Shale at depths of more than 11,000 feet total vertical depth, exhibited higher flowing tubing pressures and EURs similar to the Marcellus Shale, thus continuing to validate our internal view that the core deeper areas of the Beetaloo will be more productive and validate further evaluation.
We have capitalized A$41.1 million of expenditures with respect to the exploration and development of EP 161. We anticipate spending an additional A$4.0 million on development of EP 161 for the remainder of the fiscal year.
A native title agreement for EP 161 exists in the form of a Co-Operation and Exploration Agreement for Exploration Permit EP(A)161, between Tamboran Resources Pty Ltd, the Native Title Parties, and NLC dated April 4, 2012 (EP 161 Exploration Agreement). Elements of the EP 161 Exploration Agreement include but are not limited to Native Title Parties consent for the underlying petroleum exploration permit application (EP(A)), and assignment and confidentiality provisions. Further elements of the EP 161 Exploration Agreement provide for exploration payments, environmental protection and rehabilitation, and Aboriginal employment, training and business opportunities. It does not authorize production. Further agreement with the Native Title Party will be required, but the EP 161 Exploration Agreement sets out a process for negotiation of a production agreement and a baseline agreement as to royalties and compensation for production.
92
Table of Contents
Daly Waters Royalty holds an ORRI of 2.3% of the petroleum produced from the land over which the EP 161 was originally granted.
EP 161 will remain in effect until at least March 20, 2026.
Exploration Permit 136 and 143; Exploration Permit Application 197
On July 25, 2020, we entered into the Share Exchange Agreement with Longview Petroleum LLC and Tamboran McArthur under which the Company, through its wholly owned subsidiary, acquired 100% of the issued share capital of Sweetpea from Longview. That transaction was completed on May 21, 2021 after receiving approval from our Predecessors shareholders and Ministerial approval. Sweetpea is the registered holder of 100% of the working interests in EPs 136 and 143, and has also applied for EP(A) 197 (Sweetpea Assets).
EP 136 lies adjacent to EP 161 in the core of the Beetaloo and based on seismic data has geology we believe is comparable to EP 161s successful T1V discovery well. EP 136 is comprised of approximately 1,600 square miles within a mostly rectangular shaped tract that spans north-south with the greatest extent approximately 100 miles and as much as 16 miles in width. EP 136 is 100% owned and operated by Tamboran. During 2023, Ensign rig 970 was mobilized to the M1V well pad in EP 136. The M1V well was spudded in mid-September 2022 and reached a total depth of 10,000 feet in early October 2023, in 18.3 days. Following the completion of logging, the M1V well was successfully cased and suspended to enable potential future re-entry and side track for multi-stage stimulation work. The Ensign 970 was rigged down and released in mid-December 2022.
EP 143 is an irregular block that is comprised of approximately 800 square miles that extends approximately 27 miles west to east and 34 miles north to south. Development of EP 143 is not the current focus of our development plan. Accordingly, we intend to expend only such capital as is required for the maintenance of the permit for future assessment. We will assess prospectivity of EP 143 to determine future development opportunities. EP 143 is 100% owned and operated by Tamboran.
EP(A) 197 adjoins a portion of the northern boundary of EP 143. The irregular rectangular block contains approximately 300 square miles. As with EP 143, the development of EP(A) 197 is not the current focus of our development plan. Our plans for EP(A) 197 consist of completing the acquisition of the EP, obtaining its grant and then maintenance of the permit for future assessment of petroleum resources. We have until October 31, 2025 to negotiate and receive the consent of the traditional Aboriginal owners of the land and progress agreements with the relevant land council representing the traditional Aboriginal owners, as required under the Aboriginal Land Rights (Northern Territory) Act 1976 (Cth), as described further in BusinessEnvironmental Matters and Regulation. Once we receive such consent for exploration then we can apply formally for the grant of an EP. Like EP 143, we will assess prospectivity of the EP(A) 197 to determine future development opportunities. EP(A)197 is 100% owned by Tamboran.
On July 23, 2020, as part of our acquisition of Sweetpea, we granted an ORRI equal to an undivided 8% of 8/8ths of all petroleum produced from EP 136, 143 and EP(A) 197 (and the land over which each of those permits was originally granted), the area of mutual interest (AMI) to Tom Dugan Family Limited Partnership, LLP, Territory Oil & Gas, LLC; and Malcolm John Gerrard (together the Bayless Group) and Longview (Bayless ORRIs). On July 23, 2020, Sweetpea, the Bayless Group and Longview entered into an ORRI Termination Agreement (Termination Agreement). Under the Termination Agreement, the Bayless Group and Longview granted Sweetpea three options to require the Bayless Group to progressively reduce the 8% ORRI as follows: (i) upon payment by Sweetpea of an Initial Option Fee of $732,025 and the issue of 3,095,475 fully paid shares in Tamboran by July 1, 2021, the 8% ORRI would reduce to a 4% ORRI (Initial Option); and (ii) upon payment by Sweetpea of an Additional Option Fee of $250,000 and: (A) $7,000,000 by July 1, 2023, the 4% ORRI would reduce to 2%; and (B) $7,000,000 by July 1, 2025, the 2% ORRI would reduce to a 1% ORRI. As of the date of this prospectus, the Additional Option Fee of $250,000 has been paid. However, the payments of $7,000,000 by July 1, 2023 and $7,000,000 by July 1, 2025 have not been made.
93
Table of Contents
On or around May 19, 2021, Sweetpea exercised the Initial Option and the 8% ORRI reduced to 4%. The reduction in the 8% ORRI was formalized by execution of certain Amendment Agreements dated May 19, 2021 by the Bayless Group and Sweetpea. On or around May 19, 2021, the Additional Option Fee was paid. Each of the Bayless ORRIs was coupled with the obligation relating to the AMI, to grant additional ORRIs where additional acreage is acquired by Sweetpea within the AMI (the AMI Obligation). The Company as purchaser of the Sweetpea Assets is required to assume the AMI Obligation. On July 23, 2020, the Bayless Group, Sweetpea and Longview entered into a Limited Waiver Agreement under which the Bayless Group and Longview granted to Sweetpea an option to purchase a Limited Waiver in respect to the AMI Obligation. The effect of the Limited Waiver was that, except where clause 3(c) of the Limited Waiver Agreement applies, no person will be obliged to comply with the AMI Obligation or require that any other person assume the AMI Obligation. Clause 3(c) of the Limited Waiver Agreement provides that the Limited Waiver will never apply for the benefit of a Longview Entity. A Longview Entity is defined to mean: (i) Longview; (ii) any entity in which Longview, David N. Siegel and Robert L. Telles individually collectively, directly or indirectly, hold or are the beneficial owns of 35% or more of the equity securities; or (iii) David N. Siegel or Robert L. Telles individually. On or around July 1, 2021, Sweetpea purchased the Limited Waiver and exercised its option to cancel the AMI Obligation.
Sweetpea has granted PetroHunter Energy Corporation (Petrohunter) an ORRI of 2% (Petrohunter ORRI) of the petroleum produced from the land over which the EP 136 and EP 143 were originally granted and EP(A) 197 was applied for. The Petrohunter ORRI contains an option for Sweetpea to reduce the royalty to 1% on payment of $1,000,000 to Petrohunter by June 17, 2023 and further extinguish by agreement the remaining 1% for an amount equal to 3% of the consideration paid by the Company for Sweetpea. As of the date of this prospectus no such payments have been made.
Sweetpea has granted an undivided 1% ORRI in favor of Jeffrey J Rooney as trustee of the Siegel Dynasty Trust of all petroleum produced from the Sweetpea Assets and the land subject to the Sweetpea Assets. The beneficiaries of the Siegel Dynasty Trust are Emily Siegel and Robert Siegel, who are the children of David N. Siegel, who is a director of Longview, a director of the Predecessor and a director nominee of the Company. The ORRI extends to all extensions or renewals of each Sweetpea Assets (as applicable) and to any production licenses or subsequent rights to produce petroleum, from those lands, that are granted or issued to Sweetpea, its successors or assignees.
Daly Waters Royalty holds an ORRI of 2.3% of the petroleum produced from the land over which the EP 136, 143, and EP(A) 197 was originally granted.
An EP renewal application to extend EP 136 for a further five years was submitted to the DITT on September 2023 and is pending approval The permit is deemed to continue in force until the Minister makes a determination on the renewal application. EP 143 will remain in effect until at least March 4, 2028.
Middle Arm Development
In early June 2023, we announced the NT Government awarded us exclusive use of over 170-hectares (approximately 420 acres) site for construction of an LNG export terminal within the MASD. The MASD acreage was allocated to us on an exclusive basis for twelve months, allowing us to progress a Concept Select engineering phase, which commenced in July 2023, and we expect will be completed in February 2024. We believe the associated infrastructure at MASD provides us the opportunity to initially export up to 6.6 Mtpa through our proposed NTLNG development. We intend to seek strategic partners in financing and developing the proposed NTLNG development.
In June 2023, we announced two non-binding MOUs with bp and Shell to each purchase up to 2.2 Mtpa over a 20-year period from the proposed NTLNG development.
94
Table of Contents
Our Business Plan
Our business plan consists of three distinct phases in the development of the Beetaloo. The focus of the first phase will be on the transition from exploration activities to the commercialization of our Beetaloo properties. In furtherance of that goal, we expect to drill and complete an additional six to 10 appraisal wells by the end of 2025. Based on our review of seismic data, well logs, rock core and production data from completed appraisal wells, we have already identified what we believe to be the most productive acreage and shale benches to target for our first stage wells. Beginning in 2026, subject to approval by the Minister responsible for the Petroleum Act, we plan to market the gas from the appraisal wells, which is expected to be modest, in the Northern Territory, with the goal of generating operating cash flow for further development. The Beetaloo is currently serviced by two open-access pipelines that are sized to accommodate the ~60 MMcf/d local market and also provide access to the deeper Australian East Coast market. We have early development agreements with APA Group, Australias largest gas infrastructure company by volume (ASX: APA) whereby APA has commenced preliminary work on a project to ultimately build, own, and operate a new ~20 mile pipeline to connect our appraisal wells to the existing gas transmission network through the AGP, subject to the terms of definitive development agreements. In parallel, Tamboran, through the Beetaloo Joint Venture, is aiming to sanction a 40 MMcf/d compression facility at Shenandoah South that would upgrade the raw gas to meet sales gas quality. We expect the compression facility, together with the associated wells and gathering infrastructure, to require approximately $350 million ($135 million net to Tamboran) in capital costs. Gas sales are expected to commence from our appraisal wells in the first quarter of 2026. Through the course of the completion of the additional six to 10 appraisal wells, we believe we can reduce costs through greater efficiency while simultaneously providing us sufficient data to confirm the estimated ultimate recovery (EUR) for wells drilled in the Beetaloo. Our development plan seeks to efficiently drill from pad wells, utilizing long laterals and modern completion techniques employed by U.S. onshore operators. We expect the cost structure and production profiles achieved with our appraisal wells to lead to a financial investment decision (FID) for an initial large scale drilling program in our second phase.
The second phase of our business plan involves building our drilling program to produce natural gas to supply the Australian East Coast and Northern Territory markets. We anticipate drilling as many as 100 to 200 wells during this second phase, which may commence as early as 2026, subject to the completion of certain third-party infrastructure projects. The current pipeline infrastructure, the AGP in the Northern Territory, can export ~50 MMcf/d northbound and ~50 MMcf/d to the East Coast. We have a set of early development agreements with APA whereby APA will commence work on a project to ultimately build, own, and operate a new approximately 1,000 mile pipeline to connect the Beetaloo to the main trunk line of the East Coast Gas Grid, subject to the terms of definitive development agreements. The new pipeline is anticipated to reduce the cost of transporting gas from the Northern Territory to the East Coast by up to 50%. We have non-binding letters of intent from six of Australias largest energy retailers to purchase natural gas from us, with an aggregate volume of 875 MMcf/d for a period of up to 10 to 15 years.
In the third phase of our business plan, following commercialization of the Beetaloo, we intend to drill additional wells with the intent to supply natural gas for export through the existing LNG plants in Darwin and our proposed 6.6 Mtpa NTLNG to South and East Asian markets. Depending on the quantum of ullage in the existing LNG plants in Darwin, this phase may occur before or in parallel with the second phase. In consideration of our proposed NTLNG project, the government of the Northern Territory of Australia has awarded us exclusive use of a 170-hectare (approximately 420 acres) site for a 12-month term (which commenced June 2023) for a construction study with respect to our proposed NTLNG project within the MASD. The MASD, an industrial complex adjacent to the city of Darwin, seeks to provide infrastructure focused on low emissions operations, for the export, processing, storage, shipping and rail transportation of LNG and other hydrocarbons. The MASD precinct is currently home to an export hub with two existing and operational LNG export terminals, the Darwin LNG terminal with a capacity of 3.7 Mtpa and the Ichthys LNG terminal with a capacity of 8.9 Mtpa. The Australian government has committed A$1.5 billion in investments commencing in 2025 to further develop MASD infrastructure and access, including dredging of the deepwater port, construction of road and rail access and distribution of electricity. We estimate total time required for construction of the NTLNG project to be
95
Table of Contents
between three to five years and have non-binding memoranda of understanding with each of bp and Shell for 20-year LNG purchase contracts. We could additionally sell our future production if, for example, our NTLNG project faces any delays, through the two existing and operational LNG terminals near Darwin. We intend to seek additional strategic partners for the financing and development of these and other infrastructure projects.
Our business and development plans include the continuous focus on reducing cost while increasing production efficiencies. We believe that importing U.S. unconventional drilling and completion techniques, best-practices and technology, together with the right personnel, will reduce the incremental cost to drill and complete each subsequent well. We currently have on contract one H&P FlexRig® until August 2025 with a 10-year option to contract for up to five additional rigs. The drilling and completion costs for our most recent SS1H and A3H wells are expected to be approximately $30.3 million on average per well. We estimate the drilling and completion costs of each of the remainder of our additional appraisal wells will be approximately $26 million as a result of our application of U.S. practices, longer lateral lengths and increased number of stimulated stages. We are targeting long-term development well costs of $16 million per well at depths of approximately 9,800 feet with 60 stages. We believe by taking advantage of efficiencies related to economies of scale, continued infrastructure development in the Beetaloo and resource maturation, over time we will significantly reduce the cost to drill and complete our wells.
Agreements Relating to the Development of our Assets
TB2 Joint Venture Agreement
We are a member of the TB2 Joint Venture that wholly owns Tamboran B2 (formerly known as Origin B2) (TB2 Joint Venture Operator). The TB2 Joint Venture is governed by a shareholders and joint venture agreement dated September 18, 2022, as amended on June 21, 2023 (the TB2 Joint Venture Agreement). Under the terms of the TB2 Joint Venture Agreement, both parties own an equal share of the TB2 Joint Venture. The TB2 Joint Venture is governed by a board with a maximum of six members, with the number of directors appointed by shareholders in respect of their proportion of equity ownership. The board currently consists of four board members; two designated by the Company (Joel Riddle and Faron Thibodeaux) and two designated by Daly Waters (Dan Ferreri and Richard Veitenheimer). Pursuant to the TB2 Joint Venture Agreement, the TB2 Joint Venture will not take any of the following actions without the affirmative consent of 75% or more of the total number of votes cast by directors present and entitled to vote at a duly convened meeting of the board:
| | entering into any partnership or joint venture; |
| | entering into any new borrowing facility in excess of $5 million; |
| | decisions to dispose of or vary the terms of a permit; |
| | decisions to proceed to development or production; and |
| | approval of any work program and budget. |
In addition, without the prior approval of shareholders holding 75% or more of the total number of votes cast by shareholders present and entitled to vote at a duly convened meeting of the shareholders, the TB2 Joint Venture will not take any of the following actions:
| | amendment of the constitution; |
| | loans or financial accommodations with shareholders; |
| | incurring liability under any guarantee or indemnity; |
| | issuing new shares or other securities not contemplated by the TB2 Joint Venture Agreement; |
| | changing the issued share capital; |
| | cessation of or material alteration of the scale of operations; |
| | disposal or encumbering of the shares in a subsidiary; |
96
Table of Contents
| | seeking an initial public offering on any securities exchange. |
Each shareholder of the TB2 Joint Venture will contribute working capital in proportion with their equity interest, provided that during the sole funding period Tamboran shall be solely responsible for funding the TB2 Joint Venture, including the cost to drill and multi-stage hydraulic fracture stimulate and flow-test the two appraisal wells for at least 60 days, in the manner agreed by the shareholders. Sole funding period means the period commencing on the effective date of the TB2 Joint Venture and ending on the date that the TB2 Joint Venture Operator has drilled the two appraisal wells referred to above and each well has been the subject of flow testing with production tubing installed for at least 60 days. A cash call was issued on October 25, 2023, for work following the sole funding period for contributions of $9.4 million. Following the sole funding period, each member shall fund its respective equity share of working capital costs, but in accordance with the cash call schedule described in any approved work plan. The sole funding period for the A2H and SS1H work programs, where Tamboran will fund 77.5% of the working interest, will be completed after the flow testing of the SS1H well for 60-days, which is expected to be finalized during the first quarter of 2024. Tamboran is funding its 38.75% interest in the A3H and future activities within EP 76, 98 and 117.
Tamboran is the initial manager of the TB2 Joint Venture with responsibility to carry out the day to day operations of the TB2 Joint Venture, including managing the activities of the TB2 Joint Venture Operator in operating the properties and complying with the Farmin Agreement. The manager shall also be responsible for submitting work plans and budgets with respect to the development of the properties by the TB2 Joint Venture Operator, in accordance with the terms of the joint operating agreement between the TB2 Joint Venture Operator and Falcon.
If at any time the TB2 Joint Venture Operator determines that a discovery may be a commercial discovery, the manager shall deliver to the board of the TB2 Joint Venture within 90 days of such determination a proposed development plan for approval in accordance with the requirements of the JV Agreement and the joint operating agreement.
Following the approval by the Board of the TB2 Joint Venture of a development plan, and upon notification by the manager of the TB2 Joint Venture that the TB2 Joint Venture will lodge an application for a production license over any permit area of the TB2 Joint Venture, Daly Waters may unilaterally choose to split equally (in terms of equity interest and operated blocks in respect of the specific area) the TB2 Joint Ventures interest in such permit so each of Tamboran and Daly Waters own an equal direct participating interest in ownership of such permits and will each operate their respective properties. Such split will be effected under a checkerboard strategy, which entails Daly Waters and Tamboran selecting in lots one of two parcels of land that are laid out in a pre-determined checkerboard pattern, such that Daly Waters and Tamboran are allocated an approximately equal amount of acreage or blocks. In the blocks chosen by Daly Waters, Daly Waters would have 77.5% working interest and operate such blocks. In the blocks chosen by Tamboran, Tamboran would have 77.5% working interest and operate such blocks. Daly Waters and Tamboran would have the ability to trade blocks or other working interest, or enter into operating agreements with respect to different blocks.
Following approval by the Board of the TB2 Joint Venture of a development plan, in certain events where there is a failure to implement the checkboard strategy, Tamboran will be required to pay Daly Waters compensation in the form of a cash payment or shares as follows. In the event that either (i) Ministerial approval has not been obtained for the transfer of the area covered by the blocks of acreage selected by Daly Waters, intended to be owned (to the extent of the TB2 Joint Venture ownership immediately prior to implementation of the Checkerboard Strategy) and operated in accordance with TB2 Joint Venture Agreement in relation to the Checkerboard Strategy (as defined therein) to Daly Waters, or (ii) the formation of a new joint venture in respect of any part or parts of a specific area within the permit area as approved by the operating committee pursuant to the Beetaloo JOA (as defined below) has not been approved and given effect to under the Beetaloo JOA by December 31, 2024, Tamboran shall pay Daly Waters a cash payment of $7.5 million or issue CDIs of the Predecessor to Daly Waters with a value of $15 million based on the weighted average price of the Predecessors CDIs on the ASX. At any time after the end of the sole funding period where the Checkerboard
97
Table of Contents
Strategy has not been implemented (but before December 31, 2026), Daly Waters may elect to have us buy-back or otherwise convert its interest in the TB2 Joint Venture into a direct participating interest.
Following the end of any fiscal year, provided profits are available for distribution, the TB2 Joint Venture must pay a dividend in respect of each of the TB2 Joint Venture members respective equity interest. The TB2 Joint Venture will distribute all profits, provided that profits may be retained to meet any capital adequacy or solvency requirements and is able to pay its debts as and when they fall due, or as required by applicable law or specified in an approved work plan.
We may not dispose of shares in the TB2 Joint Venture before the end of the sole funding period without the written consent of Daly Waters, which may be given or withheld in Daly Waters sole and absolute discretion. Each of the members of the TB2 Joint Venture will also have certain pre-emptive rights. Each member will have certain drag-along and tag-along rights with respect to transfers of interest in the TB2 Joint Venture.
Beetaloo Joint Venture Agreements
The TB2 Joint Venture Operator is a party to a Farmin Agreement with Falcon (the Farmin Agreement) pursuant to which the TB2 Joint Venture Operator owns a 77.5% operated working interest and Falcon owns a 22.5% non-operated working interest in EPs 76, 98, and 117. Under the terms of the Farmin Agreement, the TB2 Joint Venture Operator will undertake operations on the properties and bear the costs of the work program up to an overall cap of A$263.8 million, following which the parties shall contribute in respect of their proportionate interests in the TB2 Joint Venture.
The TB2 Joint Venture Operator is also a party to a joint operating agreement with Falcon (the Beetaloo JOA). The Beetaloo JOA establishes the respective rights and obligations of the TB2 Joint Venture Operator and Falcon in connection with EP 76, 98, and 117. The TB2 Joint Venture Operator is designated as the operator under the Beetaloo JOA.
McArthur Joint Venture Agreement
On December 11, 2012, we entered into a joint operating agreement (the McArthur JOA) with Santos QNT under which Santos serves as the operator of EP 161. The McArthur JOA applies to operations in EP 161, EP 162, EP 189, and EP(A) 299. The McArthur JOA will remain in effect as long as any of the permits remain in force in the names of two or more parties. Our current participating interest under the McArthur JOA is 25%. We must continue to contribute our proportionate share of expenditures to maintain our interest in the underlying permits. Before incurring any commitment or expenditure greater than A$2,000,000, Santos must receive approval from an operating committee consisting of a representative from each of Tamboran and Santos. We have committed approximately $3.3 million during the 2023 calendar year drilling program. We have committed approximately $2.6 million through March 2026 based on minimum work requirements.
Drilling Contract with Helmerich & Payne International Holdings, LLC
On September 9, 2022, we, through a wholly owned subsidiary, entered into a drilling contract with H&P (as amended, the Drilling Contract). The term of the Drilling Contract commenced on July 1, 2023. Under the Drilling Contract, and associated agreements, we granted H&P a 10-year preferential right to provide drilling services to us in connection with our exploration and production activities in Australia. We paid H&P a mobilization fee of $15,000 per day plus all associated costs for shipping from Houston, Texas to the first location being the SS1H well pad. The total import cost for Rig 469 was approximately $7.5 million. We will also pay an operating rate of $39,500 per day. The contract also provides for us to pay H&P a demobilization fee equal to the documented trucking and mobilization costs to a mutually-agreed location in Australia. Under the Drilling Contract we have an option to contract for up to five additional rigs. On July 31, 2023, we, through a wholly owned subsidiary, entered into a Rig Sharing and Temporary Assignment and Assumption Agreement with the wholly owned subsidiary of the TB2 Joint Venture to utilize the Drilling Contract for the purposes of drilling the Beetaloo Joint Ventures appraisal wells.
98
Table of Contents
APA Agreements
We entered into three agreements on December 15, 2023 with APA Group (collectively, the APA Agreements) to support the development of our Beetaloo assets and enable distribution of natural gas from our assets:
| | Under the APA Partnering Agreement, we agreed to work exclusively with APA Group on pipeline projects in the Beetaloo, and subject to conditions being met, we obtained an option to acquire up to 15% of any Beetaloo pipeline project in the lead up to a final investment decision. |
| | The Early Development Agreement Sturt Plateau Pipeline Project (the SPP EDA) progressed discussions relating to the construction of the Sturt Pipeline Project, a natural gas pipeline capable of transporting up to approximately 100 TJ/day (the SPP Pipeline Project) from a proposed raw gas processing plant located near Shenandoah South to the AGP and the potential provision of gas transportation services on the AGP to enable connection of the Shenandoah South to the AGP. The SPP EDA contemplates completion of the SPP Pipeline Project by March of 2026. The delivery of the SPP Pipeline Project will be the subject of a future development agreement and the gas transport services will be the subject of a future gas transportation agreement. APA Group has commenced the Early Works defined in the SPP EDA, which include efforts to design and engineer the SPP Pipeline Project, obtain access and approvals, along with developing revised project schedules and estimates. |
| | The Early Development Agreement Beetaloo to East Coast Pipeline (the BEC EDA) progressed discussions relating to the construction of a large natural gas pipeline (the BEC Pipeline Project) to connect a central point in our Beetaloo acreage to the Australian east coast network of gas pipelines owned or operated by the APA Group (East Coast Grid) and the provision of gas transportation services on the BEC Pipeline Project to enable connection of the Beetaloo to the East Coast Grid. The delivery of the BEC Pipeline Project will be the subject of a future development agreement and the gas transport services will be the subject of a future gas transportation agreement. APA Group has commenced the Early Works defined in the BEC EDA, which include certain efforts to obtain access and approvals, along with developing revised project schedules and estimates. |
Under the SPP EDA and BEC EDA, APA has agreed to continue development of the proposed pipelines with early works expenditure of up to A$10 million on the basis that we continue to progress and achieve agreed milestones.
Origin Retail Gas Sales Agreement
On September 18, 2022, the TB2 Joint Venture Operator entered into a Gas Sales Agreement (the Gas Sales Agreement) with Origin Energy Retail Pty Ltd (Origin Retail) whereby the TB2 Joint Venture Operator has agreed to supply, and Origin Retail has agreed to purchase up to 5.97 MMboe per annum (2.99 MMboe per annum net to Tamboran), gas sourced from EP 98, 76, or 117. The start date of the supply period under the Gas Sales Agreement must be between January 1, 2025 and December 31, 2028, and the end date is 10 years following the start date unless extended. Origin Retail is not obligated to perform under the Gas Sales Agreement until the TB2 Joint Venture Operator has satisfied certain conditions precedent.
Shell Letter of Intent
On June 23, 2023, we entered into a non-binding letter of intent with Shell, a subsidiary of Shell plc, regarding the potential purchase by Shell of up to 2.2 Mtpa of LNG from our proposed NTLNG project for a 20-year term. We intend to seek to enter into an exclusive LNG sale and purchase agreement (the Shell SPA). We plan to commence negotiations in January 2024, and hope to finalize the Shell SPA in 2025. The supply period under the Shell SPA would begin upon commercial production of LNG from the Beetaloo, which must begin by January 1, 2030, and effectiveness of the SPA is subject to final investment decision of the NTLNG project by our board of directors by December 31, 2025, technical and financial diligence by Shell and other customary conditions precedent.
99
Table of Contents
BP Memorandum of Understanding
On May 19, 2023, we entered into a non-binding memorandum of understanding with bp regarding the potential purchase by bp of up to 2.2 Mtpa of LNG from our proposed NTLNG project for a 20-year term. We intend to seek to enter into negotiations for an exclusive LNG sale and purchase agreement (the bp SPA) beginning three months prior to the expected completion of the front-end engineering design and finalize the bp SPA by approximately December 2025. The supply period under the bp SPA would begin upon commercial production of LNG from the Beetaloo, and effectiveness of the bp SPA is subject to final investment decision of the NTLNG project by our board of directors by approximately December 2025.
Other Letters of Intent
We have entered into non-binding letters of intent from six of Australias largest energy retailers to purchase natural gas from us, with an aggregate 875 MMcf/d for a period of up to 10 to 15 years. We expect to negotiate definitive agreements with these counterparties as our operations further progress.
Customers and Marketing
We plan to market our natural gas under long-term agreements. Our ability to market natural gas will depend on many factors beyond our control, including the extent of domestic production and imports of oil and natural gas, available storage, the proximity of our natural gas production to pipelines and corresponding markets, the available capacity in such pipelines, the demand for natural gas and oil, the effects of weather, and the effects of state and federal regulation. There is no assurance that we will always be able to market all of our production or obtain favorable prices.
Seasonality
Weather conditions have a significant impact on the demand for natural gas used for heating loads and natural gas-fired power generation. Demand for natural gas is generally at its lowest during the spring and fall months and peaks during the summer and winter months. Demand in the winter season peaks due to residential and commercial heating load demand, while the summer season peaks due to cooling loads, which calls on increased natural gas fired power generation loads. However, seasonal anomalies such as warmer than normal winters or cooler than normal summers can lessen the magnitude of the seasonal fluctuations in demand. In addition, natural gas storage facilities are utilized to bring additional supply to the market that is utilized to meet peak demand levels during both winter and summer seasons. The Northern Territory also typically experiences greater rainfall from November to April. Although this season does present challenging conditions for operations, operators have drilled, stimulated and tested through the wet season successfully.
Competition
The oil and natural gas industry is intensely competitive, and we compete globally with other companies that have greater resources. Many of these companies not only explore for and produce natural gas, but also carry on midstream and refining operations and market petroleum and other products on a regional, national or worldwide basis. These companies may be able to pay more for productive oil and natural gas properties or to define, evaluate, bid for and purchase a greater number of properties and prospects than our financial or human resources permit. In addition, these companies may have a greater ability to continue exploration activities during periods of low natural gas market prices. Our ability to acquire additional properties and to discover reserves in the future will be dependent upon our ability to evaluate and select suitable properties and to consummate transactions in a highly competitive environment. In addition, because we have fewer financial and human resources than many companies in our industry, we may be at a disadvantage in evaluating and bidding for oil and natural gas properties.
There is also competition between natural gas producers and other industries producing energy and fuel, including coal, other petroleum products and renewables. Furthermore, competitive conditions may be
100
Table of Contents
substantially affected by various forms of energy legislation and/or regulation considered from time to time by the government of Australia. It is not possible to predict the nature of any such legislation or regulation which may ultimately be adopted or its effects upon our future operations. Such laws and regulations may substantially increase the costs of developing natural gas and may prevent or delay the commencement or continuation of a given operation. Our larger or more integrated competitors may be able to absorb the burden of existing, and any changes to, federal, state and local laws and regulations more easily than we can, which would adversely affect our competitive position.
Human Capital Resources
As of June 30, 2023, we had a total of 30 employees. We hire independent contractors on an as needed basis. We believe we have good relations with our employees. We and our employees are not members of any labor union. We prioritize local hiring for both employees and contractors, particularly in areas of field operations, to support employment opportunities in our local communities.
Safety and training
Safety is our highest priority, including the prevention of any releases from our operations. We conduct routine maintenance and inspections at our facilities, and we have established practices and operational infrastructure to control and mitigate potential spills or discharges. We also provide training to our staff and contractors that cover spill response and reporting and ensure our teams are fully trained on our response plan in the event of any releases. We believe these measures continue to strengthen our process safety culture. We have a full-time Senior Manager of Health, Safety and Environmental who is responsible for training, evaluation and risk mitigation as well as implementing safety measures.
Compensation and Benefits
We recognize that our employees are our most valuable resource and that we must provide competitive compensation to ensure we attract and retain top talent. We believe we offer competitive and comprehensive compensation and benefits packages that includes access to financial, health and wellness programs, a matched 401(k) plan, short-term and long-term incentive plans, medical, dental, and vision insurance coverage, and paid time off for holidays, sick leave, and vacation. We continue to survey and update our pay structure to stay competitive with our peers. Our compensation packages are reviewed annually by NFPCC Compensation Consulting, a leading independent global compensation consultant.
Sustainability and ESG
Sustainability is a central component of our ESG corporate strategy, including continued focus on the Companys impact on the environment, and relationships with Traditional Owners, key stakeholders and employees. As an energy company with assets in the pre-development stage, we have the opportunity to integrate environment, community and social matters into the center of what the Company delivers. By focusing on the sustainable development of our Beetaloo natural gas project, we aim to grow local jobs, strengthen communities and deliver a positive social impact. We are committed to respecting the unique environment in the Northern Territory and working closely with the local communities to understand their diverse views on development and the impact on the environment. To highlight the importance of Sustainability and ESG, the Company has a Six-Pillar Sustainability Plan, which include: (i) Community: Partnering with local and host communities to share value through the creation of local jobs and business opportunities; (ii) Climate Change: Playing an effective role in the transition to a lower carbon economy through the production of low CO2 natural gas resources (primarily through committing to net zero equity Scope 1 and Scope 2 emissions and integrating renewable energy and carbon offsets into any development); (iii) Environment: Applying technologies to minimize environmental impacts; (iv) Health and Safety: Prioritizing the health and safety of people; (v) People: Aiming to attract, develop and retain a diverse, inclusive, and competent workforce; and (vi) Economic
101
Table of Contents
Sustainability: Generating economic growth and value for investors, employees, customers and communities. Under the Safeguard Mechanism (legislation.gov.au) provides regulations that shale gas facilities will have a zero baseline meaning they must have Net Zero Scope 1 emissions by law.
Environmental Matters and Regulation
We are, and our future operations will be, subject to various stringent and complex international, foreign, federal, state and local environmental, health and safety laws and regulations governing matters including the emission and discharge of pollutants into the ground, air or water; the generation, storage, handling, use and transportation of regulated materials; and the health and safety of our employees. These laws and regulations may, among other things:
| | require the acquisition of various approvals and permits before drilling or other regulated activities commence; |
| | enjoin some or all of the operations of facilities deemed not in compliance with permits or approvals; |
| | restrict the types, quantities and concentration of various substances that can be released into the environment in connection with natural gas drilling, production and transportation activities; |
| | limit or prohibit drilling activities in certain locations lying within protected or otherwise sensitive areas; and |
| | require remedial measures to mitigate pollution from our operations. |
These laws and regulations may also restrict the rate of natural gas production below the rate that would otherwise be possible. Compliance with these laws can be costly; the regulatory burden on the natural gas industry increases the cost of doing business in the industry and consequently affects profitability.
Moreover, public interest in climate change and the protection of the environment has increased in recent years. Drilling in some areas has been opposed by activists, including environmental groups, and, in some cases, been restricted. Our operations could be adversely affected to the extent laws are enacted or other governmental action is taken that prohibits or restricts offshore drilling or imposes environmental requirements that result in increased costs to the natural gas industry in general, such as more stringent or costly waste handling, disposal or cleanup requirements.
Regulatory framework
The following is a summary of the more significant existing onshore gas laws, as amended from time to time, to which our business operations are or may be subject and for which compliance may have a material adverse impact on our capital expenditures, results of operations or financial position.
Many of these laws require us to obtain permits or other authorizations from state and/or federal agencies before initiating exploration, certain drilling, construction, production, operation, or other natural gas activities, and to maintain these permits and compliance with their requirements for on-going operations. These permits are generally subject to protest, appeal, or litigation, which can in certain cases delay or halt projects and cease production or operation of wells, pipelines, and other operations.
Regulation of our exploration activities
The Petroleum Act requires Tamboran to hold EPs in all areas where its exploration activities are proposed. The Petroleum Act is the principal legislation dealing with petroleum exploration and production activities onshore and in the territorial waters of the Northern Territory (NT). In particular, the Petroleum Act provides the legal framework for: (i) the grant of permits for exploration, production, and ancillary activities associated
102
Table of Contents
with exploiting petroleum, (ii) the renewal or transfer of those permits, (iii) the promotion of active exploration for petroleum, and (iv) the appraisal of discoveries and of the development of petroleum production if commercially viable by persons granted production licenses. Further, the Petroleum Act provides for the assessment of proposed technical works programs for the exploration, appraisal, recovery or production of petroleum, including an assessment of the financial capacity of persons proposing to carry out those programs. The Petroleum Act provides for Ministerial directions regarding resource management, approval of activity and infrastructure plans before production, audit activities by regulators, and includes a financial assurance framework that encompasses environmental securities, monitoring and compliance levies and an orphan well levy.
The objectives of the Petroleum Regulations 2020 (NT) (Petroleum Regulations) are to provide for land access agreements between interest holders and the owners or occupiers of land covered by petroleum interests, to support and enhance the integrity of onshore petroleum wells, petroleum surface infrastructure by ensuring that risks are reduced to as low as reasonably practicable, and the strategic management of petroleum production. In accordance with the Petroleum Regulations, Tamboran is required to enter into land access agreements with the owners or occupiers of the land on which it conducts its activities before it conducts regulated operations. The Petroleum Regulations govern the minimum conditions of entry into these access arrangements with the owners or occupiers. The Petroleum Regulations also prescribe the fees Tamboran must pay relating to the general administration of its petroleum titles, including fees for the grant, renewal and variation of EPs, retention licenses and production licenses.
The object of the Petroleum (Environment) Regulations 2016 (NT) (Petroleum Environment Regulations) is to ensure that regulated activities are carried out in a manner that is consistent with the principles of ecologically sustainable development, and by which the environmental impacts and risks of the activities will be reduced to a level that is as low as reasonably practicable and acceptable. The Petroleum Environment Regulations require the preparation of environment management plans for regulated activities and mandates such plans be approved by the Minister. Tamboran, as the permit holder, has environment management plans (EMP) in place in respect of all its regulated activities. These activities include conducting seismic surveys, the construction, operation, modification, decommissioning, dismantling or removal of a wells or other facilities, drilling, hydraulic fracturing, the release of contaminants or waste, and the storage and transportation of petroleum and hazardous waste. Tamborans EMPs are publicly available on the NT Government Department of Environment, Parks and Water Security website www.depws.nt.gov.au/EMPs. The EMPs describe how our regulated activities might impact the environment in which the activity occurs and establishes Tamborans obligations to ensure those impacts are managed to an environmentally acceptable level. Civil and criminal penalties apply under the Petroleum Environment Regulations for conduct which results in a contravention of an EMP, as well as for undertaking regulated activity for which there is no approved EMP.
The Petroleum Environment Regulations contain record-keeping and reporting requirements. Specifically in relation to our hydraulic fracturing activities, Tamboran is required to provide the Minister with a report about flowback fluid within 6 months of the flowback occurring. This report must contain a full human health risk assessment relating to any chemical found in the flowback fluid or water produced. Reporting is also required for incidents arising from regulated activities that have or have the potential to cause material environmental harm. Failure to comply with these reporting requirements may result in significant financial penalties.
The Code of Practice: Onshore Petroleum Activities in the NT (the Code of Practice) provides minimum standards that the onshore petroleum industry in the Northern Territory must adhere to. The Code of Practice applies to all of Tamborans regulated activities including those associated with both unconventional gas and exploration, appraisal and production activities. Tamborans Well Drilling, Hydraulic Fracture Stimulation and Well Testing EMPs must demonstrate compliance with the Code of Practice and will not be approved or renewed if they are not compliant with the requirements of the Code of Practice.
The Petroleum Royalty Act 2023 (NT) (Royalty Act) imposes a royalty rate, paid to the NT Government, for petroleum produced from a project area of 10% of the gross value of the petroleum at the well head
103
Table of Contents
(including petroleum produced from a production project area that is used or lost through venting or flaring or other means, but excluding petroleum used by the licensee for incidental purposes, petroleum used in the project area for processing or compression, or preparing petroleum for sale, petroleum returned or reinjected into a natural reservoir in the project area from which it was extracted/recovered, and petroleum produced from an exploration project area that is used or lost through venting or flaring or other means). Petroleum means a naturally occurring hydrocarbon, whether in gaseous, liquid or solid state. See Royalty Under the Petroleum Royalty Act.
As onshore gas extraction moves toward production in the Northern Territory, there could be an increased risk of litigation in the form of challenges to Ministerial approvals of EMP, which could lead to costs and delays with respect to regulated activities. The failure to comply with record-keeping and reporting requirements of the Petroleum Environment Regulations can also attract financial penalties. Tamborans competitors in the Northern Territory are subject to the same risks and requirements that affect Tamborans operations.
Regulation of GHG Emissions
The National Greenhouse and Energy Reporting Act 2007 (Cth) (NGER Act) establishes the legislative framework for reporting greenhouse gas emissions, greenhouse gas projects and energy consumption and production by corporations in Australia. The objects of the NGER Act are to introduce a single national reporting framework for the reporting and dissemination of information related to greenhouse gas emissions, greenhouse gas projects, energy consumption and energy production of corporations and to contribute to the achievement of Australias greenhouse gas emissions reduction targets. Under the NGER Act, Tamboran will report Scope 1 GHG emissions from its operations to the Australian Governments Clean Energy Regulator (CER). Furthermore, the Safeguard Mechanism, a legislative instrument sitting under the NGER Act, is designed to reduce emissions from large industrial facilities. It sets legislated limits, known as baselines, on the greenhouse gas emissions of certain facilities. The Safeguard Mechanism applies to industrial facilities emitting more than 100,000 tons of CO2e per year and requires that all emissions form the Beetaloo be offset with Australian Carbon Credit Units or Safeguard Mechanism Credits once the 100,000 tons CO2-e trigger is exceeded.
The Safeguard Mechanism requires that all Beetaloo facilities covered by the Safeguard Mechanism have Net Zero Scope 1 emissions. Accordingly, the Safeguard Mechanism will apply to Tamboran. Tamborans ability to achieve Net Zero Scope 1 emissions will depend on it being able to economically manage its carbon emissions, which could, for example, be impacted by availability of future revenues to fund various carbon initiatives, market pricing of carbon offsets, technological developments affecting operations and costs of implementing sustainable practices. Under the Safeguard Mechanism, upon exceeding the 100,000 tons CO2-e trigger in a given financial year, all Scope 1 emissions in that financial year are required to be offset. The Australian federal government has established an A$75 carbon offset price cap for FY24. The offset price cap increases by CPI plus 2% each year. While we are unable to predict the future costs or impact of compliance with the Safeguard Mechanism, we do have established procedures for the ongoing evaluation of our operations to identify costs, potential exposures and to track compliance with this legislation.
On April 17, 2018, the NT Government announced that it accepted all 135 of the recommendations set out in The Scientific Inquiry into Hydraulic Fracturing in the Northern Territory. The implementation of the recommendations has resulted in a more rigorous regulatory regime by placing additional obligations on oil and gas companies including the introduction of a stricter code of practice for decommissioning onshore shale gas wells, requiring tenement holders to provide a non-refundable levy prior to granting any further production approvals and introducing no go zones where a person cannot explore or drill for petroleum resources.
Although it is not possible at this time to predict how new laws or regulations in Australia that may be adopted or issued to address GHG emissions would impact our business, any such future laws, regulations or legal requirements imposing reporting or permitting obligations on, or limiting emissions of GHGs from, our equipment and operations could require us to incur costs to comply with new requirements and to reduce
104
Table of Contents
emissions of GHGs associated with our operations as well as delays or restrictions in our ability to permit GHG emissions from new or modified sources. In addition, substantial limitations on GHG emissions could adversely affect demand for natural gas we aim to produce.
Regulation of Environmental and Occupational Safety and Health Matters
Our operations are subject to stringent Federal Government and territory laws and regulations governing occupational safety and health aspects of our operations, the discharge of materials into the environment and the protection of the environment and natural resources (including threatened and endangered species and their habitat). Numerous governmental departments have the power to enforce compliance with these laws and regulations and the permits issued under them, often requiring difficult and costly actions.
These laws and regulations may, among other things (i) require the acquisition of permits to conduct drilling and other regulated activities; (ii) restrict the types, quantities and concentration of various substances that can be released into the environment or injected into formations in connection natural gas drilling and production activities; (iii) limit or prohibit drilling activities on certain lands lying within wilderness, wetlands and other protected areas; (iv) require remedial measures to mitigate pollution from former and on-going operations, such as specific waste removal requirements; (v) apply specific health and safety criteria addressing worker protection; and (vi) impose substantial liabilities for pollution resulting from drilling and other regulated activities. Any failure to comply with these laws and regulations may result in the assessment of administrative, civil and criminal penalties, the imposition of corrective or remedial obligations, the occurrence of delays or restrictions in permitting or performance of projects, and the issuance of orders enjoining performance of some or all of our operations.
These laws and regulations may also restrict the rate of natural gas production below the rate that would otherwise be possible. The regulatory burden on the natural gas industry increases the cost of doing business in the industry and consequently affects profitability. The trend in environmental regulation has been to place more restrictions and limitations on activities that may affect the environment, and thus any changes in environmental laws and regulations or re-interpretation of enforcement policies that result in more stringent and costly well drilling, construction, completion or water management activities, or waste handling, storage transport, disposal, or remediation requirements could have a material adverse effect on our financial position and results of operations. We may be unable to pass on such increased compliance costs to our customers once we commence production. Moreover, accidental releases or leaks may occur in the course of our operations, and we cannot assure you that we will not incur significant costs and liabilities as a result of such releases or spills, including any third-party claims for damage to property, natural resources or persons. The cost of continued compliance with existing requirements is not expected to materially affect us. However, there is no assurance that compliance costs will remain the same in the future for such existing or any new laws and regulations or that costs related to such future compliance will not have a material adverse effect on our business and operating results.
The following is a summary of the more significant existing and proposed environmental and occupational safety and health laws, as amended from time to time, to which our business operations are or may be subject and for which compliance may have a material adverse impact on our capital expenditures, results of operations or financial position.
Any of our activities which have the potential to cause a significant impact to the environment are required to be referred to the NT Environmental Protection Authority (EPA) for assessment under the Environmental Protection Act 2019 (NT) (Environment Protection Act). Tamboran has completed a self-assessment for its current environmental impact and considers its potential environmental impact to not be significant. However, it is anticipated that future developments by Tamboran could trigger a referral to, and assessment by, the EPA, and require Tamboran to obtain approvals under the Environmental Protection Act to conduct the activity (an Environmental Approval). Civil proceedings could be brought by any person who is affected by an alleged act or omission that contravenes the Environment Protection Act. Contraventions of an Environmental Approval can
105
Table of Contents
attract penalties currently ranging from $67,760 to $3,386,240. Contravention can also result in revocation of the Environmental Approval.
The Environment Protection Legislation Amendment Bill 2023 (NT) (EPLAB), assented to on December 6, 2023, amends the Environment Protection Legislation Amendment (Chain of Responsibility) Act 2022 (NT) (CoR Act) to extend chain of responsibility provisions of the CoR Act. Although the CoR Act has been assented to, its provisions have not yet commenced, but are expected to do so on July 1, 2024. The CoR Act, once commenced, amends the Environment Protection Act to introduce environmental chain of responsibility provisions. Environmental chain of responsibility laws are a regulatory approach that has been developed to protect the Australian government and taxpayers from inheriting financial liabilities that arise when Environmental Approval holders for petroleum activities contravene statutory compliance obligations, such as the costs associated with cleaning up environmental damage, by redirecting liability to a related person with a relevant connection who may not have otherwise been liable (depending on the circumstances, such as directors, shareholders and associated entities). Under the CoR Act, a petroleum activity is an activity for which an EP, retention license or production license is required. Once the provisions of the CoR Act (as amended by the EPLAB) commence, Department of Environment Parks, Water Security could issue a compliance notice to any related person with a relevant connection to an entity conducting a petroleum activity. For corporations, contraventions of a relevant notice can attract a fine of between A$67,760 and A$3,386,240 (based on current penalty unit amounts) depending on the intentions and recklessness in contravening the notice and the severity of harm to the environment caused by failure to comply.
The Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999 (Cth) (EPBC Act) is Australias primary federal environmental legislation, which provides for the protection and conservation of matters of national environment significance (MNES) and heritage. This includes the protection and management of national and internationally important plants, animals, habitats and places. The objects of the EPBC Act are to promote ecologically sustainable development through the conservation and ecologically sustainable use of natural resources, the conservation of biodiversity and co-operative approach to the protection and management of the environment involving governments, the community, landholders, and Indigenous peoples. Any person who proposes to take an action which involves a coal seam gas development or a large coal mining development that will have, or is likely to have, a significant impact on a water resource is required to submit a referral to the Australian Government Department of the Environment for a decision by the Minister on whether assessment and approval is required for that action under the EPBC Act. We have completed self-assessments as part of certain EMP applications to determine whether a MNES is likely to be impacted by the proposed activities and concluded that significant impacts to water resources and other MNES are not anticipated to occur. However, it is anticipated that any future development could require referral and assessment under the EPBC Act.
The Water Act 1992 (NT) (Water Act) controls and licenses the taking of groundwater for petroleum operations and the disposal of hydraulic fracturing waste. Specifically, the Water Act provides for the investigation, allocation, use, control, protection, management and administration of water resources in the Northern Territory and imposes restrictions and strict controls with respect to the discharge of pollutants, including spills and leaks of hazardous substances. The Water Act requires Tamboran to obtain permits to extract groundwater for petroleum operations and controls the contact of hydraulic fracturing waste with water that is not contained in the geologic formation target by the process of hydraulic fracturing. It also prohibits taking surface water and releasing wastewater into surface water. Tamboran has obtained a Water Extraction License WEL GRF 10285 (175 ML/year) (WEL) and Sweetpea Petroleum also has a Water Extraction License WEL GRF 10346 (299 ML/year) covering previous water usage for exploration activities over specific parcels of land in the Northern Territory. WELs are renewed periodically to support operational activities. The WEL will be increased to cover the future proposed exploration activities.
The Waste Management and Pollution Control Act 1998 (NT) (Waste Management Act) governs the management of waste and pollution prevention and control practices for related purposes. Tamboran is required to store, transport and dispose of waste in compliance with the requirements of the Waste Management Act. For
106
Table of Contents
instance, the transportation and disposal of waste may only be completed by a licensed contractor and at a licensed disposal facility. Any interstate disposal should be completed with an approved consignment authority. The Waste Management Act does not apply in relation to a contaminant or waste that results from, directly or indirectly, the carrying out of a petroleum exploration activity or petroleum extraction activity by a person on land on which the activity is authorized under the Petroleum Act, and where that contaminant or waste is confined within the land on which the activity is being carried out. Where any contaminant or waste is not confined within the land on which the activity is being carried out, the Waste Management Act imposes certain duties on Tamboran to take all measures that are reasonable and practicable to prevent or minimize pollution or environmental harm and reduce the amount of the waste, if it conducts an activity or performs an action that causes or is likely to cause pollution resulting in environmental harm or that generates or is likely to generate waste. We currently own, lease, or operate numerous properties that have been used for natural gas exploration for many years. Although we believe that we have utilized operating and waste disposal practices that were standard in the industry at the time, hazardous substances, waste, or petroleum hydrocarbons may have been released on, under, or from, the properties owned or leased by us, or on, under, or from, other locations, including offsite locations, where such substances have been taken for treatment or disposal. In addition, some of our properties have been operated by third parties or by previous owners or operators whose treatment and disposal of hazardous substances, waste, or petroleum hydrocarbons were not under our control. These properties and the substances disposed or released on, under or from them may be subject to the Environmental Protection Act and analogous laws. Under such laws, we could be required to undertake corrective measures, which could include removal of previously disposed substances and waste, cleanup of contaminated property, or performance of remedial plugging or pit closure operations to prevent future contamination, the costs of which could be substantial.
The Work Health and Safety (National Uniform Legislation) Act (NT) 2011 (WHS Act) seeks to secure the health and safety of workers and workplaces imposing general duty of care obligations, seeking the elimination or minimization of risks arising from work or from specified types of substances or plant, providing for workplace representation and consultation in relation to work health and safety, encouraging organizations to take a constructive role in work health and safety practices, promoting the provision of advice and training and providing for compliance and enforcement measures. Tamboran has a Safety Management Plan that outlines how it achieves the requirements of the WHS in relation to its activities. This includes the management of chemical storage dossiers, safety data sheets and appropriate procedures and controls to prevent worker exposure to hazards.
The Bushfires Management Act 2016 (Bushfires Management Act), amongst other things, establishes bushfire fuel management programs and prohibits certain activities during high fire risk periods to prevent the outbreak and spread of bush fires. During total fire ban periods, Tamboran is prohibited from undertaking flaring and is required to obtain a permit for flaring to take place during declared fire danger periods. This could lead to costs and delays with respect to Tamborans regulated activities. In accordance with the Code of Practice: Onshore Petroleum Activities in the NT, Tamboran is required to maintain a Bushfires Management Plan which includes bushfire preventative and response measures.
The Northern Territory Aboriginal Sacred Sites Act 1989 (NT) (Sacred Sites Act) establishes a procedure for the protection and registration of Aboriginal sacred sites, provides for entry onto sacred sites and the conditions to which such entry is subject, and establishes a procedure for the avoidance of sacred sites in the development and use of land. The Sacred Sites Act establishes the Aboriginal Areas Protection Authority (AAPA) for the purposes of administering the Sacred Sites Act and a procedure for the review of decisions of the AAPA by the Minister. Tamboran conducts detailed sacred sites assessments with traditional owners prior to conducting any activities and applies to the APPA for Authority Certificates. These assessments are typically designed to identify sacred places, such as dreaming tracks, song lines, and womens business places, that must be protected. The location of sacred sites are indicated on maps and Tamboran may not conduct activities that could disturb sacred sites without first obtaining clearance and authorization from the traditional owners. An Authority Certificate can be issued by the APPA under the Sacred Sites Act where it is satisfied that in relation to an application, the work or use of the land could proceed or be made without there being a substantive risk of
107
Table of Contents
damage to or interference with a sacred site on or in the vicinity of the land, or an agreement has been reached between the custodians and the applicant. Subject to the conditions (if any) of the Authority Certificate, the holder of the Authority Certificate may enter and remain on that or those parts of the land and carry out the work proposed in the application. Due to long distance direction drilling giving flexibility as to drilling pad locations, we consider that the presence of sacred sites should not interfere with future production.
The Heritage Act 2011 (NT) (Heritage Act) provides for the conservation of the Northern Territorys cultural and natural heritage. Specifically, the Heritage Act provides for the protection of Aboriginal, European and Macassan archaeological places and archaeological objects. Any interference with an archaeological place or object is strictly regulated under the Heritage Act.
The Native Title Act 1993 (Cth) (Native Title Act) recognizes and protects native title by providing that native title cannot be extinguished contrary to the Native Title Act. The objects of the Native Title Act are to provide for the recognition and protection of native title, establish ways in which future dealings affecting native title may proceed and to set standards for those dealings and mechanisms for determining claims to native title and to provide for, or permit, the validation of past acts, and intermediate period acts, invalidated because of the existence of native title. The Right to Negotiate with Native Title Owners are the most relevant provisions of the Native Title Act to Tamborans operations. The Right to Negotiate process was applied to the grant of Tamborans explorations permits, resulting in Section 31 Agreements which provide for the consent of traditional owners for its activities. The traditional owners are and continue to be represented by the Native Land Council (NLC) in respect of the Agreements. Tamboran continues to implement EPs in collaboration with the NLC, with all work programs being reviewed and approved by traditional owners.
Aboriginal Land Rights (Northern Territory) Act 1976 (Cth) (ALRA) applies to the Northern Territory and provides for the grant of certain land as Aboriginal land and the protection of sacred sites. Under ALRA the exploration for, and production of, petroleum on Aboriginal land is subject to a regime of consent being required by traditional Aboriginal owners of the land and subject to agreements being entered into with the relevant land council representing the traditional Aboriginal owners.
Compliance with the above regulations and their requirements has the potential to delay the development of natural gas projects and increase our costs of development and production, which costs could be significant. In addition, our failure to comply with any of the regulatory obligations could subject us to monetary penalties, injunctions, conditions or restrictions on operations and criminal enforcement actions.
Other Facilities
Our corporate headquarters are located at Suite 01, Level 39, Tower One, International Towers Sydney, 100 Barangaroo Avenue, Barangaroo NSW 2000, and our telephone number at such address is +61 (2) 8330-6626. Our corporate headquarters and field office facilities are leased, and we believe that they are adequate for our current needs.
Operating Hazards and Insurance
Natural gas operations are subject to many risks, including well blowouts, craterings, explosions, uncontrollable flows of oil, natural gas or well fluids, fires, pipe, casing or cement failures, abnormal pressure, pipeline leaks, ruptures or spills, vandalism, pollution, releases of toxic gases, adverse weather conditions or natural disasters and other environmental hazards and risks.
In accordance with industry practice, we maintain insurance against some, but not all, of the operating risks to which our business is exposed. We cannot provide assurance that any insurance we obtain will be adequate to cover our losses or liabilities. We have elected to self-insure for certain items for which we have determined that the cost of available insurance is excessive relative to the risks presented. In addition, certain pollution and environmental risks are not fully insurable. The occurrence of an event not fully covered by insurance could have a material adverse effect on our financial position, results of operations and future cash flows.
108
Table of Contents
Title to Properties
Under the Petroleum Act, all petroleum on or below the surface of land within the Northern Territory is and shall be deemed always to have been the property of the Crown (as described in the Petroleum Act). The property in petroleum produced from a well on an area to which a petroleum interest relates passes to the interest holder at the wellhead (and a royalty is payable by the interest holder to the Crown). Petroleum interests under the Petroleum Act primarily take the following forms Exploration Permits, Retention Licenses and Production Licenses.
Exploration Permits
Rights to conduct natural gas exploration within the Northern Territory are based on EPs. An EP grants the holder the exclusive right to explore for petroleum and to carry on such operations and execute such works as are necessary for that purpose, in the exploration permit area. This includes the rights to carry out the technical works program and other exploration for petroleum in the exploration permit area. Activities under an EP are subject to any conditions imposed on the permit by the Minister.
During the EP(A) phase, the permit holder consults with government authorities and the appropriate native title holders for the area (if there is native title land) and/or traditional owners (where the land is Aboriginal Land) in a negotiation process that determines the terms upon which the native title holders will consent to the grant of the license, including the amount of financial compensation that the permit holder will provide to the native title holders/traditional owners during the exploration period. The negotiations over Aboriginal Land are facilitated by the government regulatory body, in this case the Northern Land Council, who is responsible for assisting Aboriginal People in the Northern Territory to manage their traditional lands. After agreement is reached, which often takes between 3-5 years, the permit holder provides a work program and may receive an EP under which the permit holder has three five-year periods in which to meet or amend its obligations proposed under the EP.
The Petroleum Act requires an EP holder to notify the Minister as soon as possible of a discovery of petroleum within a permit area and within three days provide the particulars of the discovery. Upon discovery of a commercially exploitable petroleum discovery, the permit holder will enter into further discussions with local native title holders (if native title land) (including traditional owners) to enter to into an agreement which satisfies the requirements of the Native Title Act that, among other things, determines the royalty payments to the local traditional owners. Where the Minister is satisfied that the petroleum resources are potentially of a commercial quality and quantity, a permit holder is entitled to apply for either: (a) a production license, in relation to the whole or part of its EP if the discovery is an accumulation of petroleum that is commercially able to be immediately exploited; or (b) one or more retention licenses.
Production Licenses
An EP holder is entitled to apply for a production license if a commercially exploitable petroleum discovery is made. An application for a production license is required to include certain information regarding the license area, a proposed technical works program for the proposed license area and evidence that the applicant has the appropriate technical and financial capability.
A production license under the Petroleum Act is a statutory right which constitutes personal property. A production license (or an interest in a production license) may be transferred with the approval of the Minister and is capable of being given as security for financial accommodation or other commitments. There are processes and limits related to the Ministers ability to terminate the production license before the expiry of its term due to a default of the production license holder and the production license cannot be compulsorily acquired by the Northern Territory or the Federal Government without the payment of just terms compensation to the license holder.
109
Table of Contents
A production license holder has exclusive rights to explore for petroleum, recover it from the license area, and to carry out such operations in the license area as are necessary for the exploration for, and recovery of, petroleum. The Minister may grant the production license subject to such conditions as the Minister deems appropriate and may direct the holder of a production license to maintain, increase or reduce the rate of recovery of petroleum from the area.
A production license may be granted for an initial term of 21 or 25 years and may be renewed.
Retention Licenses
A retention license grants the licensee the exclusive right to carry on in the license area such geological, geophysical, and geochemical programs and other operations and works, including appraisal drilling, as reasonably necessary to evaluate the potential of the petroleum believed to be present in the license area. Where the Minister has received an application for a retention license and is satisfied that the applicant has complied with the requirements of the Petroleum Act the Minister will decide whether to grant or refuse to grant the retention license.
The initial term of a retention license is five years and may be renewed for subsequent periods, subject to the Ministers approval.
Conditions of EPs granted under the Petroleum Act
An EP is granted subject to conditions that the EP holder must comply with, including meeting minimum work obligations and conducting all operations with reasonable diligence and in accordance with good oilfield practice and the approved technical work program. Each Instrument of Grant for each of EP 76, EP 98, EP 117, EP 136, EP 143 and EP 161 contains standard conditions, including as follows:
| | Condition 5 of each Instrument of Grant provides that the permittee shall indemnify and hold indemnified at all times the Territory and its servants and agents from claims, actions, suits and demands whether debt, damages, costs or otherwise arising out of a breach of the duties and obligations, whether express or implied, of the permittee at common law, or of the Claim or of any law in force in the Territory that is applicable and whether such breach shall be that of the permittee or any of its subcontractors, servants, employees or agents; |
| | Condition 10 of each Instrument of Grant allows the Minister to require, at any time, the title holder to provide security in the form and for the amount that the Minister thinks fit for the purpose of securing the title holders performance of its obligations under the relevant EP, to secure the permittees compliance with these permit conditions and/or for securing the payment by the permittee compensation that may be payable for the effect of the grant, renewal or variation of the permit on native title rights and interests; and |
| | each Instrument of Grant also provides that the title holder must not commence any seismic survey or drilling of a well unless the Minister is provided with the relevant details (including the geographic position of the well or area of the seismic survey) and the necessary approval has been obtained from the Minister. |
Variation, suspension or waiver of a condition of an EP
An EP holder may lodge an application for a variation, suspension or waiver of a condition of an EP. Under the guidelines Criteria for Assessment of Petroleum Exploration Permit Applications issued by the Department of Industry Tourism and Trade, an application to suspend, extend, waive or vary EP conditions is required to be submitted within three months prior to expiry of the current work program year. Generally, work programs cannot be reduced by a variation. All variations are subject to the discretion of the Minister and are considered on a case-by-case basis.
110
Table of Contents
An EP holder may apply to the Minister to suspend and extend the period for completing the permit holders work program commitments.
A suspension will defer the end date of a current permit year but will not change the end date of subsequent permit years. A suspension and extension will defer the end date of the current permit year and all subsequent permit years. Where a condition of an EP is suspended the Minister may extend the term of the permit by a period not exceeding the period of the suspension.
The terms of each of the EPs have previously been extended via applications to the Minister for suspension and extension of the dates for completion of the minimum work program obligations.
Ministerial approval in relation to dealings and transfers
Any instrument by which a legal or equitable interest in or affecting an existing or future EP is or may be created, assigned, affected or dealt with, whether directly or indirectly must be approved by the Minister and an entry made in the Public Register in order to be effective.
Statutory annual fees
An EP holder is required to pay an annual fee in relation to each EP. There are no outstanding annual fees payable in respect of the EPs.
Term and Renewals of the Exploration Permit
An EP remains in force for a five-year term commencing on the day on which it was granted or last renewed. An EP may be renewed for a maximum of two subsequent terms.
An application for renewal must, amongst other things, be in an approved form and manner and be accompanied by a report specifying the permittees restoration and rehabilitation plan of the land with respect to the blocks that may be affected by the permittees operations. The Minister will not accept an application for renewal of an EP if an application is received after expiry of the permit.
As part of the Ministers decision to renew an EP, the Minister may reduce the number of blocks in respect of which the permit is in force. If the Minister proposes to act in this way, the Minister must issue a notice to the permittee inviting the permittee to make a submission regarding the reduction (within the period specified in the notice). A title holder seeking a renewal can apply for an exemption, for a period not exceeding 12 months, from the requirement to reduce the number of blocks in a renewal application. An exemption may provide for: (a) a deferral of the reduction in the permit area; or (b) a reduction in the permit area by a lesser number of blocks.
The Minister may refuse to renew the permit where an EP holder has not complied with the Petroleum Act, any directions, or the conditions to which the EP is subject, or the Minister is not satisfied that circumstances exist to justify the renewal of the permit.
Surrender of a permit
A permittee may apply to surrender all or part of a permit area, subject to the requirements of the Petroleum Act. The Petroleum Act provides that an application for surrender of all or part of a permit area may not be made unless: (a) all operations carried on in the proposed surrender area have ceased; (b) all of the environmental outcome required under the Petroleum Act or another Act, including remediation and rehabilitation of land (including affected adjacent land), have been met; and (c) any approved environment management plan that applied in relation to the proposed surrender area ceases to be in force in relation to the proposed surrender area.
111
Table of Contents
The Minister may require that further conditions be complied with before accepting a surrender, or where the Minister is satisfied that the circumstances justify the acceptance of a surrender, accept a partial surrender where the retained area is not one discrete area, or is less than the minimum allowable size.
EP Conditions
Each EP is subject to minimum work obligations. Except for EP(A) 197, each EP contains specific minimum work obligations. The minimum work obligations for EP(A) 197 will be agreed between Sweetpea and the NT Government prior to grant of the EP. The minimum work obligations in respect of the EPs that need to be completed in the near future include:
| | EP 76: carrying out of formation evaluation of acquired data and integration of new core data into exploration models with estimated expenditure of A$250,000 to be completed by May 30, 2024; |
| | EP 98: drilling and hydraulic fracture stimulation of one horizontal exploration well to be completed by May 30, 2024 with estimated expenditure of A$20 million; |
| | EP 117: that between May 31, 2023 and May 30, 2025 the following work is completed with an estimated expenditure of A$30 million: (a) drilling one vertical (pilot) well and side-track one horizontal multistage fracture stimulated well; (b) formation evaluation of acquired data; and (c) further static and dynamic reservoir modelling; |
| | EP:136: renewal of this EP and confirmation of required minimum work obligations is pending following submission of an application to renew EP 136 dated September 28, 2023; |
| | EP 143: that between April 5, 2023 and April 4, 2024 the following work is completed with an estimated expenditure of A$400,000: (a) performing geological and geographical studies and integration of 2D seismic data; (b) assessing commercialization opportunities; (c) conducting desktop baseline environmental assessments; (d) preparing and commencing negotiations of land access; (e) designing and planning for 125km of 2D seismic survey; |
| | EP 161: that between March 21, 2023 and March 20, 2025 the following work is completed with an estimated expenditure of A$12 million: (a) acquiring processing and interpret 200km of 2D seismic data; (b) drill 2 two (2) vertical exploration wells; (c) geological and geophysical studies. |
A failure to comply with these conditions may result in the Minister: (a) cancelling the permit in relation to any or all of the blocks the subject of the permit; or (b) refusing an application for renewal of the Tenement.
If these obligations are not able to be met by the required dates, the Company may be able to apply to the Minister to request that the work program be varied in accordance with the process described in the Variation, suspension or waiver of a condition of an EP section above. However, a variation may not necessarily be granted.
Overlapping Tenements
Generally, the existence of overlapping tenure in respect of the different types of resources governed by separate statutes is expected and not uncommon in the Northern Territory. The same land shares different use and may contain concurrent extraction rights. For example, Tamboran owns petroleum extraction rights in the Beetaloo, but there are also multiple pastoral leaseholders who lease the rights to graze livestock on the surface. Additionally, there are various mineral rights such as precious metal (gold, silver) and base metal (iron ore, copper, nickel) rights overlayed in the Beetaloo, along with deep geothermal rights, sand and aggregate mining rights.
The Northern Territory legislative regime does not prescribe a general order of precedence or priority of any particular form of tenure over another. Instead, there are general obligations in the Mineral Titles Act 2010 (NT)
112
Table of Contents
that the holder of an EP must conduct authorized activities in relation to the title area in a way that interferes as little as possible with the rights of other occupiers of land in the vicinity of the title area. Furthermore, the Energy Pipelines Act 1981 (NT) imposes restrictions on people undertaking certain works within the vicinity of a pipeline including crossing it with certain machinery or detonating explosives in the region. Additionally, the Geothermal Energy Act 2009 (NT) imposes an obligation on the holders of geothermal titles to consult with the petroleum title holders before conducting geothermal activities on land that is subject to mining or petroleum titles. The Petroleum Act provides that the Minister must not grant an EP over an area that is already the subject of another EP or a license. Aside from the requirement that EPs and other petroleum permits cannot overlap, the Petroleum Act is silent on the question of overlapping tenements with respect to non-petroleum permits, other than that it provides for exclusivity of interest to the title holder. Each of our EPs were issued under the Petroleum Act. If there is any doubt as to whether an activity proposed to be carried out on the tenements will interfere with the rights of another permit holder, an appropriate consultation process will need to take place with the relevant titleholder.
Unit Development
If the Minister is satisfied that a petroleum pool extends beyond a license area and it is desirable, for the purpose of securing economy and efficiency, that the petroleum pool should be worked as one unit, the Minister may, amongst other things, require the licensee and the licensee of each adjacent area to enter into a scheme for registration under the Petroleum Act to work and develop the petroleum pool as one unit. Where a scheme is not furnished within the time specified or where the Minister does not approve the scheme furnished to him, the Minister must prepare a scheme and supply it to each permit holder and that scheme must be complied with. An agreement must be registered under the Petroleum Act in order to have effect. This type of agreement, similar to forced pooling or unitization, has not occurred for shale in Australia to date.
Access Authorities
An EP holder may apply for an access authority to conduct certain activities in an area outside the permit holder or licensees permit area. An access authority authorizes the holder to carry on in the access authority area exploration for petroleum or operations relating to the recovery of petroleum in or from the EP, license, lease or petroleum title in respect of which the application was made and any other operations specified in the access authority.
Reserved Blocks / No-go zones
A Reserved Block (also called a no-go zone) is an area where a person cannot explore or drill for petroleum resources. These areas can include towns, parks, reserves and areas of high ecological value. Under the Petroleum Act, the Minister can declare that a block (not being a block in relation to which an EP or license is in force) will not be the subject of a grant of an EP or license. If there is a declaration in force in relation to a block, the Minister cannot grant an EP or license over the block. There are two Reserved Blocks that are located adjacent to the areas covered by EP 98 and EP 143, these include Reserved Block 200 and Reserved Block 85.
Reserved Block 200 was previously included within the area covered by EP 98. Reserved Block 200 is comprised of an area of 115.8 km2 and includes the entire area of the Bullwaddy Conservation Reserve. Reserve Block 200 has been relinquished from EP 98 and no longer forms part of this EP. The area of EP 143 includes the 2 km buffer around the Town of Newcastle Waters. The Reserved Block 85 is located within the buffer area comprising 0.238 km2 near the Town of Newcastle Waters. The buffer area near the Town of Newcastle Waters was always excluded from the area covered by EP 143.
Royalties under the Royalty Act.
Under the Royalty Act, the Company is required to pay an overriding statutory royalty to the NT Government of 10% of the gross value (net of certain expenses), at the well-head, of all petroleum produced from
113
Table of Contents
our assets. The gross value of that petroleum at the well-head means the sales value of the petroleum, minus the lesser of the deductible costs of the petroleum in the royalty year and the deductible cap for the petroleum for the royalty year. The costs that constitute deductible costs are post-wellhead treatment, processing, refining, storage, transport and sales costs. The deduction cap is 75% of the sales value of petroleum. Deductible costs which exceed the deduction cap can be carried forward to be deducted in future periods.
Legal Proceedings
From time to time, we may be subject to various claims, title matters and legal proceedings arising in the ordinary course of business, including environmental claims, health and safety claims, contamination claims, personal injury and property damage claims, claims related to joint interest billings and other matters under natural gas operating agreements and other contractual disputes. While the outcome and impact on the Company cannot be predicted with certainty, we believe that our ultimate liability with respect to any such matters will not have a significant impact or material adverse effect on our financial positions, results of operations or cash flows. Our results of operations and future cash flows, however, could be significantly impacted in the reporting periods in which such matters are resolved.
114
Table of Contents
Directors and Executive Officers
The following table provides information regarding the individuals who are expected to constitute our executive officers and directors upon completion of this offering. Executive officers serve at the discretion of our board of directors and until their successors are elected and qualified.
| Name |
Age |
Current Position(s) with the Company |
||
| Joel Riddle |
49 | Chief Executive Officer and Director |
||
| Eric Dyer |
41 | Chief Financial Officer |
||
| Faron Thibodeaux |
63 | Chief Operating Officer |
||
| Richard Stoneburner |
71 | Chairman Nominee |
||
| Fredrick Barrett |
62 | Director Nominee |
||
| John Bell |
53 | Director Nominee |
||
| Ryan Dalton |
44 | Director Nominee |
||
| Patrick Elliott |
71 | Director Nominee |
||
| Stephanie Reed |
41 | Director Nominee |
||
| The Hon. Andrew Robb AO |
72 | Director Nominee |
||
| David Siegel |
62 | Director Nominee |
Joel RiddleChief Executive Officer and Director. Joel Riddle joined our Predecessor as Chief Executive Officer in September 2013, was appointed as a Director of our Predecessor in December 2018 and has served as Chief Executive Officer and Director of the Company since October 2023. Mr. Riddle brings over 25 years of experience in the upstream oil and gas industry. Prior to joining our Predecessor, Mr. Riddle served as Vice President, Commercial and Planning at Cobalt International Energy (Cobalt) from 2006 to 2013, where he worked closely with executive management in the initial evaluation and implementation of the exploration growth strategy in the Gulf of Mexico and West Africa and played a role in Cobalts initial public offering. Cobalt filed a voluntary petition for bankruptcy on December 14, 2017. Prior to his position with Cobalt, Mr. Riddle served in various management positions including business development, commercial and strategic planning with Unocal Corporation from 2002-2005 and Murphy Oil Corporation from 2005-2006. Prior to Unocal Corporation, from 2001-2002, Mr. Riddle was a senior associate with Andersen Consulting, serving upstream exploration and production clients on strategy and performance improvement engagements. Mr. Riddle began his career in 1997 as a senior reservoir engineer with ExxonMobil, serving various assignments focused on upstream oil and gas operations in the Gulf of Mexico. Mr. Riddle received a Bachelor of Science with Honors in Mechanical Engineering from the University of Florida and a Master of Business Administration from the University of Chicago. We believe Mr. Riddle is qualified to be on our board of directors due to his extensive experience with the Company and the global energy industry and his technical acumen.
Eric DyerChief Financial Officer. Eric Dyer joined our Predecessor as Chief Financial Officer in November 2019 and has served as Chief Financial Officer of the Company since October 2023. Mr. Dyer has over 20 years of experience in finance in the energy, infrastructure, and sustainability sectors. Prior to joining the Company, Mr. Dyer worked at EAS Advisors LLC, a boutique investment bank in New York, from December 2010 to November 2019, where he served as Head of Energy. Prior to EAS Advisors, he served in various investment banking and capital markets roles with firms such as Atlantic-Pacific Capital, Execution LLC, IHS Markit and RBC Capital Markets. Mr. Dyer received a Bachelor of Science in Finance from the University of Minnesota.
Faron ThibodeauxChief Operating Officer. Faron Thibodeaux joined our Predecessor as Chief Operating Officer in February 2021. Mr. Thibodeaux has over 40 years of technical and operations experience in the energy industry. Mr. Thibodeaux previously worked at Apache Corporation from April 2008 to November 2020, where he ultimately held the position of Vice President of Drilling, Completions and Engineering of Apache
115
Table of Contents
Corporation. He was also formerly General Manager for Apache Australia and a board member of the Permian Basin Petroleum Association. Prior to working with Apache, Mr. Thibodeaux worked for Chevron. Mr. Thibodeaux received a Bachelor of Science in Petroleum Engineering from the University of Louisiana at Lafayette.
Richard StoneburnerChairman Nominee. Richard (Dick) Stoneburner has served on the board of directors of our Predecessor since May 2016 and was named Chairman of our Predecessor in February 2021. Mr. Stoneburner has approximately 45 years of experience in upstream oil and gas exploration and production. Since 2013, Mr. Stoneburner has been a Partner and Senior Advisor for Pine Brook Partners, a private equity firm focusing on investments in the energy sector. Mr. Stoneburner was a Co-Founder and former President and Chief Operating Officer of Petrohawk Energy Corporation from 2003-2011 and President North America Shale Production Division for BHP Billiton Petroleum from 2011-2012. Prior to co-founding Petrohawk in 2003, Mr. Stoneburner was Executive Vice President Exploration for 3TEC Energy Corporation and worked for several E&P companies, including Hugoton Energy Corporation, Stoneburner Exploration Inc., Weber Energy and Texas Oil & Gas. Mr. Stoneburner currently serves on the board of Sitio Royalties Corp. (NYSE: STR) (formerly Brigham Minerals, Inc.; NYSE: MNRL), a position he has held since 2018. He also previously served on the board of Yuma Energy, Inc. (NYSE American: YUMA) from 2014-2020 and currently serves on the boards of private companies in the oil and gas industry. Mr. Stoneburner received a Bachelor in Science in Geological Sciences from the University of Texas at Austin and a Master of Science in Geology from Wichita State University. We believe Mr. Stoneburner is qualified to be on our board of directors due to his extensive leadership experience and professional experience in upstream oil and gas exploration and production.
Fredrick BarrettDirector Nominee. Fredrick Barrett has served as an independent Director for our Predecessor since September 2014 and has over 35 years of experience in the oil and gas resources industry. Mr. Barrett served as an independent Non-Executive Director on the Board of Asian American Gas Energy Holdings (AAG), a leading coalbed methane natural gas company focused in China, from 2015-2018. Mr. Barrett served as Chairman of the New Business Committee for AAG from 2016-2018. During 2014 and 2015, Mr. Barrett served on the Unconventional Advisory Panel at Santos Ltd (ASX: STO), an independent exploration and production oil and gas company headquartered in Adelaide, Australia. Mr. Barrett no longer serves in any advisory function for Santos. Mr. Barrett co-founded Bill Barrett Corporation (NYSE: BBG) in January 2002 and served in various positions from 2002-2013, including President and Chief Operating Officer from 2002-2006 and Chief Executive Officer and Chairman of the Board from 2006-2013. Prior to that, Mr. Barrett was a senior exploration geologist for Barrett Resources Corp. (NYSE: BRR) in the U.S. Rocky Mountain Region from 1989 to 2001, and a lead geologist for various Rockies areas from 1989 to 1996. Mr. Barrett was a Co-Founder and Partner in Terred Oil Company from 1987 to 1989, a private oil and gas partnership that provided geologic oil and gas services for the U.S. Rocky Mountain Region. Mr. Barrett worked as a project and wellsite geologist for various periods from 1983 to 1986 for Barrett Resources and held similar roles for various periods for the Barrett Energy and Aeon Energy companies from 1981 to 1983. Mr. Barrett received a Bachelor of Science in Geology from Ft. Lewis College and a Master of Science in Geology from Kansas State University. He is also a graduate of the Harvard Business School Advanced Management Program. We believe Mr. Barrett is qualified to be on our board of directors due to his public company experience and technical background.
John BellDirector Nominee. John Bell has served as a Director for our Predecessor since April 2023. Mr. Bell has been Senior Vice President of International and Offshore Operations of Helmerich & Payne, Inc. (NYSE: HP) (H&P) since 2020 and oversees H&Ps drilling operations in South America, the Middle East, and the Gulf of Mexico. Mr. Bell joined H&P in 1998 as a Business Systems Analyst and has held a variety of senior leadership positions from Vice President of Human Resources to Vice President of Corporate Services. Early in his career, Mr. Bell was involved in and led various projects focused on improving rig operations such as rig moves, offshore crane operations, and maintenance systems. During his time in corporate roles, Mr. Bell held leadership roles in a variety of initiatives, most notably Workforce Staffing, global Human Resources cloud-based system, and global ERP implementation. He is a current member of the Executive Leadership Team.
116
Table of Contents
Mr. Bell serves on the Baylor University Hankamer School of Business Advisory Board. Mr. Bell received a Bachelor of Business Administration with a double major in Economics and Marketing from Baylor University. We believe Mr. Bell is qualified to be on our board of directors due to his drilling operational experience.
Ryan DaltonDirector Nominee. Ryan Dalton has served as a Director of our Predecessor since September 2023. Mr. Dalton has over 20 years of financial experience, including a decade in the oil & gas industry. Mr. Dalton most recently served as Executive Vice President, Chief Financial Officer, at Parsley Energy, Inc. (NYSE: PE) from 2012-2021, until being acquired by Pioneer Natural Resources. Prior to joining Parsley Energy, Mr. Dalton served as an investment banker in Rothschilds restructuring group, and as a consultant at Alix Partners. Mr. Dalton received a Bachelor of Business Administration in Finance from Southern Methodist University and a Master of Business Administration from the University of Virginia. We believe that Mr. Dalton is qualified to be on our board of directors due to his background in corporate finance, strategic planning, public and private capital raising, as well as risk management.
Patrick ElliottDirector Nominee. Patrick Elliott is a founding shareholder and joined the board of our Predecessor in February 2009, serving as the Chairman from February 2009 to November 2020. Mr. Elliott has over 40 years of diverse experience working in commercial and management roles in the upstream oil and gas mineral resources industries. Mr. Elliott has served on the boards of Cap-XX Ltd (LON: CPX) since 2011, Rockfire Resources plc (LON: ROCK) since March 2019, Argonaut Resources N.L. (ASX: ARE) from 1993 to October 2023, and Ioneer Ltd (ASX: INR) from June 2003 to November 2020. Mr. Elliott has served on boards of numerous private companies over the last 40 years. Mr. Elliott is a Certified Practicing Accountant in Australia. Mr. Elliott received a Bachelor in Commerce (Accounting and Financial Management) from the University of New South Wales and a Master of Business Administration in Mineral Economics from the Macquarie Graduate School of Management. We believe that Mr. Elliott is qualified to be on our board of directors due to his corporate finance and investment experience.
Stephanie ReedDirector Nominee. Stephanie Reed has served as a Director of our Predecessor since September 2023. Ms. Reed has over 15 years of experience in the oil and gas industry. Ms. Reed has been a Partner of Formentera Partners since April 2022, where she oversees all aspects of funds business development efforts, and land geosciences, legal, human resources, and marketing & midstream, while additionally assisting with asset management and operations. Ms. Reed previously served as Vice President of Oil & Gas Marketing & Midstream at Pioneer Natural Resources USA (NYSE: PXD) from January 2021 to April 2022. While at Pioneer, Ms. Reed served on the Cybersecurity Steering Committee. Prior to joining Pioneer, Ms. Reed served in several roles at Parsley Energy, Inc. (NYSE: PE), from January 2010 to January 2021, including Senior Vice President, Land, Marketing & Midstream. While at Parsley, Ms. Reed oversaw all business development, land, regulatory, midstream, and marketing business units. Ms. Reed also served on the Parsleys Executive Personnel Committee and Management Team, Corporate Governance Committee, Financial Reporting Committee, IT Steering Committee, and Sustainability Committee. Ms. Reed graduated from Texas Tech University with a Bachelors in Applied Science and a Master of Business Administration. We believe Ms. Reed is qualified to be on our board of directors due to her experience in the oil & gas industry.
Andrew RobbDirector Nominee. The Hon. Andrew Robb AO has served as a Director of our Predecessor since April 2023. Mr. Robb served as a Member of Australias House of Representatives from 2004-2016 and as Australias Minister for Trade, Investment and Tourism from 2013-2016. While serving as Minister for Trade, Investment and Tourism, Mr. Robb negotiated Free Trade Agreements with South Korea, Japan and China; the 12 country Trans Pacific Partnership (TPP) free trade agreement; the Comprehensive Strategic Partnership with Singapore; and conducted 85 investment roundtables with 28 countries. While serving in the House of Representatives, Mr. Robb also held positions as Chairman of the Governments Workplace Relations Taskforce, Assistant Minister for Immigration and Multicultural Affairs and then Minister for Vocational and Further Education. In Opposition, Mr. Robb held positions as Shadow Minister for Foreign Affairs, Shadow Minister for Infrastructure and Climate Change, Chairman of the Coalition Policy Development Committee and Shadow Minister for Finance, Deregulation and Debt Reduction. Mr. Robb was awarded the Office of the Order of
117
Table of Contents
Australia (AO) for his service to agriculture, politics, and the community. Mr. Robb retired from politics in 2016 and currently serves as Chairman of The Robb Group, CBMA and CLARA Energy and as a Board Member of the Kidman cattle enterprise, CNSDose, Mind Medicine Australia, CDMA, and strategic advisor to Seafarms Ltd, as well as a range of national and international businesses. Mr. Robb previously served as a director of Ten Network Holdings (ASX: TEN) from 2016-2017, in addition to previously serving as a director of other privately held companies. Mr. Robb received a Diploma in Agricultural Science from Dookie Agricultural College and a Bachelors in Economics from LaTrobe University. We believe that Mr. Robb is qualified to be on our board of directors due to his extensive leadership and international trade experience.
David SiegelDirector Nominee. David Siegel has served as a Director of our Predecessor since March 2021. Mr. Siegel has 30 years of experience in the aerospace and aviation industry. Since October 2017, Mr. Siegel has acted as a Senior Advisor for Apollo Global Management. Mr. Siegel served as Chairman of Sun Country Airlines (NASDAQ: SNCY) from April 2018 to February 2023, as a director of Genesis Park Acquisition Corp (formerly NYSE: GNPK) from November 2020 to September 2021 and currently serves on the boards of private airline companies. Prior to joining Apollo, Mr. Siegel served as Chief Executive Officer for a number of operators, including Ansett Worldwide Aviation Services from 2016-2017, Frontier Airlines (NASDAQ: ULCC) from 2012-2015, XOJET from 2008-2010, US Airways (formerly NYSE: LCC) from 2002-2004, during which he successfully guided the company through bankruptcy and returned it to profitability in 2003, and Avis Budget Group Inc. (NASDAQ: CAR). After beginning his career as a consultant at Bain & Company, where he worked from 1983 to 1990, Mr. Siegel served in various senior management roles at Continental Airlines, Inc. (formerly NYSE: CAL) and Northwest Airlines Corp. (formerly NYSE: NWA). Mr. Siegel holds a Bachelor of Science from Brown University and a Master of Business Administration from Harvard Business School. We believe that Mr. Siegel is qualified to be on our board of directors due to his substantial experience in managing public companies.
Board of Directors
The number of members of our board of directors will be determined from time to time by resolution of the board of directors. We expect our board of directors will consist of nine persons upon the consummation of this offering.
Our board of directors will be divided into three classes of directors, with each class to be as equal in number as possible, and with the directors serving staggered three-year terms. The term of office of the Class I directors, consisting of , will expire at our first annual meeting of stockholders following the completion of this offering. The term of office of the Class II directors, consisting of , will expire at our second annual meeting of stockholders following the completion of this offering. The term of office of the Class III directors, consisting of , will expire at our third annual meeting of stockholders following the completion of this offering. See Description of Capital Stock Anti-Takeover ProvisionsClassified Board of Directors for more information.
Director Independence
Upon completion of this offering, we expect members of our board of directors will qualify as independent under the listing standards of the NYSE. Our board of directors has determined that each of is independent as defined under the NYSE corporate governance standards. Richard Stoneburner will be the chairman of the board of directors.
Committees of the Board of Directors
Our board of directors will establish standing committees in connection with the discharge of its responsibilities. Upon the completion of this offering, these committees will include an Audit and Risk Management Committee, a Compensation Committee, a Nominations & Governance Committee, and a
118
Table of Contents
Sustainability Committee. The composition and responsibilities of each of the committees of our board of directors are described below and each committee will have a charter. Members will serve on these committees until their resignation or until as otherwise determined by our board of directors.
Audit and Risk Management Committee
The Audit and Risk Management Committee will oversee the conduct of our financial reporting processes, including (i) reviewing with management and the outside auditors the audited financial statements included in our annual reports filed with the SEC; (ii) reviewing with management and the outside auditors the interim financial results included in our quarterly reports filed with the SEC; (iii) discussing with management and the outside auditors the quality and adequacy of internal controls; (iv) reviewing the independence of the outside auditors; (v) reviewing with management relevant corporate risks; and (vi) reviewing with management and outside reserve auditors our annual reserves report.
Our Audit and Risk Management Committee will have a minimum of three members. Upon the completion of this offering, we expect the members of our Audit and Risk Management Committee will be . will serve as the chair of the Audit and Risk Management Committee. All members of our Audit and Risk Management Committee will be independent as defined in the NYSE corporate governance standards and Rule 10A-3 of the Exchange Act. All members of our Audit and Risk Management Committee will, in the judgment of our board of directors, be financially literate, or become so within a reasonable period of time after appointment to the Audit and Risk Management Committee, and at least one member of the Audit and Risk Management Committee will qualify as an audit committee financial expert as defined under the SOX and applicable SEC regulations. The Audit and Risk Management Committee will operate under a written charter that satisfies the applicable rules and regulations of the SEC and the listing standards of the NYSE, and the Audit and Risk Management Committee will review the charter annually. A copy of the Audit and Risk Management Committee Charter will be available for review on our website.
Nominations & Governance Committee
The Nominations & Governance Committee will be responsible for (i) advising our board of directors about the appropriate composition of our board of directors and its committees; (ii) identifying and evaluating candidates for board service with appropriate qualifications and diversity; (iii) recommending director nominees for election at annual meetings of stockholders or for appointment to fill vacancies and newly created directorships; and (iv) recommending the directors to serve on each committee of our board of directors. The Nominations & Governance Committee will also be responsible for periodically reviewing and making recommendations to our board of directors regarding corporate governance policies and responses to stockholder proposals, conducting an annual performance review of our board of directors and its committees, implementation of a succession plan at the board and executive level and reviewing whether our directors satisfy applicable independence requirements.
Upon the completion of this offering, we expect the members of our Nominations & Governance Committee will be . will serve as the chair of the Nominations & Governance Committee. The Nominations & Governance Committee will operate under a written charter that satisfies the applicable rules and regulations of the SEC and the listing standards of the NYSE, and the Nominations & Governance Committee will review the charter annually. A copy of the Nominations & Governance Committee Charter will be available for review on our website.
Compensation Committee
The Compensation Committee will review, evaluate and recommend to our board of directors compensation policies with respect to our directors, executive officers and senior management and determine if they remain effective to attract, motivate and retain key talent. The Compensation Committee will make recommendations to
119
Table of Contents
the board of directors regarding corporate performance goals and objectives relevant to the CEO and management, and evaluate their performance annually in light of those goals and objectives. The Committee will review and recommend to the board of directors, with respect to executive officers, their annual base salary, short term incentives, and long term incentive equity plans, as well as employment, and similar agreements. The Compensation Committee will also have the responsibility to review, determine, and recommend to the board of directors the compensation fees of the directors related to annual retainers and committee fees. The committee will also have the right and the responsibility to retain a compensation consultant, and periodically review the consultant for independence purposes. The committee will also have responsibility in preparing relevant disclosure, as necessary and required by the SEC.
Upon the completion of this offering, we expect the members of our Compensation Committee will be . will serve as the chair of the Compensation Committee. The Compensation Committee will operate under a written charter that satisfies the applicable rules and regulations of the SEC and the listing standards of the NYSE, and the Compensation Committee will review the charter annually. A copy of the Compensation Committee Charter will be available for review on our website.
Sustainability Committee
The Sustainability Committee will oversee our policies, initiatives, and strategies regarding environmental, social, and other sustainability matters, including our sustainability plan.
Upon the completion of this offering, we expect the members of our Sustainability Committee will be . will serve as the chair of the Sustainability Committee. The Sustainability Committee will operate under a written charter and the Sustainability Committee will review the charter annually. A copy of the Sustainability Committee Charter will be available for review on our website.
Compensation Committee Interlocks and Insider Participation
None of our executive officers serve on the board of directors or compensation committee of another public company that has an executive officer that serves on our board or compensation committee. No member of our board is an executive officer of another public company in which one of our executive officers serves as a member of the board of directors or compensation committee of that company.
Code of Business Conduct and Ethics
Upon the completion of this offering, our board of directors will adopt a new Code of Business Conduct and Ethics applicable to all the Companys employees, officers and directors. The Code of Business Conduct and Ethics will cover compliance with law; fair and honest dealings with the Company, its competitors and others; full, fair and accurate disclosure to the public; and procedures for compliance with the Code of Business Conduct and Ethics. This Code of Business Conduct and Ethics will be available on the Companys website.
Corporate Governance Guidelines
Upon the completion of this offering, our board of directors will adopt corporate governance guidelines in accordance with the corporate governance rules of the NYSE.
120
Table of Contents
EXECUTIVE AND DIRECTOR COMPENSATION
This section discusses the material components of the executive compensation program for our executive officers who are named in the 2023 Summary Compensation Table below. In fiscal 2023, our named executive officers and their positions were as follows:
| | Joel Riddle, our Managing Director and Chief Executive Officer; |
| | Eric Dyer, our Chief Financial Officer; and |
| | Faron Thibodeaux, our Chief Operating Officer. |
This discussion may contain forward-looking statements that are based on our current plans, considerations, expectations and determinations regarding future compensation programs. Actual compensation programs that we adopt following the completion of this offering may differ materially from the currently planned programs summarized in this discussion.
2023 Summary Compensation Table
The following table sets forth information concerning the compensation of our named executive officers for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2023.
| Name and Principal |
Year | Salary ($)(1) | Non-Equity Incentive Plan Compensation ($) (2) |
All Other Compensation ($) |
Total (3) | |||||||||||||||
| Joel Riddle (4) |
2023 | 565,658 | 525,781 | 17,021(5) | 1,108,460 | |||||||||||||||
| Managing Director and Chief Executive Officer |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Eric Dyer (4) |
2023 | 449,738 | 210,313 | | 660,051 | |||||||||||||||
| Chief Financial Officer |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Faron Thibodeaux |
2023 | 396,229 | 240,600 | 12,505(6) | 649,334 | |||||||||||||||
| Chief Operating Officer |
||||||||||||||||||||
| (1) | Amounts included for Messrs. Riddle and Dyer include base salary earned during fiscal 2023 as well as the payment of accrued but unused leave (which was US$132,764 for Mr. Riddle and US$86,402 for Mr. Dyer). Our Predecessors Remuneration Committee determined to pay out accrued but unused leave to Messrs. Riddle and Dyer in June 2023 in an effort to decrease the recorded annual leave liability held by the predecessor. |
| (2) | Amounts reflect the amount of cash performance-based bonuses earned for the period from July 1, 2022 through October 30, 2022 based on actual performance pursuant to our short-term incentive plan. We provide additional information regarding the annual bonuses in Narrative to Summary Compensation Table2023 Bonuses below. |
| (3) | Amounts reported in this table include compensation paid by Tamboran Resources Limited and Tamboran Services Pty Ltd, in the case of Messrs. Riddle and Dyer, and Tamboran Resources USA, LLC, in the case of Mr. Thibodeaux, in each case, prior to the corporate reorganization. |
| (4) | All amounts paid to Messrs. Riddle and Dyer were paid in Australian dollars and have been converted to U.S. dollars using a conversion rate of A$1.00 to US$0.673, which was the average exchange rate from the period between July 1, 2022 and June 30, 2023. |
| (5) | Amount reflects Companys compulsory contributions to Mr. Riddles Australian superannuation account. |
| (6) | Amount reflects 401(k) Company matching contributions. |
121
Table of Contents
Narrative to Summary Compensation Table
Base Salaries
The named executive officers receive a base salary to compensate them for services rendered to our company. The base salary payable to each named executive officer is intended to provide a fixed component of compensation reflecting the executives skill set, experience, role and responsibilities. Base salary is reviewed annually and may be adjusted based upon individual performance and competitive benchmarks that may be reviewed from time to time to ensure competitiveness.
For the year ended June 30, 2023, Mr. Riddles annual base salary was $441,656, Mr. Dyers annual base salary was $353,325, and Mr. Thibodeauxs annual base salary was $404,250 (Messrs. Riddles and Dyers annual base salaries have been converted using a conversion rate of A$1.00 to US$0.673).
Annual Bonuses
We provide annual incentive cash bonuses to our named executive officers under our short-term incentive plan, which we refer to as our STI Plan. Under the STI Plan, annual bonuses are determined based on achievement of Company results using strategic objectives and metrics, as described below. While the STI Plan bonus period typically aligns with our fiscal year, the 2023 fiscal year covered two separate bonus periods. In connection with our acquisition of Origin B2 (now known as Tamboran B2), we expanded the 2022 fiscal bonus year to remain in place through October 2022 (the FY2022 Extended Bonus Period). Commencing in January 2024, we expect to begin awarding bonuses under our STI Plan based on calendar year performance.
Bonuses for the FY2022 Extended Bonus Period were based on achievement of corporate goals related to health and safety, operations budget cost, commercial and operations project delivery, finances, and environmental, social and corporate governance. The target performance bonus amounts for Messrs. Riddle, Dyer and Thibodeaux was 100%, 50% and 50%, respectively, of the named executive officers annual base salary. For the FY2022 Extended Bonus Period, the named executive officers were eligible to receive up to 100% of the executives target bonus opportunity.
For the FY2022 Extended Bonus Period, the level of achievement of corporate goals resulted in a payout of 100% of each named executive officers target bonus. The amounts of such bonuses paid to our named executive officers are set forth above in the Summary Compensation Table in the column entitled Non-Equity Incentive Plan Compensation.
Equity Compensation
2021 Option Awards
Tamboran Resources Limited adopted the Tamboran Resources Limited Equity Incentive Plan (the Equity Incentive Plan) in May 2021 in connection with becoming a publicly listed company in Australia and to assist in the motivation and retention of selected company employees and directors. All incentives granted prior to May 2021 were cancelled and options to purchase shares of Tamboran Resources Limited were granted to key employees and directors, including our named executive officers.
In connection with the corporate reorganization, we amended the terms of each of the outstanding options to acquire ordinary shares of Tamboran Resources Limited so that the entitlements of option holders to be issued ordinary shares in Tamboran Resources Limited instead became entitlements to be issued CDIs in the Company.
No awards were made to our named executive officers during the fiscal year ended June 30, 2023.
122
Table of Contents
Other Elements of Compensation
Retirement Plans
We contribute to the Australian superannuation defined contribution scheme that provides eligible Australian employees (including Mr. Riddle) with an opportunity to save for retirement on a pre-tax basis. We pay superannuation in accordance with legislative requirements and our minimum contribution is set by legislation. We offer flexibility for salary sacrifice to be added to the superannuation scheme and any actual increase in our contribution to the superannuation scheme is subject to legislative rules at the time. We do not contribute to a superannuation scheme for Mr. Dyer because the terms of his visa do not require this contribution.
With respect to our eligible employees in the United States (including Mr. Thibodeaux), we maintain a 401(k) retirement savings plan. Mr. Thibodeaux is eligible to participate in the 401(k) plan on the same terms as other full-time employees. Currently, we match contributions made by participants in the 401(k) plan up to 4% of the employee contributions, and these matching contributions are fully vested as of the date on which the contribution is made. We believe that providing a vehicle for tax-deferred retirement savings though our 401(k) plan, and making matching contributions, adds to the overall desirability of our executive compensation package and further incentivizes our employees, including Mr. Thibodeaux, in accordance with our compensation policies.
Employee Benefits and Perquisites and Tax Equalization Arrangements
Health/Welfare Plans.
All of our eligible U.S. employees, including Mr. Thibodeaux, may participate in the following health and welfare plans:
| | medical, dental and vision benefits; |
| | short-term and long-term disability insurance; and |
| | life insurance. |
All of our eligible Australian employees, including Messrs. Riddle and Dyer, may participate in the following health and welfare plans:
| | life and total permanent disablement cover; and |
| | salary continuance cover. |
We believe the perquisites described above are necessary and appropriate to provide a competitive compensation package to our named executive officers.
Tax Equalization Arrangements
Consistent with arrangements with other employees on rotational assignments, in connection with Mr. Thibodeauxs rotational assignment from the United States to Australia during the 12-month period beginning in January 2023, Tamboran Resources Limited has agreed to provide Mr. Thibodeaux with tax equalization at U.S. income tax rates for the employment income earned relating to the assignment. The scope of income subject to the arrangement is limited to the fixed base salary earned during assignment. The effect of the tax equalization arrangement is to make relevant payments to Mr. Thibodeaux such that Mr. Thibodeaux will be responsible for the same level of income and social security taxes on his Tamboran employment income as he would have incurred had he solely worked in the United States.
123
Table of Contents
Outstanding Equity Awards at Fiscal Year-End
The following table summarizes the number of shares of common stock underlying outstanding equity incentive plan awards for each named executive officer as of June 30, 2023.
| Option Awards (1) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Name |
Grant Date |
Number of Securities Underlying Unexercised Options (#) Exercisable |
Number of Securities Underlying Unexercised Options (#) Unexercisable |
Equity Incentive Plan Awards: Number of Securities Underlying Unexercised Unearned Options (#) |
Option Exercise Price ($)(2) |
Option Expiration Date |
||||||||||||||||
| Joel Riddle | May 20, 2021 (3) | 3,267,500 | | | 0.25 | 05/20/2026 | ||||||||||||||||
| May 20, 2021 (3) | 5,500,000 | | | 0.18 | 05/20/2026 | |||||||||||||||||
| May 20, 2021 (4) | | | 2,750,000 | 0.31 | 05/20/2026 (8) | |||||||||||||||||
| May 20, 2021 (5) | | | 2,750,000 | 0.31 | 05/20/2026 (8) | |||||||||||||||||
| May 20, 2021 (6) | | | 2,750,000 | 0.31 | 05/20/2026 (8) | |||||||||||||||||
| May 20, 2021 (7) | | | 2,750,000 | 0.31 | 05/20/2026 (8) | |||||||||||||||||
| Eric Dyer | May 20, 2021 (3) | 3,000,000 | | | 0.25 | 05/20/2026 | ||||||||||||||||
| May 20, 2021 (4) | | | 1,250,000 | 0.31 | 05/20/2026 (8) | |||||||||||||||||
| May 20, 2021 (5) | | | 1,250,000 | 0.31 | 05/20/2026 (8) | |||||||||||||||||
| May 20, 2021 (6) | | | 1,250,000 | 0.31 | 05/20/2026 (8) | |||||||||||||||||
| May 20, 2021 (7) | | | 1,250,000 | 0.31 | 05/20/2026 (8) | |||||||||||||||||
| Faron Thibodeaux | May 20, 2021 (4) | | | 1,250,000 | 0.31 | 05/20/2026 (8) | ||||||||||||||||
| May 20, 2021 (5) | | | 1,250,000 | 0.31 | 05/20/2026 (8) | |||||||||||||||||
| May 20, 2021 (6) | | | 1,250,000 | 0.31 | 05/20/2026 (8) | |||||||||||||||||
| May 20, 2021 (7) | | | 1,250,000 | 0.31 | 05/20/2026 (8) | |||||||||||||||||
| (1) | Each option listed in the table below was granted pursuant to the Equity Incentive Plan. In connection with the corporate reorganization, the terms of each outstanding option to acquire ordinary shares of Tamboran Resources Limited were amended such that the entitlement to be issued ordinary shares of Tamboran Resources Limited instead became entitlements to be issued CDIs in the Company. Each CDI represents beneficial ownership of 1/200th of a share of our common stock. |
| (2) | Exercise prices have been converted to U.S. dollars using a conversion rate of A$1.00 to US$0.777, which was the conversion rate in effect on the date of grant. |
| (3) | This option vested and became exercisable upon issuance. |
| (4) | This option vests and becomes exercisable if Tamboran Resources Limiteds 90-day trailing volume-weighted average price of a share (or VWAP) equals or exceeds $0.78 per share (converted to U.S. dollars using a conversion rate of A$1.00 to US$0.777, which was the conversion rate in effect on the date of grant), provided, unless otherwise determined by our board of directors, the executive remains employed through such time. |
| (5) | This option vests and becomes exercisable if Tamboran Resources Limiteds 90-day trailing VWAP equals or exceeds $1.17 per share (converted to U.S. dollars using a conversion rate of A$1.00 to US$0.777, which was the conversion rate in effect on the date of grant), provided, unless otherwise determined by our board of directors, the executive remains employed through such time. |
| (6) | This option vests and becomes exercisable if Tamboran Resources Limiteds 90-day trailing VWAP equals or exceeds or equals $1.55 per share (converted to U.S. dollars using a conversion rate of A$1.00 to US$0.777, which was the conversion rate in effect on the date of grant), provided, unless otherwise determined by our board of directors, the executive remains employed through such time. |
| (7) | This option vests and becomes exercisable if Tamboran Resources Limiteds 90-day trailing VWAP equals or exceeds $1.94 per share (converted to U.S. dollars using a conversion rate of A$1.00 to US$0.777, which |
124
Table of Contents
| was the conversion rate in effect on the date of grant), provided, unless otherwise determined by our board of directors, the executive remains employed through such time. |
| (8) | This option will expire on May 20, 2026 or, if the option vests prior to such date, the date that is five years after the applicable vesting date, provided that the executive remains employed through such time (unless otherwise determined by our board of directors). |
Executive Compensation Arrangements
The following is a summary of the compensatory agreements we have entered into with our named executive officers.
Employment Agreement with Joel Riddle. Tamboran Resources Limited is party to an employment contract with our Chief Executive Officer Joel Riddle, which was entered into during April of 2021. Mr. Riddles employment contract has an initial three-year term and is subject to automatic 12-month extension terms, unless either we or Mr. Riddle give 90 days notice to the other party of an intent not to extend the contract.
Pursuant to his employment agreement, Mr. Riddle is entitled to receive: (i) a base salary, which is currently $441,656, (converted from Australian dollars to U.S. dollars using a conversion rate of A$1.00 to US$0.673) and (ii) Company superannuation contributions as a percentage of Mr. Riddles base salary (currently 11%, subject to statutory limits on contributions). In addition, Mr. Riddle is eligible to receive: (a) equity awards pursuant to the Companys long-term incentive program, (b) an annual performance bonus with a target amount equal to 100% of Mr. Riddles base salary, and (c) a commercial discovery bonus equal to 100% of his base salary if the Company finds oil or gas via an established well or wells that can be linked to a pathway of commerciality for the Company, as determined by the Board in its discretion. Mr. Riddle is also entitled to life insurance, private health insurance, international medical and emergency coverage and paid and unpaid leave in accordance with applicable law.
We may terminate Mr. Riddles employment by providing him with 6 months notice or pay in lieu of notice (except in connection with a termination as a result of Mr. Riddles serious misconduct, in which case he can be terminated immediately). In addition, the Board may, in its discretion, determine to pay Mr. Riddle a pro-rated portion of his annual bonus in respect of any fiscal year in which Mr. Riddle terminates, except under certain circumstances involving the termination of Mr. Riddles employment for serious misconduct.
Pursuant to his employment agreement, Mr. Riddle is subject to perpetual confidentiality obligations, intellectual property invention assignment provisions, and non-competition and non-solicitation covenants applying during employment and for up to 12 months following termination of employment.
Employment Agreement with Eric Dyer. Tamboran Resources Limited is party to an employment contract with our Chief Financial Officer Eric Dyer, which was entered into during May of 2021. Mr. Dyers employment contract has an initial three-year term and is subject to automatic 12-month extension terms, unless either we or Mr. Dyer give 90 days notice to the other party of an intent not to extend the contract.
Pursuant to his employment agreement, Mr. Dyer is entitled to receive a base salary, which is currently $353,325 (converted from Australian dollars to U.S. dollars using a conversion rate of A$1.00 to US$0.673). In addition, Mr. Dyer is eligible to receive: (a) equity awards pursuant to the Companys long-term incentive program and (b) an annual performance bonus with a target amount equal to 50% of Mr. Dyers base salary. Mr. Dyer is also entitled to life insurance, private health insurance, international medical and emergency coverage and paid and unpaid leave in accordance with relevant law.
We may terminate Mr. Dyers employment by providing him with 3 months notice or pay in lieu of notice (except in connection with a termination as a result of Mr. Dyers serious misconduct, in which case he can be terminated immediately). In addition, the Board may, in its discretion, determine to pay Mr. Dyer a pro-rated portion of his annual bonus in respect of any fiscal year in which Mr. Dyer terminates, except under certain circumstances involving the termination of Mr. Dyers employment for serious misconduct.
125
Table of Contents
Pursuant to his employment agreement, Mr. Dyer is subject to perpetual confidentiality obligations, intellectual property invention assignment provisions, and non-competition and non-solicitation covenants applying during employment and for up to 12 months following termination of employment.
Employment Agreement with Faron Thibodeaux. Tamboran Resources USA LLC is party to an employment agreement with our Chief Operating Officer Faron Thibodeaux, which was entered into during August of 2021. In addition, we are party to an Assignment Letter with Mr. Thibodeaux, which we entered into in January 2023 in connection with Mr. Thibodeauxs assignment to Australia. The details of the assignment letter are described above under Tax Equalization Arrangements.
Pursuant to his employment agreement, Mr. Thibodeaux is entitled to receive a base salary, which is currently $404,250. In addition, Mr. Thibodeaux is eligible to receive: (a) an annual performance bonus with a target equal to 50% of Mr. Thibodeauxs base salary, and (b) equity awards pursuant to the Companys long-term incentive program. In addition, Mr. Thibodeaux is entitled to participate in the Companys retirement, health and welfare, and other employee benefit programs in which management employees are generally eligible to participate. The Company also pays Mr. Thibodeaux a $100 monthly personal phone and internet expense stipend.
Pursuant to his employment agreement, if Mr. Thibodeauxs employment is terminated by us without cause, in addition to accrued entitlements, he shall be entitled to receive: (i) three months base salary continuation; and (ii) Company-paid health continuation coverage for three months. Such payments and benefits are subject to Mr. Thibodeauxs timely execution and delivery of a release of claims in our favor and his continued compliance with certain restrictive covenants.
Pursuant to his employment agreement, Mr. Thibodeaux is also subject to perpetual confidentiality obligations and non-solicitation and non-competition covenants applying during employment and for 12 months post-termination.
Director Compensation
The following table shows the total compensation paid to each individual who served as a non-employee director of Tamboran Resources Limited during the fiscal year ended June 30, 2023. Our Chief Executive Officer Joel Riddle served as the managing director on our board but received no additional compensation for his service as a director. See section titled Executive Compensation for more information.
| Name |
Fees Earned or Paid in Cash ($) |
All Other Compensation ($) |
Total ($) | |||||||||
| Richard Stoneburner |
148,686 | | 148,686 | |||||||||
| Fred Barrett |
108,137 | | 108,137 | |||||||||
| Patrick Elliot (1) |
99,267 | | 99,267 | |||||||||
| David Siegel |
99,688 | | 99,688 | |||||||||
| Andrew Robb (2)(3) |
22,069 | | 22,069 | |||||||||
| John Bell (4) |
| | | |||||||||
| Dan Chandra (5) |
72,279 | | 72,279 | |||||||||
| Ann Diamant (2)(6) |
77,195 | 8,105 | (5) | 85,300 | ||||||||
| (1) | Amount included for Mr. Elliot was converted from Australian dollars to U.S. dollars using a conversion rate of A$1.00 to US$0.673, which was the average exchange rate from the period between July 1, 2022 and June 30, 2023. |
| (2) | Amounts included for Mr. Robb and Ms. Diamant were paid in Australian dollars and have been converted to U.S. dollars using a conversion rate of A$1.00 to US$0.673, which was the average exchange rate from the period between July 1, 2022 and June 30, 2023. |
| (3) | Mr. Robb was appointed to the board of directors on April 16, 2023. |
126
Table of Contents
| (4) | Mr. Bell was appointed to the board of directors on April 16, 2023. In accordance with Helmerich & Payne requirements, Mr. Bell is not provided compensation for his role on the board of directors. |
| (5) | Mr. Chandra and Ms. Diamant resigned from the board of directors on April 16, 2023. |
| (6) | Amounts reflect our compulsory contributions to Ms. Diamants superannuation account (paid in Australian dollars and been converted to U.S. dollars using a conversion rate of A$1.00 to US$0.673). |
The table below shows the aggregate numbers of option awards (exercisable and unexercisable) held as of June 30, 2023 by each non-employee director. In connection with the corporate reorganization, the terms of each outstanding option to acquire ordinary shares of Tamboran Resources Limited were amended such that the entitlement to be issued ordinary shares of Tamboran Resources Limited instead became entitlements to be issued CDIs in the Company. Each CDI represents beneficial ownership of 1/200th of a share of our common stock. None of the non-employee directors held outstanding stock awards at 2023 fiscal-year end.
| Name |
Options Outstanding at Fiscal Year End |
|||
| Richard Stoneburner |
483,393 | |||
| Fred Barrett |
733,393 | |||
| Patrick Elliot |
233,393 | |||
| David Siegel |
233,393 | |||
| Andrew Robb |
| |||
| John Bell |
| |||
| Dan Chandra |
233,393 | |||
| Ann Diamant |
233,393 | |||
Pre-IPO Non-Employee Director Compensation
Each of our non-employee directors is paid an annual fee in respect of their service on the board of directors. The actual annual fee awarded to each director for fiscal 2023 service is set forth above in the Director Compensation table in the column entitled Fees Earned or Paid in Cash. Prior to the IPO, we paid our non-employee directors the annual base fees set forth in the tables below:
| Director fees per annum including statutory entitlements: |
||||
| Chairman |
$ | 148,060 | (1) | |
| Non-Executive Director |
$ | 74,030 | (1) | |
| Chairman of the following Committees received the following annual fees: |
||||
| Committee |
Chairman Fee | (1) | ||
| Audit and Risk Management |
$ | 16,825 | ||
| Remuneration Committee |
$ | 16,825 | ||
| Nomination and Governance Committee |
$ | 16,825 | ||
| ESG Committee |
$ | 16,825 |
Directors participating on a committee of the board of directors also received an annual fee of $8,412 (1).
| (1) | Amounts to Australian directors were paid in Australian dollars and converted to U.S. dollars using a conversion rate of A$1.00 to $0.673. |
In addition, as required by law, Ms. Diamant received a $8,105 superannuation contribution (paid in Australian dollars, converted to U.S. dollars using a conversion rate of A$1.00 to US$0.673).
127
Table of Contents
New Non-Employee Director Compensation Program
We intend to approve and implement a compensation program for our non-employee directors that consists of annual retainer fees and long-term equity awards.
Equity Incentive Plans
Tamboran Resources Limited Equity Incentive Plan
Tamboran Resources board of directors adopted the Equity Incentive Plan in May 2021 in connection with becoming a publicly listed company in Australia. The Equity Incentive Plan provides for the grant of options and performance rights. As of , 2024, options covering a total of CDIs at a weighted average exercise price of $ remained outstanding under our Equity Incentive Plan. All outstanding awards will continue to be governed by their existing terms, as amended in connection with our corporate reorganization as described above.
128
Table of Contents
The following table sets forth certain information regarding the beneficial ownership of our common stock immediately following the completion of this offering by (i) each NEO, director and director nominee of the Company, (ii) all executive officers, directors and director nominees of the Company as a group, and (iii) each person known to the Company to own beneficially more than 5% of any class of our voting securities. Except as otherwise indicated, (a) the persons or entities identified in the table have sole voting and investment power with respect to all shares shown as beneficially owned by them and (b) the current directors, director nominees and executive officers have not pledged any of such shares as security. All information with respect to beneficial ownership has been furnished by the respective 5% or more stockholders, directors, director nominees or executive officers, as the case may be.
The following information has been presented in accordance with the SECs rules and is not necessarily indicative of beneficial ownership for any other purpose. Under the SECs rules, beneficial ownership of a class of capital stock as of any date includes any shares of that class as to which a person, directly or indirectly, has or shares voting power or investment power as of that date and also any shares as to which a person has the right to acquire sole or shared voting or investment power as of or within 60 days after that date through the exercise of any stock option, warrant or other right (including any conversion or redemption right).
We have based our calculation of the percentage of beneficial ownership prior to this offering on shares of common stock outstanding. We have based our calculation of the percentage of beneficial ownership after this offering on shares of our common stock outstanding immediately following the completion of this offering, assuming that the underwriters do not exercise their option to purchase additional shares. For purposes of the table and notes below, holdings of CDIs representing shares of our common stock are represented as one share of common stock for every 200 CDIs held by a shareholder, rounded to the nearest share.
Unless otherwise indicated, the address of each beneficial owner listed in the table below is c/o Tamboran Resources Corporation, Suite 01, Level 39, Tower One, International Towers Sydney, 100 Barangaroo Avenue, Barangaroo NSW 2000, Australia.
| Beneficial Ownership Before the Offering |
Beneficial Ownership After the Offering |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common Stock |
Total Voting Power Before the Offering |
Common Stock | Total Voting Power After the Offering |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Name of Beneficial Owner |
Shares | % | % | Shares | % | % | ||||||||||||||||||
| 5% or more Stockholders: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sheffield Holdings, LP(1) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nuveen LLC |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The Baupost Group, L.L.C. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Morgan Stanley Australia Ltd |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Helmerich & Payne |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Named Executive Officers, Director Nominees and Directors: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Joel Riddle |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Eric Dyer |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Faron Thibodeaux |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Richard Stoneburner |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fredrick Barrett |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| John Bell |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ryan Dalton |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patrick Elliot |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stephanie Reed |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Andrew Robb |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| David Siegel |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| * | Less than 1%. |
129
Table of Contents
CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS
We describe below transactions and series of similar transactions, during our last three fiscal years or currently proposed, to which we were a party or will be a party, in which:
| | the amounts involved exceeded or will exceed $120,000; and |
| | any of our directors, director nominees, executive officers or beneficial holders of more than 5% of any class of our voting securities, or any immediate family member of any such person, had, or will have, a direct or indirect material interest. |
Other than as described below, there have not been, nor are there any currently proposed, transactions or series of similar transactions meeting these criteria to which we have been or will be a party other than compensation arrangements, which are described where required under Executive and Director Compensation.
TB2 Joint Venture Agreement
EPs 76, 98, and 117 are 77.5% owned and operated by the TB2 Joint Venture between us and Daly Waters. Daly Waters is owned by Bryan Sheffield. Additionally, Mr. Sheffield beneficially owns approximately 17% of our common stock. Mr. Sheffield previously had the right to appoint two directors to the board of directors of our Predecessor. See Business Shareholders and Joint Venture Agreement for more information.
Drilling Contract with Helmerich & Payne International Holdings, LLC
On September 9, 2022, a wholly owned subsidiary of ours entered into a drilling contract with a subsidiary of H&P to drill, test, complete, re-complete or workover development and exploration wells. John Bell, a director nominee, is a Senior Vice President, International & Offshore, at H&P and was appointed by H&P to the board of our Predecessor in connection with H&Ps investment in our Predecessor. Mr. Bell was not selected to serve on the board of the Company pursuant to an arrangement between H&P and the Company. For additional information, see Business Agreements Relating to the Development of our Assets Drilling Contract with Helmerich & Payne International Holdings, LLC.
Convertible Notes
On July 6, 2023, we agreed to issue up to $9 million of our five-year Convertible Notes from time to time to H&P for purposes of funding reimbursement of H&Ps mobilization and related reimbursable costs for Rig 469 as well as other working capital requirements. The Convertible Notes may be converted into a maximum 64,311,438 shares of the Companys common stock. The Convertible Notes accrue interest at 5.5% per annum on the amount drawn and outstanding. As of the date of this prospectus, we have not borrowed any amount under the Convertible Notes. See Liquidity and Capital ResourcesConvertible Notes.
Sweetpea Transaction
On July 25, 2020, we entered into the Share Exchange Agreement with Longview Petroleum LLC under which the Company, through its wholly owned subsidiary, acquired 100% of the issued share capital of Sweetpea from Longview. That transaction was completed on May 21, 2021 after receiving approval from our Predecessors shareholders and ministerial approval. Sweetpea is the registered holder of 100% of the working interests in EPs 136 and 143, and has also applied for EP(A) 197 (Sweetpea Assets). David N. Siegel, who is a director of the Predecessor and a director nominee of the Company, was also and currently is a director of Longview.
Sweetpea has also granted an undivided 1% ORRI in favor of Jeffrey J Rooney as trustee of the Siegel Dynasty Trust of all petroleum produced from the Sweetpea Assets and the land subject to the Sweetpea Assets.
130
Table of Contents
The beneficiaries of the Siegel Dynasty Trust are Emily Siegel and Robert Siegel, who are the children of David N. Siegel. Sweetpea additionally has an obligation to David N. Siegal and/or Longview to grant additional ORRIs where additional acreage is acquired by Sweetpea within the area of mutual interest consisting of EP 136, EP 143 and EP(A) 197. For additional information, see Business Our Assets.
Indemnification Agreements with our Directors and Officers
We intend to enter into indemnification agreements, to be effective upon the completion of this offering, with each of our directors and officers. The indemnification agreements and our governing documents will require us to indemnify our directors and officers to the fullest extent permitted by Delaware law. Subject to certain limitations, the indemnification agreements and our governing documents will also require us to advance expenses incurred by our directors and officers. For more information regarding these agreements, see Description of Capital Stock Limitations of Liability and Indemnification.
Policies and Procedures Regarding Related Party Transactions
Upon completion of this offering, we expect that our board of directors will adopt a new written Code of Business Conduct and Ethics that complies with all applicable requirements of the SEC and NYSE and that contains conflict of interest policies governing transactions involving any director, executive officer or beneficial owner of more than 5% of any class of our voting securities that could be deemed to present a conflict of interest.
Upon completion of this offering, we expect that our board of directors will adopt a written related party transactions policy, pursuant to which our Audit and Risk Management Committee will be responsible for reviewing and either approving, ratifying or disapproving such transactions with our directors, officers or beneficial owners of more than 5% of any class of our voting securities, or any immediate family member of any of the foregoing persons. In considering a related party transaction, our Audit and Risk Management Committee will take into account relevant facts and circumstances relating to whether the transaction is in the best interests of the Company, including the following:
| | the materiality of the transaction to the related party and the Company; |
| | the business purpose for and reasonableness of the transaction; and |
| | whether the transaction is comparable to a transaction that could be available with an unrelated party or is on terms that the Company offers generally to persons who are not related parties. |
131
Table of Contents
General
The following description summarizes certain important terms of our capital stock and of our governing documents, as each will be in effect upon the completion of this offering. For a complete description of the matters set forth in this section titled Description of Capital Stock, you should refer to our governing documents, which are included as exhibits to the registration statement of which this prospectus forms a part, and to the applicable provisions of Delaware law.
Upon completion of this offering, our authorized capital stock will consist of 10,000,000,000 shares of common stock, $0.001 par value per share, of which shares (or shares if the underwriters exercise in full their option to purchase additional shares) will be issued and outstanding and 1,000,000,000 shares of preferred stock, $0.0001 par value per share, of which no shares will be issued and outstanding. In addition, shares of our common stock will be reserved for issuance pursuant to our Equity Incentive Plan (which excludes any potential annual evergreen increases pursuant to the terms of the Equity Incentive Plan), including shares of common stock that may be issued upon vesting of equity awards that we expect to be granted in connection with this offering. See Executive and Director Compensation Equity Incentive Plan.
Common Stock
Holders of shares of our common stock are entitled to one vote for each share held of record on all matters on which stockholders are entitled to vote generally, including the election or removal of directors elected by our stockholders generally. Holders of our common stock do not have cumulative voting rights in the election of directors.
Holders of shares of our common stock are entitled to receive dividends when, as and if declared by our board of directors out of funds legally available therefor, subject to any statutory or contractual restrictions on the payment of dividends and to any restrictions on the payment of dividends imposed by the terms of any outstanding preferred stock. See Dividend Policy.
Upon our liquidation, dissolution or winding up and after payment in full, or provision for payment, of all amounts required to be paid to creditors and to the holders of preferred stock having liquidation preferences, if any, the holders of shares of our common stock will be entitled to receive pro rata our remaining assets available for distribution.
All shares of our common stock that will be outstanding at the time of the completion of the offering will be fully paid and non-assessable. Our common stock will not be subject to further calls or assessments by us. Holders of shares of our common stock do not have preemptive, subscription, redemption or conversion rights. There will be no redemption or sinking fund provisions applicable to our common stock. The rights powers, preferences and privileges of our common stock will be subject to those of the holders of any shares of our preferred stock or any other series or class of stock we may authorize and issue in the future.
Preferred Stock
No shares of preferred stock will be issued or outstanding immediately after the offering contemplated by this prospectus. Our certificate of incorporation authorizes our board of directors to establish one or more series of preferred stock. Unless required by law or any stock exchange, the authorized shares of preferred stock will be available for issuance without further action by the holders of our common stock. Our board of directors is able to determine, with respect to any series of preferred stock, the designations, powers, rights, and preferences of the shares of each such series, and the qualifications, limitations and restrictions thereof, to the fullest extent now or
132
Table of Contents
hereinafter permitted by our governing documents and the laws of the State of Delaware, including, without limitation:
| | voting powers (if any); |
| | dividend rights; |
| | dissolution rights; |
| | conversion rights; |
| | exchange rights; and |
| | redemption rights thereof; |
| | as shall be expressed in a resolution or resolutions adopted by our board of directors (or such committee thereof) providing for the issuance of such series of preferred stock. |
CHESS Depositary Interests
In the corporate reorganization, the Companys shareholders received CDIs, representing interests in the shares of our common stock. One of our CDIs represents a beneficial interest in 1/200th of a share of our common stock. The Company delivered the shares of our common stock represented by the CDIs to a depositary (CHESS Depositary Nominees Pty Ltd, a subsidiary of the ASX), which holds such shares on behalf of the holders of the CDIs. The holders of the CDIs are the beneficial owners of, and are entitled to exchange their CDIs for, the underlying shares of our common stock held by the depositary. In addition, holders of CDIs are generally entitled to exercise the same voting and other rights as holders of our common stock, although they are required to exercise those rights indirectly through the depositary unless they request the depositary to grant them a proxy to vote directly or exchange their CDIs for the underlying shares of our common stock. Nonetheless, holders of CDIs have substantially the same economic, voting and other rights as holders of our common stock and the CDIs therefore should be considered as the functional equivalents of shares of our common stock. In addition, holders of shares of our common stock, including shares sold in this offering, are permitted to deliver those shares to the depositary in exchange for CDIs.
The purpose of the CDIs is to facilitate trading, settlement and clearance of interests in our shares of common stock in Australia by shareholders of the Company. Because our common stock will not be listed on a securities exchange in Australia, Australian residents wishing to trade our common stock would be required to do so through the NYSE in transactions settled in U.S. dollars, which may be inconvenient due to time zone and currency differences, among other factors. However, because the CDIs are listed on the ASX, the Company shareholders who received CDIs in the corporate reorganization are able to trade those CDIs on a local Australian market in transactions settled in Australian dollars.
Holders of CDIs are generally entitled to surrender those CDIs to the depositary in exchange for the underlying shares of common stock, and holders of our common stock will generally be entitled to deliver those shares to the depositary in exchange for CDIs representing those shares. Holding shares of common stock will, however, prevent a person from selling their shares of common stock on the ASX, as only CDIs can be traded on that market. However, investors purchasing shares of our common stock in this offering will not be able to freely resell those shares, or CDIs representing those shares, in Australia during the 12 months after the issue date of those shares in this offering and therefore will not be able to take advantage of any liquidity that may be available for CDIs traded on the Australian Securities Exchange during that period. We intend to apply to the Australian Securities and Investments Commission for waivers from the application of these resale restrictions; however, there is no certainty that all or any of the requested waivers will be granted or, if granted, that such waivers will provide relief from all of these resale restrictions. See Risk Factors Risks Relating to our Common Stock Investors purchasing shares of our common stock in this offering will not be able to freely sell those shares, or CDIs representing those shares, in Australia during the 12 months after the issue date of those shares in this offering and therefore will not be able to take advantage of any liquidity that may be available for CDIs traded on the Australian Securities Exchange during that period.
133
Table of Contents
Dividends
The DGCL permits a corporation to declare and pay dividends on shares of its capital stock out of surplus or, if there is no surplus, out of its net profits for the fiscal year in which the dividend is declared and/or the preceding fiscal year. Surplus is defined as the excess of the net assets of the corporation over the amount determined to be the capital of the corporation by its board of directors. The capital of the corporation is typically calculated to be (and cannot be less than) the aggregate par value of all issued shares of capital stock. Net assets equals the fair value of the total assets minus total liabilities. The DGCL also provides that dividends may not be paid out of net profits if, after the payment of the dividend, remaining capital would be less than the capital represented by the outstanding stock of all classes having a preference upon the distribution of assets. Declaration and payment of any dividend will be subject to the discretion of our board of directors. See Dividend Policy.
Annual Stockholder Meetings
Our bylaws provide that, if required by applicable law, an annual stockholder meeting will be held for the election of directors at a date, time and place, or by means of remote communication, either within or without the State of Delaware, as designated by resolution of our board of directors. Any other proper business may be transacted at the annual meeting.
Anti-Takeover Provisions
Our governing documents and the DGCL contain provisions, which are summarized in the following paragraphs, that are intended to enhance the likelihood of continuity and stability in the composition of our board of directors. These provisions are intended to avoid costly takeover battles, reduce our vulnerability to a hostile or abusive change of control and enhance the ability of our board of directors to maximize stockholder value in connection with any unsolicited offer to acquire us. However, these provisions may have an anti-takeover effect and may delay, deter or prevent a merger or acquisition of the Company by means of a tender offer, a proxy contest or other takeover attempt that a stockholder might consider in its best interest, including those attempts that might result in a premium over the prevailing market price for the shares of common stock held by stockholders.
Authorized but Unissued Capital Stock
Delaware law does not require stockholder approval for any issuance of shares that are authorized and available for issuance. However, the listing requirements of the NYSE, which would apply so long as our common stock remains listed on the NYSE, require stockholder approval of certain issuances equal to or exceeding 20% of the then outstanding voting power of our capital stock or then outstanding number of shares of common stock. These additional shares may be used for a variety of corporate purposes, including future public offerings, to raise additional capital or to facilitate acquisitions.
Our board of directors may generally issue shares of one or more series of preferred stock on terms calculated to discourage, delay or prevent a change of control of the Company or the removal of our management. Moreover, our authorized but unissued shares of preferred stock will be available for future issuances in one or more series without stockholder approval and could be utilized for a variety of corporate purposes, including future offerings to raise additional capital, to facilitate acquisitions and employee benefit plans.
One of the effects of the existence of authorized and unissued and unreserved common stock or preferred stock may be to enable our board of directors to issue shares to persons friendly to current management, which issuance could render more difficult or discourage an attempt to obtain control of the Company by means of a merger, tender offer, proxy contest or otherwise, and thereby protect the continuity of our management and possibly deprive our stockholders of opportunities to sell their shares of common stock at prices higher than prevailing market prices.
134
Table of Contents
Classified Board of Directors
Our certificate of incorporation provides that our board of directors will be divided into three classes of directors, with each class to be as equal in number as possible, and with the directors serving staggered three-year terms. As a result, approximately one-third of our board of directors will be elected each year. The classification of directors will have the effect of making it more difficult for stockholders to change the composition of our board of directors. Our certificate of incorporation provides that, subject to any rights of holders of preferred stock to elect additional directors under specified circumstances, the total number of directors will be determined from time to time by the affirmative vote of a majority of the total number of directors then in office.
Removal of Directors; Vacancies and Newly Created Directorships
Under the DGCL, unless otherwise provided in our certificate of incorporation, directors serving on a classified board may be removed by the stockholders only for cause. Our certificate of incorporation provides that directors may be removed only for cause and only by the affirmative vote of the holders of at least two-thirds in voting power of all the then-outstanding shares of our stock entitled to vote generally in the election of directors. In addition, our certificate of incorporation provides that any vacancies on our board of directors, and any newly created directorships, will be filled by a majority of the total number of directors then in office, even if less than a quorum, or by a sole remaining director.
No Cumulative Voting
Under the DGCL, the right to vote cumulatively does not exist unless the certificate of incorporation specifically authorizes cumulative voting. Our certificate of incorporation does not authorize cumulative voting. Therefore, stockholders holding a majority in voting power of the shares of our stock entitled to vote generally in the election of directors will be able to elect all our directors.
Special Stockholder Meetings
Our certificate of incorporation provides that, subject to the rights of the holders of any series of preferred stock, special meetings of our stockholders may be called for any purpose or purposes, at any time only by or at the direction of our board of directors by the affirmative vote of a majority of the total number of directors then in office, the chairperson of our board of directors, or our Chief Executive Officer, and may not be called by any other person or persons. Our bylaws prohibit the conduct of any business at a special meeting other than as specified in the notice for such meeting. These provisions may have the effect of deterring, delaying or discouraging hostile takeovers, or changes in control or management of the Company.
Director Nominations and Stockholder Proposals
Our bylaws establish advance notice procedures with respect to stockholder proposals and the nomination of candidates for election as directors, including nominations made by or at the direction of the board of directors or a committee of the board of directors. In order for any matter to be properly brought before a meeting, a stockholder will have to comply with advance notice requirements and provide us with certain information. Generally, to be timely, a stockholders notice must be received at our principal executive offices not later than the close of business on the 90th day nor earlier than the close of business on the 120th day prior to the first anniversary date of the immediately preceding annual meeting of stockholders. Our bylaws also specify requirements as to the form and content of a stockholders notice. Our bylaws allow the chairman of the meeting at a meeting of the stockholders to adopt rules and regulations for the conduct of meetings which may have the effect of precluding the conduct of certain business at a meeting if the rules and regulations are not followed. These provisions may also defer, delay or discourage a potential acquirer from conducting a solicitation of proxies to elect the acquirers own slate of directors or otherwise attempting to influence or obtain control of the Company.
135
Table of Contents
Stockholder Action by Written Consent
Under the DGCL, any action required to be taken at any annual or special meeting of the stockholders may be taken without a meeting, without prior notice and without a vote if a consent or consents in writing, setting forth the action so taken, is or are signed by the holders of outstanding stock having not less than the minimum number of votes that would be necessary to authorize or take such action at a meeting at which all shares of our stock entitled to vote thereon were present and voted, unless our certificate of incorporation provides otherwise. Our certificate of incorporation precludes stockholder action by written consent at any time, subject to the rights of the holders of any series of preferred stock.
Supermajority Provisions
Our governing documents provide that our board of directors is expressly authorized to make, repeal, alter, amend and rescind, in whole or in part, our bylaws by the affirmative vote of a majority of the total number of directors then in office, without the assent or vote of the stockholders in any matter not inconsistent with the laws of the State of Delaware or our certificate of incorporation. Any amendment, alteration, rescission or repeal of any provision of our bylaws, or the adoption of any provision inconsistent with our bylaws, by our stockholders requires the affirmative vote of the holders of at least two-thirds of the voting power of all the then-outstanding shares of our stock entitled to vote thereon, voting together as a single class, in addition to any vote of the holders of any class or series of our capital stock required by our governing documents or applicable law or securities exchange rule or regulation.
The DGCL provides generally that the affirmative vote of a majority of the outstanding shares entitled to vote thereon, voting together as a single class, is required to amend a corporations certificate of incorporation, unless the certificate of incorporation requires a greater percentage.
Our certificate of incorporation provides that, in addition to any vote required by our governing documents or applicable law or securities exchange rule or regulation, the following provisions in our certificate of incorporation may be amended, altered, repealed or rescinded, in whole or in part, or any provision inconsistent therewith may be adopted, only by the affirmative vote of the holders of at least 66 2/3% in voting power all the then-outstanding shares of our stock entitled to vote thereon, voting together as a single class:
| | the provisions requiring a vote of at least two-thirds all of the then outstanding shares of voting stock of the Company entitled to vote generally in an election of directors for stockholders to amend our bylaws; |
| | the provisions providing for a classified board of directors (the election and term of our directors); |
| | the provisions regarding removal of directors; |
| | the provisions regarding filling vacancies on our board of directors and newly-created directorships; |
| | the provisions eliminating monetary damages for breaches of fiduciary duty by a director or officer; |
| | the provisions regarding indemnification and advancement of expenses to certain indemnitees in connection with certain proceedings; |
| | the provisions regarding stockholder action by written consent; |
| | the provisions regarding calling special meetings of stockholders. |
| | the amendment provision requiring that the above provisions be amended with a majority vote or a 66 2/3% supermajority vote, as applicable, of stockholders. |
The combination of the classification of our board of directors, the lack of cumulative voting and the supermajority voting requirements in certain circumstances will make it more difficult for our existing stockholders to replace our board of directors as well as for another party to obtain control of us by replacing our
136
Table of Contents
board of directors. Because our board of directors has the power to retain and discharge our officers, these provisions could also make it more difficult for existing stockholders or another party to effect a change in management.
These provisions may have the effect of deterring hostile takeovers or delaying or preventing changes in control of us or our management, such as a merger, reorganization or tender offer. These provisions are intended to enhance the likelihood of continued stability in the composition of our board of directors and its policies and to discourage certain types of transactions that may involve an actual or threatened acquisition of the Company. These provisions are designed to reduce our vulnerability to an unsolicited acquisition proposal. The provisions are also intended to discourage certain tactics that may be used in proxy fights.
However, such provisions could have the effect of discouraging others from making tender offers for our shares and, as a consequence, they also may inhibit fluctuations in the market price of our shares that could result from actual or rumored takeover attempts. Such provisions may also have the effect of preventing changes in management.
Dissenters Rights of Appraisal and Payment
Under the DGCL, with certain exceptions, our stockholders will have appraisal rights in connection with a merger or consolidation of the Company. Pursuant to the DGCL, stockholders who properly request and perfect appraisal rights in connection with such merger or consolidation will have the right to receive payment of the fair value of their shares as determined by the Delaware Court of Chancery.
Stockholders Derivative Actions
Under the DGCL, any of our stockholders may bring an action in our name to procure a judgment in our favor, also known as a derivative action, provided that the stockholder bringing the action is a holder of our shares at the time of the transaction to which the action relates or such stockholders stock thereafter devolved by operation of law.
Choice of Forums
Our certificate of incorporation provides that unless we consent in writing to the selection of an alternative forum, the Court of Chancery of the State of Delaware will, to the fullest extent permitted by law, be the sole and exclusive forum for any (i) derivative action or proceeding brought on behalf of the Company, (ii) action asserting a claim of breach of a fiduciary duty owed by any director, officer or employee of the Company to the Company or our stockholders, (iii) action asserting a claim against the Company or any director or officer of the Company arising pursuant to any provision of the DGCL or our governing documents, or (iv) action asserting a claim against the Company or any director, officer or employee of the Company, which claim is governed by the internal affairs doctrine. Notwithstanding the foregoing sentence, the federal district courts of the United States of America will be the exclusive forum for the resolution of any complaint asserting a cause of action arising under U.S. federal securities laws, including the Securities Act. Any person or entity purchasing or otherwise acquiring any interest in shares of capital stock of the Company will be deemed to have notice of and consented to the forum provisions in our certificate of incorporation. However, the enforceability of similar forum provisions in other companies certificates of incorporation has been challenged in legal proceedings, and it is possible that a court could find these types of provisions to be unenforceable.
Section 203 of the Delaware General Corporation Law
We are not governed by Section 203 of the Delaware General Corporation Law. Section 203 of the Delaware General Corporation Law regulates corporate acquisitions and provides that specified persons who, together with affiliates and associates, own, or within three years did own, 15% or more of the outstanding voting
137
Table of Contents
stock of a corporation may not engage in business combinations with the corporation for a period of three years after the date on which the person became an interested stockholder unless:
| | prior to such time, the corporations board of directors approved either the business combination or the transaction which resulted in the stockholder becoming an interested stockholder; |
| | upon consummation of the transaction which resulted in the stockholder becoming an interested stockholder, the interested stockholder owned at least 85% of the corporations outstanding voting stock at the time the transaction commenced, other than statutorily excluded shares; or |
| | at or after the time a person became an interested stockholder, the business combination is approved by the corporations board of directors and authorized at an annual or special meeting of stockholders by the affirmative vote of at least two-thirds of the outstanding voting stock which is not owned by the interested stockholder. |
The term business combination is defined to include mergers, asset sales and other transactions in which the interested stockholder receives or could receive a financial benefit on other than a pro rata basis with other stockholders.
Limitations of Liability and Indemnification
The DGCL authorizes corporations to limit or eliminate the personal liability of directors and certain officers to corporations and their stockholders for monetary damages for breaches of directors or certain officers fiduciary duties, subject to certain exceptions. Our certificate of incorporation includes a provision that eliminates the personal liability of our directors and officers for monetary damages to the Company or its stockholders for any breach of fiduciary duty as a director or an officer, to the fullest extent permitted by the DGCL. The effect of these provisions is to eliminate the rights of us and our stockholders, through stockholders derivative suits on our behalf, to recover monetary damages from a director or an officer for breach of fiduciary duty as a director or an officer, including breaches resulting from grossly negligent behavior. However, exculpation does not apply to any breaches of the duty of loyalty, any acts or omissions not in good faith or that involve intentional misconduct or knowing violation of law, any authorization of dividends or stock redemptions or repurchases paid or made in violation of the DGCL, or for any transaction from which the director derived an improper personal benefit.
Our certificate of incorporation and our bylaws generally provide that we must indemnify and advance expenses to our directors and officers to the fullest extent permitted by the DGCL. We believe that these indemnification and advancement provisions are useful to attract and retain qualified directors and executive officers.
The limitation of liability, indemnification and advancement provisions in our certificate of incorporation and our bylaws may discourage stockholders from bringing a lawsuit against directors or officers for breach of their fiduciary duty. These provisions also may have the effect of reducing the likelihood of derivative litigation against directors and officers, even though such an action, if successful, might otherwise benefit us and our stockholders. In addition, your investment may be adversely affected to the extent we pay the costs of settlement and damage awards against directors and officers pursuant to these indemnification provisions.
There is currently no pending material litigation or proceeding involving any of our directors, officers or employees for which indemnification is sought.
Indemnification Agreements
We intend to enter into an indemnification agreement with each of our directors and officers as described in Certain Relationships and Related Party Transactions Indemnification Agreements with our Directors and
138
Table of Contents
Officers. Insofar as indemnification for liabilities arising under the Securities Act may be permitted to directors or officers, we have been informed that in the opinion of the SEC such indemnification is against public policy and is therefore unenforceable.
Transfer Agent and Registrar
Upon completion of this offering, the transfer agent and registrar for our common stock will be . The transfer agent and registrars address is .
Listing
We intend to apply to list our common stock on the NYSE under the symbol TBN.
139
Table of Contents
SHARES ELIGIBLE FOR FUTURE SALE
We cannot predict the effect, if any, that market sales of shares of our common stock or the availability of shares of our common stock for sale will have on the market price of our common stock prevailing from time to time. Future sales of our common stock (including CDIs representing those shares) in the public market, or the perception that those sales may occur, could adversely affect the prevailing market price of our common stock at such time, which could make it more difficult for you to sell your shares of common stock at a time and price that you consider appropriate, and could impair our ability to raise equity capital or use our common stock as consideration for acquisitions of other businesses, investments or other corporate purposes in the future.
Sale of Restricted Securities
Immediately upon completion of this offering, there will be outstanding shares of common stock (or if the underwriters exercise in full their option to purchase additional shares). Of these outstanding shares, shares of our common stock to be sold in this offering (or shares if the underwriters exercise in full their option to purchase additional shares) will be freely tradable without further restriction or registration under the Securities Act. Any shares purchased in this offering by our affiliates, as that term is defined in Rule 144 under the Securities Act, may be sold in the public market only if registered or if they qualify for an exemption from registration under Rule 144 or Rule 701 under the Securities Act, which rules are summarized below. The number of shares of common stock outstanding following this offering includes shares represented by CDIs.
As a result of the lock-up agreements described below and the provisions of Rule 144 and Rule 701 under the Securities Act, the shares of our common stock (excluding the shares to be sold in this offering) that will be available for sale in the public market are as follows:
| | shares will be eligible for sale on the date of this prospectus or prior to 180 days after the date of this prospectus; and |
| | shares will be eligible for sale upon the expiration of the lock-up agreements beginning 180 days after the date of this prospectus and when permitted under Rule 144 or Rule 701. |
Lock-Up Arrangements
In connection with the completion of this offering, all of our directors and executive officers and certain of our shareholders will enter into lock-up agreements with the underwriters pursuant to which they will agree not to offer, pledge, sell, contract to sell, sell any option or contract to purchase, purchase any option or contract to sell, grant any option, right or warrant to purchase, lend or otherwise transfer or dispose of, directly or indirectly, any shares of common stock or any securities convertible into or exercisable or exchangeable for shares of common stock for a period of at least 180 days following the date of this prospectus, subject to certain exceptions. As a result of these contractual restrictions, shares of our common stock and the other securities subject to lock-up agreements will not be eligible for sale until these agreements expire or the restrictions are waived by the underwriters. The representatives of the underwriters may, in their discretion, release any of the securities subject to lock-up restrictions with the underwriters in whole or in part at any time. See Underwriting.
Rule 144
In general, under Rule 144 as in effect on the date of this prospectus, once we have been subject to public company reporting requirements for at least 90 days, a person who has beneficially owned shares proposed to be sold for at least six months, including the holding period of any prior owner other than an affiliate of us, and who is not deemed to have been one of our affiliates for purposes of the Securities Act at any time during the 90 days preceding a sale, will be entitled to sell, upon expiration of the lock-up agreements described above, such shares
140
Table of Contents
without complying with the manner of sale, volume limitation or notice provisions of Rule 144, subject to compliance with the public information requirements of Rule 144. Such a non-affiliated person who has beneficially owned the shares proposed to be sold for at least one year, including the holding period of any prior owner other than an affiliate of us, will be entitled to sell these shares without limitation.
In general, under Rule 144, our affiliates or persons selling shares on behalf of our affiliates will be entitled to sell upon expiration of the 180-day lock-up period described above, within any three-month period, a number of shares that does not exceed the greater of:
| | 1% of the number of shares of our common stock then outstanding, which will equal approximately shares immediately after this offering (or shares if the underwriters elect to exercise in full their option to purchase additional shares); or |
| | the average weekly trading volume of our common stock on the NYSE during the four calendar weeks before a notice of the sale is filed on Form 144 with respect to such sale. |
Sales by our affiliates or persons selling shares on behalf of our affiliates under Rule 144 also are subject to manner of sale and notice provisions and to the availability of public information about us.
Rule 701
In general, under Rule 701 under the Securities Act, any of our employees, directors, officers, consultants or advisors who purchases shares from us in connection with a compensatory stock or option plan or other written agreement before the effective date of this offering is entitled to sell such shares 90 days after the effective date of this offering in reliance on Rule 144, without having to comply with the holding period requirement of Rule 144 and, in the case of non-affiliates, without having to comply with the public information, volume limitation or notice filing provisions of Rule 144. The SEC has indicated that Rule 701 will apply to typical stock options granted by an issuer before it becomes subject to the reporting requirements of the Exchange Act, along with the shares acquired upon exercise of such options, including exercises after the date of this prospectus.
Section 3(a)(10)
Section 3(a)(10) of the Securities Act is an exemption from registration for offers and sales of securities in specified exchange transactions, subject to certain requirements, including obtaining approval from a court or authorized governmental entity that the exchange is fair to the security holders participating in the exchange. Section 3(a)(10) generally allows a stockholder who received shares of our common stock or CDIs pursuant to the corporate reorganization, who is not deemed to be an affiliate (as defined above) of our company and who has not been such an affiliate of ours within 90 days of the corporate reorganization, to sell these shares and CDIs without regard to Rule 144. Section 3(a)(10) also permits stockholders who are affiliates of our company to sell their shares and CDIs received in the corporate reorganization under Rule 144. The shares of our common stock and CDIs distributed in the corporate reorganization were entitled to the exemption provided by Section 3(a)(10), subject to the foregoing limitation applicable to affiliates.
Registration Statement on Form S-8
We intend to file with the SEC a registration statement on Form S-8 under the Securities Act promptly after the completion of this offering to register shares of our common stock subject to equity-based incentive awards which were granted under the Equity Incentive Plan, and which are reserved for future issuance under our Equity Incentive Plan. See Executive and Director Compensation Equity Incentive Plan. The registration statement on Form S-8 is expected to become effective immediately upon filing, and shares of our common stock covered by the registration statement will then become eligible for sale in the public market, subject to the Rule 144 limitations applicable to affiliates and vesting restrictions.
141
Table of Contents
The following is a summary of certain considerations associated with the acquisition and holding of shares of our common stock by employee benefit plans that are subject to Title I of the Employee Retirement Income Security Act of 1974, as amended (ERISA), plans, individual retirement accounts and other arrangements that are subject to Section 4975 of the Code or employee benefit plans that are governmental plans (as defined in Section 3(32) of ERISA), certain church plans (as defined in Section 3(33) of ERISA), non-U.S. plans (as described in Section 4(b)(4) of ERISA) or other plans that are not subject to the foregoing but may be subject to provisions under any other federal, state, local, non-U.S. or other laws or regulations that are similar to such provisions of ERISA or the Code (collectively, Similar Laws), and entities whose underlying assets are considered to include plan assets of any such plan, account or arrangement (each, a Plan).
This summary is based on the provisions of ERISA and the Code (and related regulations and administrative and judicial interpretations) as of the date of this registration statement. This summary does not purport to be complete, and no assurance can be given that future legislation, court decisions, regulations, rulings or pronouncements will not significantly modify the requirements summarized below. Any of these changes may be retroactive and may thereby apply to transactions entered into prior to the date of their enactment or release. This discussion is general in nature and is not intended to be all inclusive, nor should it be construed as investment or legal advice.
General Fiduciary Matters
ERISA and the Code impose certain duties on persons who are fiduciaries of a Plan subject to Title I of ERISA or Section 4975 of the Code (an ERISA Plan) and prohibit certain transactions involving the assets of an ERISA Plan and its fiduciaries or other interested parties. Under ERISA and the Code, any person who exercises any discretionary authority or control over the administration of an ERISA Plan or the management or disposition of the assets of an ERISA Plan, or who renders investment advice for a fee or other compensation to an ERISA Plan, is generally considered to be a fiduciary of the ERISA Plan.
In considering an investment in shares of our common stock with a portion of the assets of any Plan, a fiduciary should consider the Plans particular circumstances and all of the facts and circumstances of the investment and determine whether the acquisition and holding of shares of our common stock is in accordance with the documents and instruments governing the Plan and the applicable provisions of ERISA, the Code, or any Similar Law relating to the fiduciarys duties to the Plan, including, without limitation:
| | whether the investment is prudent under Section 404(a)(1)(B) of ERISA and any other applicable Similar Laws; |
| | whether, in making the investment, the ERISA Plan will satisfy the diversification requirements of Section 404(a)(1)(C) of ERISA and any other applicable Similar Laws; |
| | whether the investment is permitted under the terms of the applicable documents governing the Plan; |
| | whether in the future there may be no market in which to sell or otherwise dispose of the shares of our common stock; |
| | whether the acquisition or holding of the shares of our common stock will constitute a prohibited transaction under Section 406 of ERISA or Section 4975 of the Code (see discussion under Prohibited Transaction Issues); and |
| | whether the Plan will be considered to hold, as plan assets, (i) only shares of our common stock or (ii) an undivided interest in our underlying assets (see the discussion under Plan Asset Issues). |
Prohibited Transaction Issues
Section 406 of ERISA and Section 4975 of the Code prohibit ERISA Plans from engaging in specified transactions involving plan assets with persons or entities who are parties in interest, within the meaning of
142
Table of Contents
ERISA, or disqualified persons, within the meaning of Section 4975 of the Code, unless an exemption is available. A party in interest or disqualified person who engages in a non-exempt prohibited transaction may be subject to excise taxes and other penalties and liabilities under ERISA and the Code. In addition, the fiduciary of the ERISA Plan that engages in such a non-exempt prohibited transaction may be subject to excise taxes, penalties and liabilities under ERISA and the Code. The acquisition and/or holding of shares of our common stock by an ERISA Plan with respect to which the issuer, the initial purchaser, or a guarantor is considered a party in interest or a disqualified person may constitute or result in a direct or indirect prohibited transaction under Section 406 of ERISA and/or Section 4975 of the Code, unless the investment is acquired and is held in accordance with an applicable statutory, class or individual prohibited transaction exemption.
Because of the foregoing, shares of our common stock should not be acquired or held by any person investing plan assets of any Plan, unless such acquisition and holding will not constitute a non-exempt prohibited transaction under ERISA and the Code or a similar violation of any applicable Similar Laws.
Plan Asset Issues
Additionally, a fiduciary of a Plan should consider whether the Plan will, by investing in us, be deemed to own an undivided interest in our assets, with the result that we would become a fiduciary of the Plan and our operations would be subject to the regulatory restrictions of ERISA, including its prohibited transaction rules, as well as the prohibited transaction rules of the Code and any other applicable Similar Laws.
The Department of Labor (the DOL) regulations provide guidance with respect to whether the assets of an entity in which ERISA Plans acquire equity interests would be deemed plan assets under some circumstances. Under these regulations, an entitys assets generally would not be considered to be plan assets if, among other things:
(a) the equity interests acquired by ERISA Plans are publicly offered securities (as defined in the DOL regulations) i.e., the equity interests are part of a class of securities that is widely held by 100 or more investors independent of the issuer and each other, are freely transferable, and are either registered under certain provisions of the federal securities laws or sold to the ERISA Plan as part of a public offering under certain conditions;
(b) the entity is an operating company (as defined in the DOL regulations) i.e., it is primarily engaged in the production or sale of a product or service, other than the investment of capital, either directly or through a majority-owned subsidiary or subsidiaries; or
(c) there is no significant investment by benefit plan investors (as defined in the DOL regulations) i.e., immediately after the most recent acquisition by an ERISA Plan of any equity interest in the entity, less than 25% of the total value of each class of equity interest (disregarding certain interests held by persons (other than benefit plan investors) with discretionary authority or control over the assets of the entity or who provide investment advice for a fee (direct or indirect) with respect to such assets, and any affiliates thereof) is held by ERISA Plans, individual retirement accounts and certain other Plans (but not including governmental plans, foreign plans and certain church plans), and entities whose underlying assets are deemed to include plan assets by reason of a Plans investment in the entity.
Due to the complexity of these rules and the excise taxes, penalties and liabilities that may be imposed upon persons involved in non-exempt prohibited transactions, it is particularly important that fiduciaries, or other persons considering acquiring and/or holding shares of our common stock on behalf of, or with the assets of, any Plan, consult with their counsel regarding the potential applicability of ERISA, Section 4975 of the Code and any Similar Laws to such investment and whether an exemption would be applicable to the acquisition and holding of shares of our common stock. Purchasers of shares of our common stock have the exclusive responsibility for ensuring that their acquisition and holding of shares of our common stock complies with the fiduciary
143
Table of Contents
responsibility rules of ERISA and does not violate the prohibited transaction rules of ERISA, the Code or applicable Similar Laws. The sale of shares of our common stock to a Plan is in no respect a representation by us or any of our affiliates or representatives that such an investment meets all relevant legal requirements with respect to investments by any such Plan or that such investment is appropriate for any such Plan.
144
Table of Contents
MATERIAL U.S. FEDERAL INCOME TAX CONSEQUENCES TO NON-U.S. HOLDERS OF OUR COMMON STOCK
The following discussion is a summary of the material U.S. federal income tax consequences to Non-U.S. Holders (as defined below) of the purchase, ownership, and disposition of our common stock issued pursuant to this offering, but does not purport to be a complete analysis of all potential tax effects. The effects of other U.S. federal tax laws, such as estate and gift tax laws, and any applicable state, local, or non-U.S. tax laws are not discussed.
This discussion is based on the Code, Treasury Regulations promulgated thereunder, judicial decisions, and published rulings and administrative pronouncements of the U.S. Internal Revenue Service (the IRS), in each case in effect as of the date hereof. These authorities may change or be subject to differing interpretations. Any such change or differing interpretation may be applied retroactively in a manner that could adversely affect a Non-U.S. Holder. We have not sought and will not seek any rulings from the IRS regarding the matters discussed below. There can be no assurance the IRS or a court will not take a contrary position to that discussed below regarding the tax consequences of the purchase, ownership, and disposition of our common stock.
This discussion is limited to Non-U.S. Holders that hold our common stock as a capital asset within the meaning of Section 1221 of the Code (generally, property held for investment). This discussion does not address all U.S. federal income tax consequences relevant to a Non-U.S. Holders particular circumstances, including the impact of the Medicare contribution tax on net investment income and the alternative minimum tax. In addition, it does not address consequences relevant to Non-U.S. Holders subject to special rules, including, without limitation:
| | U.S. expatriates and former citizens or long-term residents of the United States; |
| | persons holding our common stock as part of a hedge, straddle, or other risk reduction strategy or as part of a conversion transaction or other integrated investment; |
| | banks, insurance companies, and other financial institutions; |
| | brokers, dealers, or traders in securities; |
| | controlled foreign corporations, passive foreign investment companies, and corporations that accumulate earnings to avoid U.S. federal income tax; |
| | partnerships or other entities or arrangements treated as partnerships for U.S. federal income tax purposes (and investors therein); |
| | tax-exempt organizations or governmental organizations; |
| | persons deemed to sell our common stock under the constructive sale provisions of the Code; |
| | persons who hold or receive our common stock pursuant to the exercise of any employee stock option or otherwise as compensation; |
| | tax-qualified retirement plans; and |
| | qualified foreign pension funds as defined in Section 897(l)(2) of the Code and entities all of the interests of which are held by qualified foreign pension funds. |
If an entity or arrangement treated as a partnership for U.S. federal income tax purposes holds our common stock, the tax treatment of a partner in the partnership will depend on the status of the partner, the activities of the partnership, and certain determinations made at the partner level. Accordingly, partnerships holding our common stock and the partners in such partnerships should consult their tax advisors regarding the U.S. federal income tax consequences to them.
THIS DISCUSSION IS FOR INFORMATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY AND IS NOT TAX ADVICE. INVESTORS SHOULD CONSULT THEIR TAX ADVISORS WITH RESPECT TO THE APPLICATION OF
145
Table of Contents
THE U.S. FEDERAL INCOME TAX LAWS TO THEIR PARTICULAR SITUATIONS AS WELL AS ANY TAX CONSEQUENCES OF THE PURCHASE, OWNERSHIP, AND DISPOSITION OF OUR COMMON STOCK ARISING UNDER THE U.S. FEDERAL ESTATE OR GIFT TAX LAWS OR UNDER THE LAWS OF ANY STATE, LOCAL, OR NON-U.S. TAXING JURISDICTION OR UNDER ANY APPLICABLE INCOME TAX TREATY.
Definition of a Non-U.S. Holder
For purposes of this discussion, a Non-U.S. Holder is any beneficial owner of our common stock that is neither a U.S. person nor an entity treated as a partnership for U.S. federal income tax purposes. A U.S. person is any person that, for U.S. federal income tax purposes, is or is treated as any of the following:
| | an individual who is a citizen or resident of the United States; |
| | a corporation (or any other entity treated as a corporation for U.S. federal income tax purposes) created or organized under the laws of the United States, any state thereof, or the District of Columbia; |
| | an estate, the income of which is subject to U.S. federal income tax regardless of its source; or |
| | a trust if (1) a court within the United States is able to exercise primary supervision over the administration of the trust and one or more United States persons (within the meaning of Section 7701(a)(30) of the Code) have the authority to control all substantial decisions of the trust, or (2) it has a valid election in effect to be treated as a United States person for U.S. federal income tax purposes. |
Distributions
As described in the section entitled Dividend Policy, we do not anticipate declaring or paying dividends to holders of our common stock in the foreseeable future. However, if we do make distributions of cash or property on our common stock, such distributions will constitute dividends for U.S. federal income tax purposes to the extent paid from our current or accumulated earnings and profits, as determined under U.S. federal income tax principles. Amounts not treated as dividends for U.S. federal income tax purposes will constitute a return of capital and first be applied against and reduce a Non-U.S. Holders adjusted tax basis in its common stock, but not below zero. Any excess will be treated as capital gain and will be treated as described below under Sale or Other Taxable Disposition.
Subject to the discussion below on effectively connected income, dividends paid to a Non-U.S. Holder will be subject to U.S. federal withholding tax at a rate of 30% of the gross amount of the dividends (or such lower rate specified by an applicable income tax treaty, provided the Non-U.S. Holder furnishes a valid IRS Form W-8BEN or W-8BEN-E (or other applicable documentation) certifying qualification for the lower treaty rate). A Non-U.S. Holder that does not timely furnish the required documentation, but that qualifies for a reduced treaty rate, may obtain a refund of any excess amounts withheld by timely filing an appropriate claim for refund with the IRS. Non-U.S. Holders should consult their tax advisors regarding their entitlement to benefits under any applicable income tax treaty.
If dividends paid to a Non-U.S. Holder are effectively connected with the Non-U.S. Holders conduct of a trade or business within the United States (and, if required by an applicable income tax treaty, a permanent establishment or fixed base in the United States to which such dividends are attributable), the Non-U.S. Holder will be exempt from the U.S. federal withholding tax described above. To claim the exemption, the Non-U.S. Holder must furnish to the applicable withholding agent a valid IRS Form W-8ECI, certifying that the dividends are effectively connected with the Non-U.S. Holders conduct of a trade or business within the United States.
Any such effectively connected dividends will be subject to U.S. federal income tax on a net income basis at the regular rates. A Non-U.S. Holder that is a corporation also may be subject to a branch profits tax at a rate of
146
Table of Contents
30% (or such lower rate specified by an applicable income tax treaty) on such effectively connected dividends, as adjusted for certain items. Non-U.S. Holders should consult their tax advisors regarding any applicable tax treaties that may provide for different rules.
Sale or Other Taxable Disposition
A Non-U.S. Holder will not be subject to U.S. federal income tax on any gain realized upon the sale or other taxable disposition of our common stock unless:
| | the gain is effectively connected with the Non-U.S. Holders conduct of a trade or business within the United States (and, if required by an applicable income tax treaty, a permanent establishment or fixed base in the United States to which such gain is attributable); |
| | the Non-U.S. Holder is a nonresident alien individual present in the United States for 183 days or more during the taxable year of the disposition and certain other requirements are met; or |
| | our common stock constitutes a U.S. real property interest (USRPI) by reason of our status as a U.S. real property holding corporation (USRPHC) for U.S. federal income tax purposes. |
Gain described in the first bullet point above generally will be subject to U.S. federal income tax on a net income basis at the regular rates. A Non-U.S. Holder that is a corporation also may be subject to a branch profits tax at a rate of 30% (or such lower rate specified by an applicable income tax treaty) on such effectively connected gain, as adjusted for certain items.
A Non-U.S. Holder described in the second bullet point above will be subject to U.S. federal income tax at a rate of 30% (or such lower rate specified by an applicable income tax treaty) on gain realized upon the sale or other taxable disposition of our common stock, which may be offset by U.S. source capital losses of the Non-U.S. Holder (even though the individual is not considered a resident of the United States), provided the Non-U.S. Holder has timely filed U.S. federal income tax returns with respect to such losses.
With respect to the third bullet point above, we believe we currently are not, and do not anticipate becoming, a USRPHC. Because the determination of whether we are a USRPHC depends, however, on the fair market value of our USRPIs relative to the fair market value of our non-U.S. real property interests and our other business assets, there can be no assurance we currently are not a USRPHC or will not become one in the future. Even if we are or were to become a USRPHC, gain arising from the sale or other taxable disposition of our common stock by a Non-U.S. Holder will not be subject to U.S. federal income tax if our common stock is regularly traded, as defined by applicable Treasury Regulations, on an established securities market and such Non-U.S. Holder owned, actually and constructively, 5% or less of our common stock throughout the shorter of the five-year period ending on the date of the sale or other taxable disposition or the Non-U.S. Holders holding period.
Non-U.S. Holders should consult their tax advisors regarding potentially applicable income tax treaties that may provide for different rules.
Information Reporting and Backup Withholding
Payments of dividends on our common stock will not be subject to backup withholding, provided the applicable withholding agent does not have actual knowledge or reason to know the holder is a United States person and the holder either certifies its non-U.S. status, such as by furnishing a valid IRS Form W-8BEN, W-8BEN-E, or W-8ECI, or otherwise establishes an exemption. However, information returns are required to be filed with the IRS in connection with any distributions on our common stock paid to each Non-U.S. Holder, regardless of whether such distributions constitute dividends or whether any tax was actually withheld. In addition, proceeds of the sale or other taxable disposition of our common stock within the United States or
147
Table of Contents
conducted through certain U.S.-related brokers generally will not be subject to backup withholding or information reporting if the applicable withholding agent receives the certification described above and does not have actual knowledge or reason to know that such holder is a United States person or the holder otherwise establishes an exemption. Proceeds of a disposition of our common stock conducted through a non-U.S. office of a non-U.S. broker generally will not be subject to backup withholding or information reporting.
Copies of information returns that are filed with the IRS may also be made available under the provisions of an applicable treaty or agreement to the tax authorities of the country in which the Non-U.S. Holder resides or is established.
Backup withholding is not an additional tax. Any amounts withheld under the backup withholding rules may be allowed as a refund or a credit against a Non-U.S. Holders U.S. federal income tax liability, provided the required information is timely furnished to the IRS.
Additional Withholding Tax on Payments Made to Foreign Accounts
Withholding taxes may be imposed under Sections 1471 to 1474 of the Code (such Sections commonly referred to as the Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act, or FATCA) on certain types of payments made to non-U.S. financial institutions and certain other non-U.S. entities. Specifically, a 30% withholding tax may be imposed on dividends on, or (subject to the proposed Treasury Regulations discussed below) gross proceeds from the sale or other disposition of, our common stock paid to a foreign financial institution or a non-financial foreign entity (each as defined in the Code), unless (1) the foreign financial institution undertakes certain diligence and reporting obligations, (2) the non-financial foreign entity either certifies it does not have any substantial United States owners (as defined in the Code) or furnishes identifying information regarding each substantial United States owner, or (3) the foreign financial institution or non-financial foreign entity otherwise qualifies for an exemption from these rules. If the payee is a foreign financial institution (that is not otherwise exempt) and is subject to the diligence and reporting requirements in (1) above, it must enter into an agreement with the U.S. Department of the Treasury requiring, among other things, that it undertake to identify accounts held by certain specified United States persons or United States owned foreign entities (each as defined in the Code), annually report certain information about such accounts, and withhold 30% on certain payments to non-compliant foreign financial institutions and certain other account holders. Foreign financial institutions located in jurisdictions that have an intergovernmental agreement with the United States governing FATCA may be subject to different rules.
Under the applicable Treasury Regulations and administrative guidance, withholding under FATCA generally applies to payments of dividends on our common stock. While withholding under FATCA would have applied also to payments of gross proceeds from the sale or other disposition of stock on or after January 1, 2019, proposed Treasury Regulations eliminate FATCA withholding on payments of gross proceeds entirely. Taxpayers generally may rely on these proposed Treasury Regulations until final Treasury Regulations are issued.
Prospective investors should consult their tax advisors regarding the potential application of withholding under FATCA to their investment in our common stock.
148
Table of Contents
BofA Securities, Inc. and Citigroup Global Markets Inc. are acting as representatives of each of the underwriters named below. Subject to the terms and conditions set forth in an underwriting agreement among us and the underwriters, we have agreed to sell to the underwriters, and each of the underwriters has agreed, severally and not jointly, to purchase from us, the number of shares of common stock set forth opposite its name below.
| Underwriter |
Number of Shares |
|||
| BofA Securities, Inc. |
||||
| Citigroup Global Markets Inc |
||||
|
|
|
|||
| Total |
||||
|
|
|
|||
Subject to the terms and conditions set forth in the underwriting agreement, the underwriters have agreed, severally and not jointly, to purchase all of the shares sold under the underwriting agreement if any of these shares are purchased. If an underwriter defaults, the underwriting agreement provides that the purchase commitments of the nondefaulting underwriters may be increased or the underwriting agreement may be terminated.
We have agreed to indemnify the underwriters against certain liabilities, including liabilities under the Securities Act, or to contribute to payments the underwriters may be required to make in respect of those liabilities.
The underwriters are offering the shares, subject to prior sale, when, as and if issued to and accepted by them, subject to approval of legal matters by their counsel, including the validity of the shares, and other conditions contained in the underwriting agreement, such as the receipt by the underwriters of officers certificates and legal opinions. The underwriters reserve the right to withdraw, cancel or modify offers to the public and to reject orders in whole or in part.
Commissions and Discounts
The representatives have advised us that the underwriters propose initially to offer the shares to the public at the public offering price set forth on the cover page of this prospectus and to dealers at that price less a concession not in excess of $ per share. After the initial offering, the public offering price, concession or any other term of the offering may be changed.
The following table shows the public offering price, underwriting discount and proceeds before expenses to us. The information assumes either no exercise or full exercise by the underwriters of their option to purchase additional shares.
| Per Share | Without Option |
With Option |
||||||||||
| Public offering price |
$ | $ | $ | |||||||||
| Underwriting discount |
$ | $ | $ | |||||||||
| Proceeds, before expenses, to us |
$ | $ | $ | |||||||||
The expenses of the offering, not including the underwriting discount, are estimated at $ and are payable by us.
Option to Purchase Additional Shares
We have granted an option to the underwriters, exercisable for 30 days after the date of this prospectus, to purchase up to additional shares at the public offering price, less the underwriting discount. If the
149
Table of Contents
underwriters exercise this option, each will be obligated, subject to conditions contained in the underwriting agreement, to purchase a number of additional shares proportionate to that underwriters initial amount reflected in the above table.
No Sales of Similar Securities
We, our executive officers and directors and our other existing security holders have agreed not to sell or transfer any common stock or securities convertible into, exchangeable for, exercisable for, or repayable with common stock, for 180 days after the date of this prospectus without first obtaining the written consent of BofA Securities, Inc. and Citigroup Global Markets Inc. Specifically, we and these other persons have agreed, with certain limited exceptions, not to directly or indirectly
| | offer, sell, issue, contract to sell, pledge or otherwise dispose of any common stock, |
| | offer, sell, issue, contract to sell, contract to purchase or grant any option, right or warrant to purchase any common stock, |
| | enter into any swap, hedge or any other agreement that transfers, in whole or in part, the economic consequences of ownership of any common stock, |
| | establish or increase a put equivalent position or liquidate or decrease a call equivalent position in any common stock, or |
| | file a registration statement relating to any common stock, or publicly disclose the intention to take any such action, without the prior written consent of BofA Securities, Inc. and Citigroup Global Markets Inc. |
This lock-up provision applies to common stock and to securities convertible into or exchangeable or exercisable for or repayable with common stock. It also applies to common stock owned now or acquired later by the person executing the agreement or for which the person executing the agreement later acquires the power of disposition.
New York Stock Exchange Listing
We expect the shares to be approved for listing on the New York Stock Exchange under the symbol TBN. In order to meet the requirements for listing on that exchange, the underwriters have undertaken to sell a minimum number of shares to a minimum number of beneficial owners as required by that exchange.
Before this offering, there has been no public market for our common stock. The initial public offering price will be determined through negotiations between us and the representatives. In addition to prevailing market conditions, the factors to be considered in determining the initial public offering price are:
| | the currently prevailing general conditions in equity securities markets, including current market valuations of publicly traded companies that the representatives believe to be comparable to us, |
| | our financial information, |
| | the history of, and the prospects for, our company and the industry in which we compete, |
| | an assessment of our management, its past and present operations, and the prospects for, and timing of, our future revenues, |
| | the present state of our development, and |
| | the above factors in relation to market values and various valuation measures of other companies engaged in activities similar to ours. |
An active trading market for the shares may not develop. It is also possible that after the offering the shares will not trade in the public market at or above the initial public offering price.
150
Table of Contents
The underwriters do not expect to sell more than 5% of the shares in the aggregate to accounts over which they exercise discretionary authority.
Price Stabilization, Short Positions and Penalty Bids
Until the distribution of the shares is completed, SEC rules may limit underwriters and selling group members from bidding for and purchasing our common stock. However, the representatives may engage in transactions that stabilize the price of the common stock, such as bids or purchases to peg, fix or maintain that price.
In connection with the offering, the underwriters may purchase and sell our common stock in the open market. These transactions may include short sales, purchases on the open market to cover positions created by short sales and stabilizing transactions. Short sales involve the sale by the underwriters of a greater number of shares than they are required to purchase in the offering. Covered short sales are sales made in an amount not greater than the underwriters option to purchase additional shares described above. The underwriters may close out any covered short position by either exercising their option to purchase additional shares or purchasing shares in the open market. In determining the source of shares to close out the covered short position, the underwriters will consider, among other things, the price of shares available for purchase in the open market as compared to the price at which they may purchase shares through the option granted to them. Naked short sales are sales in excess of such option. The underwriters must close out any naked short position by purchasing shares in the open market. A naked short position is more likely to be created if the underwriters are concerned that there may be downward pressure on the price of our common stock in the open market after pricing that could adversely affect investors who purchase in the offering. Stabilizing transactions consist of various bids for or purchases of shares of common stock made by the underwriters in the open market prior to the completion of the offering.
The underwriters may also impose a penalty bid. This occurs when a particular underwriter repays to the underwriters a portion of the underwriting discount received by it because the representatives have repurchased shares sold by or for the account of such underwriter in stabilizing or short covering transactions.
Similar to other purchase transactions, the underwriters purchases to cover the syndicate short sales may have the effect of raising or maintaining the market price of our common stock or preventing or retarding a decline in the market price of our common stock. As a result, the price of our common stock may be higher than the price that might otherwise exist in the open market. The underwriters may conduct these transactions on the New York Stock Exchange, in the over-the-counter market or otherwise.
Neither we nor any of the underwriters make any representation or prediction as to the direction or magnitude of any effect that the transactions described above may have on the price of our common stock. In addition, neither we nor any of the underwriters make any representation that the representatives will engage in these transactions or that these transactions, once commenced, will not be discontinued without notice.
Electronic Distribution
In connection with the offering, certain of the underwriters or securities dealers may distribute prospectuses by electronic means, such as e-mail.
Other Relationships
Some of the underwriters and their respective affiliates have engaged in, and may in the future engage in, investment banking and other commercial dealings in the ordinary course of business with us or our affiliates. They have received, or may in the future receive, customary fees and commissions for these transactions.
In addition, in the ordinary course of their business activities, the underwriters and their respective affiliates may make or hold a broad array of investments and actively trade debt and equity securities (or related derivative
151
Table of Contents
securities) and financial instruments (including bank loans) for their own account and for the accounts of their customers. Such investments and securities activities may involve securities and/or instruments of ours or our affiliates. The underwriters and their affiliates may also make investment recommendations and/or publish or express independent research views in respect of such securities or financial instruments and may hold, or recommend to clients that they acquire, long and/or short positions in such securities and instruments.
152
Table of Contents
The validity of the common stock offered hereby and certain other legal matters in connection with this offering will be passed upon for us by Latham & Watkins LLP, Austin, Texas. Certain legal matters in connection with this offering will be passed upon for the underwriters by Clifford Chance US LLP, Houston, Texas.
153
Table of Contents
The consolidated financial statements of Tamboran Resources Limited at June 30, 2023 and 2022, and for each of the two years in the period ended June 30, 2023 appearing in this prospectus and Registration Statement have been audited by Ernst & Young, independent registered public accounting firm, as set forth in their report thereon (which contains an explanatory paragraph describing conditions that raise substantial doubt about the Companys ability to continue as a going concern as described in Note 1 to the consolidated financial statements) appearing elsewhere herein, and are included in reliance upon such report given on the authority of such firm as experts in accounting and auditing.
From February to October 2023, Ernst & Young (EY) provided tax credit advisory services under a contingent fee arrangement to the Predecessor. This fee arrangement is permissible under the International Ethics Standards Board for Accountants Code of Ethics and Australian home country independence rules but is inconsistent with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission and Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) independence rules. The contingent fee arrangement was terminated prior to EY becoming engaged as the Predecessors auditor under PCAOB standards. Total fees received by EY under the contingent fee arrangement were insignificant to the respective parties.
After careful consideration of the facts and circumstances and the applicable independence rules, EY has concluded that (i) the aforementioned matter does not impair its ability to exercise objective and impartial judgment in connection with its audits of the Predecessors consolidated financial statements, and (ii) a reasonable investor with knowledge of all relevant facts and circumstances would reach the same conclusion. After considering this matter, management and the Audit & Risk Management Committee concurred with EYs conclusions.
154
Table of Contents
WHERE YOU CAN FIND MORE INFORMATION
We have filed with the SEC a registration statement on Form S-1 under the Securities Act with respect to the shares of common stock offered by this prospectus. This prospectus, which constitutes a part of the registration statement, does not contain all of the information set forth in the registration statement, some of which is contained in exhibits to the registration statement as permitted by the rules and regulations of the SEC. For further information with respect to us and our common stock, we refer you to the registration statement, including the exhibits filed as part of the registration statement. Statements contained in this prospectus concerning the contents of any contract or any other document are not necessarily complete, and each such statement is qualified in all respects by reference to the full text of such contract or other document filed as an exhibit to the registration statement.
The SEC maintains an internet website that contains reports, proxy and information statements, and other information regarding issuers that file electronically with the SEC at www.sec.gov. Our filings with the SEC, including the registration statement, are available to you for free on the SECs internet website.
Upon completion of this offering, we will become subject to the informational and reporting requirements of the Exchange Act and, in accordance with those requirements, will file reports and proxy and information statements with the SEC.
We also maintain an internet website at www.tamboran.com and we expect to make our periodic reports and other information filed with or furnished to the SEC available, free of charge, through our website, as soon as reasonably practicable after those reports and other information are electronically filed with or furnished to the SEC. Information on or accessible through our website is not incorporated by reference into this prospectus and does not constitute a part of this prospectus.
155
Table of Contents
TAMBORAN RESOURCES LIMITED
INDEX TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
| Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm (PCAOB: 1435) |
F-2 | |||
| Audited Consolidated Financial Statements: |
||||
| F-3 | ||||
| F-4 | ||||
| Consolidated Statements of Stockholders Equity for the Years Ended June 30, 2023 and 2022 |
F-5 | |||
| Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows for the Years Ended June 30, 2023 and 2022 |
F-6 | |||
| F-7 | ||||
| Unaudited Information: |
||||
| F-28 |
F-1
Table of Contents
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Shareholders and the Board of Directors of Tamboran Resources Limited
Opinion on the Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Tamboran Resources Limited and subsidiaries (the Company) as of June 30, 2023 and 2022, the related consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive income, shareholders equity and cash flows for each of the two years in the period ended June 30, 2023 and 2022, and the related notes (collectively referred to as the consolidated financial statements). In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company at June 30, 2023 and 2022, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the two years in the period ending June 30, 2023, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
The Companys Ability to Continue as a Going Concern
The accompanying consolidated financial statements have been prepared assuming that the Company will continue as a going concern. As discussed in Note 1 to the financial statements, the Company has suffered recurring losses from operations, has a working capital deficiency, and has stated that substantial doubt exists about the Companys ability to continue as a going concern. Managements evaluation of the events and conditions and managements plans regarding these matters are also described in Note 1. The consolidated financial statements do not include any adjustments that might result from the outcome of this uncertainty.
Basis for Opinion
These financial statements are the responsibility of the Companys management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Companys financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB) and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. The Company is not required to have, nor were we engaged to perform, an audit of its internal control over financial reporting. As part of our audits, we are required to obtain an understanding of internal control over financial reporting but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Companys internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion.
Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
/s/ Ernst & Young
We have served as the Companys auditor since 2019.
Sydney, Australia
February 1, 2024
F-2
Table of Contents
TAMBORAN RESOURCES LIMITED
(In dollars)
| June 30, | ||||||||||||
| Note | 2023 | 2022 | ||||||||||
| ASSETS |
||||||||||||
| Current assets |
||||||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 6,426,306 | $ | 18,469,563 | ||||||||
| Restricted cash |
629,830 | | ||||||||||
| Accounts receivable, net |
829,753 | 209,608 | ||||||||||
| Assets held for sale |
4 | 8,818,509 | | |||||||||
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
317,634 | 2,465,185 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Total current assets |
17,022,032 | 21,144,356 | ||||||||||
| Natural gas properties, successful efforts method: |
||||||||||||
| Unproved properties |
4 | 163,385,971 | 55,469,992 | |||||||||
| Property, plant and equipment, net |
4 | 197,571 | 11,278,723 | |||||||||
| Operating lease right-of-use assets |
5 | 459,113 | 748,471 | |||||||||
| Prepaid expenses and other non-current assets |
1,788,168 | 706,860 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Total non-current assets |
165,830,823 | 68,204,046 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| TOTAL ASSETS |
$ | 182,852,855 | $ | 89,348,402 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| LIABILITIES AND SHAREHOLDERS EQUITY |
||||||||||||
| Current liabilities |
||||||||||||
| Accounts payable and accrued expenses |
6 | $ | 14,471,663 | $ | 2,905,657 | |||||||
| Current portion of operating lease obligations |
5 | 280,962 | 131,391 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Total current liabilities |
14,752,625 | 3,037,048 | ||||||||||
| Operating lease obligations |
5 | 198,743 | 636,312 | |||||||||
| Asset retirement obligations |
7 | 7,182,739 | 903,169 | |||||||||
| Other non-current liabilities |
8 | 137,802 | 90,547 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Total non-current liabilities |
7,519,284 | 1,630,028 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Total liabilities |
22,271,909 | 4,667,076 | ||||||||||
| Commitments and contingencies (Note 13) |
||||||||||||
| Shareholders equity |
||||||||||||
| Common stock, no par value; unlimited shares authorized; 1,416,010,751 and 747,359,518 shares issued and outstanding as at June 30, 2023 and 2022, respectively |
9 | 252,177,665 | 167,562,860 | |||||||||
| Additional paid-in capital |
7,128,236 | 6,219,331 | ||||||||||
| Accumulated other comprehensive loss |
(10,770,359 | ) | (12,672,912 | ) | ||||||||
| Accumulated deficit |
(108,461,300 | ) | (76,427,953 | ) | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Total Tamboran Resources shareholders equity |
140,074,242 | 84,681,326 | ||||||||||
| Noncontrolling interest |
20,506,704 | | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Total shareholders equity |
160,580,946 | 84,681,326 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| TOTAL LIABILITIES AND SHAREHOLDERS EQUITY |
$ | 182,852,855 | $ | 89,348,402 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
F-3
Table of Contents
TAMBORAN RESOURCES LIMITED
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS AND COMPREHENSIVE LOSS
(In dollars)
| For the years ended June 30, | ||||||||||||
| Note | 2023 | 2022 | ||||||||||
| Revenue and other operating income |
$ | | $ | | ||||||||
| Operating costs and expenses |
||||||||||||
| Compensation and benefits, excluding stock-based compensation |
(5,432,367 | ) | (2,627,281 | ) | ||||||||
| Stock-based compensation |
(908,905 | ) | (1,056,819 | ) | ||||||||
| Consultancy, legal and professional fees |
(6,817,659 | ) | (2,707,880 | ) | ||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization |
4 | (118,331 | ) | (127,540 | ) | |||||||
| Loss on of assets classified as held for sale |
4 | (12,584,768 | ) | | ||||||||
| Accretion of asset retirement obligations |
7 | (600,959 | ) | (78,993 | ) | |||||||
| Exploration expense |
(2,793,036 | ) | (1,707,377 | ) | ||||||||
| General and administrative |
(2,763,470 | ) | (1,636,727 | ) | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Total operating costs and expenses |
(32,019,495 | ) | (9,942,617 | ) | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Loss from operations |
(32,019,495 | ) | (9,942,617 | ) | ||||||||
| Other income (expense) |
||||||||||||
| Interest income (expense), net |
31,001 | (6,297 | ) | |||||||||
| Foreign exchange gain, net |
130,329 | 470,925 | ||||||||||
| Other expenses |
(337,451 | ) | (144,079 | ) | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Total other (expense)/income |
(176,121 | ) | 320,549 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Net loss |
(32,195,616 | ) | (9,622,068 | ) | ||||||||
| Less: Net loss attributable to non-controlling interest |
(162,269 | ) | | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Net loss attributable to Tamboran Resources shareholders |
$ | (32,033,347 | ) | $ | (9,622,068 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Comprehensive loss |
||||||||||||
| Net loss |
$ | (32,195,616 | ) | $ | (9,622,068 | ) | ||||||
| Other comprehensive income (loss) |
||||||||||||
| Foreign currency translation |
1,632,670 | (7,277,704 | ) | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Total comprehensive loss |
(30,562,946 | ) | (16,899,772 | ) | ||||||||
| Less: Total comprehensive loss attributable to noncontrolling interest |
(107,614 | ) | | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Total comprehensive loss attributable to Tamboran Resources shareholders |
$ | (30,455,332 | ) | $ | (16,899,772 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Net loss per common share |
||||||||||||
| Basic and diluted |
12 | $ | (0.026 | ) | $ | (0.014 | ) | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Weighted average number of common shares outstanding |
||||||||||||
| Basic and diluted |
12 | 1,210,408,816 | 708,265,427 | |||||||||
F-4
Table of Contents
TAMBORAN RESOURCES LIMITED
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF STOCKHOLDERS EQUITY
(In dollars)
| Common stock |
Additional paid-in capital |
Accumulated other comprehensive loss |
Accumulated deficit |
Total Tamboran Resources shareholders equity |
Noncontrolling interest |
Total shareholders equity |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance at July 1, 2021 |
$ | 143,580,043 | $ | 5,162,512 | $ | (5,395,208 | ) | $ | (66,805,885 | ) | $ | 76,541,462 | $ | | $ | 76,541,462 | ||||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock, net of issuance cost |
23,982,817 | | | | 23,982,817 | | 23,982,817 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock-based compensation |
| 1,056,819 | | | 1,056,819 | | 1,056,819 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Foreign exchange translation |
| | (7,277,704 | ) | | (7,277,704 | ) | | (7,277,704 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Net loss |
| | | (9,622,068 | ) | (9,622,068 | ) | | (9,622,068 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Balance at June 30, 2022 |
167,562,860 | 6,219,331 | (12,672,912 | ) | (76,427,953 | ) | 84,681,326 | | 84,681,326 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock, net of issuance cost |
84,614,805 | | | | 84,614,805 | | 84,614,805 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Contributions from noncontrolling interestholders |
| | | | | 20,938,856 | 20,938,856 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock-based compensation |
| 908,905 | | | 908,905 | 908,905 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Foreign exchange translation |
| | 1,902,553 | | 1,902,553 | | 1,632,670 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Net loss |
| | | (32,033,347 | ) | (32,033,347 | ) | (162,269 | ) | (32,195,616 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Balance at June 30, 2023 |
$ | 252,177,665 | $ | 7,128,236 | $ | (10,770,359 | ) | $ | (108,461,300 | ) | $ | 140,074,242 | $ | 20,506,704 | $ | 160,580,946 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
F-5
Table of Contents
TAMBORAN RESOURCES LIMITED
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
(In dollars)
| For the years ended June 30, | ||||||||
| 2023 | 2022 | |||||||
| Cash flows from operating activities: |
||||||||
| Net loss |
$ | (32,195,616 | ) | $ | (9,622,068 | ) | ||
| Adjustments to reconcile net loss to net cash provided by operating activities: |
||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization |
118,331 | 127,540 | ||||||
| Stock-based compensation |
908,905 | 1,056,819 | ||||||
| Foreign exchange gain, net |
(130,329 | ) | (470,925 | ) | ||||
| Loss on assets classified as held for sale |
12,584,768 | | ||||||
| Accretion of asset retirement obligations |
600,959 | 78,993 | ||||||
| Changes in operating assets and liabilities: |
||||||||
| Accounts receivables |
(620,145 | ) | 95,938 | |||||
| Prepaid expenses and other assets |
215,655 | (780,588 | ) | |||||
| Accounts payable and accrued expenses |
5,666,375 | (515,536 | ) | |||||
| Other non-current liabilities |
47,255 | 19,028 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Net cash used in operating activities |
(12,803,842 | ) | (10,010,799 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Cash flows from investing activities: |
||||||||
| Payment for expenses relating to acquisitions |
| (745,888 | ) | |||||
| Payments for investments |
(809,700 | ) | (148,546 | ) | ||||
| Payments for property, plant and equipment |
(12,835,149 | ) | (11,053,232 | ) | ||||
| Payments for exploration and evaluation |
(100,522,571 | ) | (26,798,269 | ) | ||||
| Proceeds from sale of property, plant and equipment |
2,463,100 | | ||||||
| Proceeds from government grants for exploration |
4,239,622 | | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Net cash used in investing activities |
(107,464,698 | ) | (38,745,935 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Cash flows from financing activities: |
||||||||
| Proceeds from issue of shares |
88,704,922 | 24,964,736 | ||||||
| Contributions received from noncontrolling interestholders |
20,938,856 | | ||||||
| Proceeds from issue of securities, awaiting issuance |
629,830 | | ||||||
| Share issue transaction costs |
(4,090,117 | ) | (981,919 | ) | ||||
| Repayment of lease liabilities |
| (242,318 | ) | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Net cash from financing activities |
106,183,491 | 23,740,499 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Net increase/(decrease) in cash and cash equivalents and restricted cash |
(14,085,049 | ) | (25,016,235 | ) | ||||
| Cash and cash equivalents and restricted cash at the beginning of period |
18,469,563 | 47,426,342 | ||||||
| Effects of exchange rate changes on cash and cash equivalents |
2,671,622 | (3,940,544 | ) | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Cash and cash equivalents and restricted cash at the end of period |
$ | 7,056,136 | $ | 18,469,563 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Supplemental cash flow information: |
||||||||
| Non-cash investing and financing activities: |
||||||||
| Accrued capital expenditure |
$ | 5,269,801 | $ | 1,846,005 | ||||
| Asset retirement obligations |
$ | (5,698,464 | ) | $ | (459,021 | ) | ||
| Equity-based stock compensation |
$ | (908,905 | ) | $ | (1,056,819 | ) | ||
| Right-of-use assets and lease liabilties |
$ | 289,358 | $ | 970,320 | ||||
F-6
Table of Contents
TAMBORAN RESOURCES LIMITED
NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 1 Nature of the Organization and Business
Organization
Tamboran Resources Limited (the Company or Tamboran and together with its consolidated subsidiaries, the Group) is a growth-oriented natural gas company with a vision of supporting the net zero CO2 energy transition in Australia and Asia-Pacific through developing low CO2 unconventional gas resources in the Northern Territory of Australia. The Company was established in 2009 as an Australian private entity pursuing unconventional shale exploration opportunities. On July 2, 2021, the Company became public and commenced trading as a listed entity on the Australian Stock Exchange (ASX). The Group is in the exploration stage with current focus on exploiting its primary assets, which are rights to working interests (Tenements) in exploration acreage in the Beetaloo sub-basin (Beetaloo or Beetaloo Basin), Northern Territory (NT), Australia. During November 2022, Tamboran completed the acquisition of Beetaloo Basin assets via exploration permits EP 76, 98 and 117 in a 50:50 joint venture with Daly Waters Energy, LP (DWE), a wholly owned subsidiary of Sheffield Holdings, LP (Sheffield), a related party. DWE and Tamboran each hold 38.75% with existing partner, Falcon Oil and Gas Australia Limited (Falcon or Falcon Oil & Gas), holding the remaining 22.5% working interest. The acquisition positions Tamboran as the largest acreage owner in the Beetaloo Basin, with approximately 1.9 million net prospective acres. To date, the Group has not determined whether the Tenements contains any natural gas reserves that are economically recoverable. Therefore, the Group has no revenues from its gas operations as of June 30, 2023.
Going concern and Managements liquidity plans
The accompanying consolidated financial statements have been prepared on the basis that the Group will continue as a going concern which contemplates the realization of assets and the satisfaction of liabilities in the ordinary and usual course of business.
As of June 30, 2023, the Group has:
| | not generated revenues since inception, and is unlikely to generate earnings in the immediate or foreseeable future; |
| | a working capital deficit of $6,549,102 (excluding assets of disposal group held for sale); |
| | an accumulated deficit of $108,461,300 since inception; and |
| | significant expenditures planned for the unproved properties in the next twelve months. |
These factors raise substantial doubt regarding the Groups ability to continue as a going concern for the 12 months following the date these financial statements were available for issuance. The continuation of the Group as a going concern is dependent upon the ability of the Group to obtain necessary additional capital to fund ongoing exploration projects and/or obtain oil and gas producing properties to attain future profitable operations. No assurance can be given that the Company will be successful in these efforts in the future.
Management has several plans in various stages of progress to source additional funding to provide operating capital for continued growth of the Group. Therefore, these consolidated financial statements do not include any adjustments related to the recoverability and classification of recorded asset amounts and classification of liabilities that might be necessary should the Group be unable to continue as a going concern.
F-7
Table of Contents
Note 2 Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Basis of Preparation
The accompanying consolidated financial statements have been prepared in conformity with the accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (U.S. GAAP) and rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC).
Managements Use of Estimates
The preparation of the Groups consolidated financial statements in conformity with U.S. GAAP requires management to make judgements, estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, revenues and expenses, as well as various disclosures in these consolidated financial statements. Management bases its judgements, estimates and assumptions on historical experience and on other various factors, including expectations of future events management believes to be reasonable under the circumstances. The most significant estimates included in, but not limited to, the preparation of these consolidated financial statements are related to asset retirement obligations, stock-based compensation and recoverability of oil and gas properties.
Although management believes these estimates are reasonable, these estimates and assumptions are subject to a number of risks and uncertainties that may cause actual results to differ materially from such estimates.
Principles of Consolidation
The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of the Company, all of its wholly owned subsidiaries and the variable interest entities (VIE), for which the Company or any of its subsidiaries is a primary beneficiary. All intercompany transactions, balances and unrealized gains on transactions between entities in the Group are eliminated upon consolidation. Unrealized losses are also eliminated unless the transaction provides evidence of the impairment of the asset transferred. Accounting policies of subsidiaries have been changed where necessary to ensure consistency with the policies adopted by the Group.
Under ASC 810, Consolidation, a reporting entity is the primary beneficiary if the reporting entity has both of the following characteristics: (a) the power to direct the activities of the VIE that most significantly affect the VIEs economic performance; and (b) the obligation to absorb losses, or the right to receive benefits, that could potentially be significant to the VIE.
Foreign Currency Translation
These consolidated financial statements are presented in US dollars ($ or dollars) and the functional currency of the Company is the Australian Dollar (A$). Adjustments resulting from the translation of functional currency financial statements to reporting currency are accumulated and reported as a part of Accumulated Other Comprehensive Loss, a separate component of shareholders equity.
Foreign currency transactions
Foreign currency transactions are translated into the Companys functional currency using the exchange rates prevailing at the dates of the transactions. Foreign exchange gains and losses resulting from the settlement of such transactions and from the translation at financial year-end exchange rates of monetary assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currencies are recognized in the consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive loss.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
Cash represents cash deposits held at financial institutions. Cash equivalents include short-term highly liquid investments of sufficient credit quality that are readily convertible to known amounts of cash and have
F-8
Table of Contents
original maturities of three months or less. As of June 30, 2023, the Group had $629,830 in restricted cash, which relates to cash received for shares, for which the shares had not yet been issued. The Group had no restricted cash as of June 30, 2022.
Accounts Receivable
As of June 30, 2023 and 2022, accounts receivable includes goods and services tax receivable from the Australian Taxation Office.
Accounts receivable are recognized net of an allowance for doubtful accounts for expected credit losses, in the period when the Groups right to consideration is unconditional. The Group has no allowance for doubtful accounts related to its accounts receivable for any reporting period presented.
Government Grants
Government grants are recorded as a reduction of the related expense or cost of the asset acquired or constructed. Government grants are recognized when there is reasonable assurance that the Group has met the requirements of the approved grant program and there is reasonable assurance that the grant will be received.
Grants that compensate the Group for expenses incurred are recognized in the consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive loss in reduction thereof on a systematic basis in the same years in which the related expenses are recognized. Grants that compensate the Group for the cost of an asset are recognized as a reduction in the carrying amount of the asset (i.e. the asset is accounted for on the basis of its net acquisition cost). The grant is then recognized in the consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive loss over the life of the depreciable asset in the form of reduced depreciation expense.
As of June 30, 2022, the Group had earned but not yet received $1,785,749, related to these grants and incentives included in prepaid expenses and other current assets, respectively. As of June 30, 2023, the Group had received a total of $4,239,622 related to these grants and incentives including the portion which had been earned but not yet received as of the previous balance sheet date.
Natural Gas Properties
The Group is in the exploration stage and has not yet realized any revenues from its operations. The Group holds a number of exploration permits that are grouped into areas of interest according to geographical and geological attributes. Expenditure incurred in each area of interest is accounted for using the successful efforts method, as defined within ASC 932, Extractive Activities Oil and Gas.
Under this method, all general exploration and evaluation costs such as geological and geophysical costs are expensed as incurred. The direct costs of acquiring the rights to explore, drilling exploratory wells and evaluating the results of drilling are capitalized as exploration and evaluation assets (as a part of unproved properties) pending the determination of the results of the well. If a well does not result in hydrocarbons being present, the previously capitalized costs are immediately expensed.
The carrying amounts of exploration and evaluation assets are reviewed at each reporting date to determine whether any indicators of impairment are present. Indicators of impairment include, but are not limited to:
| | the right to explore has expired, or will expire in the near future, and is not expected to be renewed; |
| | further exploration for and evaluation of resources in the specific area is not budgeted or planned for; |
| | the Group has decided to discontinue activities in the area; or |
F-9
Table of Contents
| | there is sufficient data to indicate the carrying value is unlikely to be recovered in full, from successful development or by sale based on changes brought by economic factors, commodity price outlook, favorable and/or unfavorable exploration activity on the property being evaluated and/or adjacent property. |
Where an indicator of impairment exists for an unproved property and it is determined that future appraisal drilling or development activities are unlikely to occur, an impairment expense is recorded.
Upon approval of the commercial development of a project, the exploration and evaluation asset is classified as a development asset. Once production commences, development assets are transferred to property, plant and equipment and are depleted using the unit-of-production method based upon estimates of proved developed reserves.
Property, Plant and Equipment
Property, plant and equipment is stated at historical cost less accumulated depreciation and impairment, if any. Historical cost includes expenditure that is directly attributable to the acquisition of these items.
Depreciation is calculated on a straight-line basis over the expected useful lives of the asset as follows:
| Leasehold improvements | Shorter of useful life (5 years) or unexpired period of lease term | |
| Machinery work-in-progress | Not depreciated until machinery is fully operational |
An item of property, plant and equipment is derecognized upon disposal or when there is no future economic benefit to the Group. Gains and losses between the carrying amount and the disposal proceeds are taken to profit or loss.
Intangible Assets
Intangible assets acquired as part of a business combination, other than goodwill, are initially measured at their fair value at the date of the acquisition. Intangible assets acquired separately are initially recognized at cost. Indefinite life intangible assets are not amortized and are subsequently measured at cost less any impairment. Finite life intangible assets are subsequently measured at cost less amortization and any impairment. The gains or losses recognized in consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive loss arising from the derecognition of intangible assets are measured as the difference between net disposal proceeds and the carrying amount of the intangible asset. The method and useful lives of finite life intangible assets are reviewed annually.
Changes in the expected pattern of consumption or useful life are accounted for prospectively by changing the amortization method or period.
Leases
The Group accounts for leases under ASC 842, Leases. The Group determines if an arrangement is a lease at inception of the arrangement and if such lease will be classified as an operating lease or a finance lease. As of June 30, 2023 and 2022, all of the Groups leases are classified as operating leases.
Operating leases are included in Operating lease right-of-use assets within the Groups consolidated balance sheet and represent the Groups right to use an underlying asset for the lease term. The Groups related obligation to make lease payments are included in Current portion of operating lease obligations and Operating lease obligations within the Groups consolidated balance sheet. Operating lease right-of-use (ROU) assets and liabilities are recognized at lease commencement date based on the present value of lease payments over the lease term. As the Groups lease does not provide an implicit rate, the Group used its incremental borrowing rate, which is the rate incurred to borrow on a collateralized basis over a similar term, an amount equal to the lease payments in a similar economic environment.
F-10
Table of Contents
Lease expense for lease payments is recognized on a straight-line basis over the lease term.
Leases with a lease term of 12 months or less are not recorded on the balance sheet and are recognized as
lease expense on a straight-line basis over the lease term. When it is reasonably certain the Group will exercise an option to extend the short term lease beyond 12 months, the cost will be capitalized.
As of June 30, 2023 and 2022, the Groups operating ROU assets and corresponding current and non-current lease liabilities relate to its office, which expires March 10, 2025.
Impairment of Long-lived Assets
Impairment of long-lived assets is recorded when indicators of impairment are present and the undiscounted cash flows estimated to be generated by those assets are less than the assets carrying value. The carrying value of the asset is then reduced to its estimated fair value which is usually measured based on an estimate of future discounted cash flows.
Joint Interest Activities
Some of the Groups exploration, development and production activities are conducted jointly with other entities whereby each party holds an undivided interest in each asset and is proportionately liable for each liability in the scope of such arrangement. The Group has recognized its proportionate share of assets, liabilities, revenues and expenses in respect of such arrangements. These have been incorporated in the consolidated financial statements under the appropriate classifications.
Asset Retirement Obligation
The Groups asset retirement obligation relates to the plugging, dismantling, removal, site reclamation and similar activities of its natural gas properties. The Group accrues the costs to dismantle and remove gas-related facilities upon exhaustion of reserves and related surface reclamation in accordance with ASC 410, Asset Retirement and Environmental Obligations. The Group recognizes the fair value of an asset retirement obligation as liabilities with an increase to the carrying amounts of the related long-lived assets in the period in which it is incurred if a reasonable estimate of fair value can be made. The asset retirement obligation is recorded as a liability at its estimated present value of expected future net cash flows and are discounted using the Groups credit adjusted risk-free rate. Over time, the liability is accreted to its present value, and the capitalized cost is depleted over the useful life of the related asset. Estimates are regularly reviewed by management and are revised for changes in future estimated costs and regulatory requirements. Revisions to estimated asset retirement obligations will result in an adjustment to the related capitalized asset and corresponding liability. Upon settlement of the liability, the Group either settles the obligation for its recorded amount or incurs a gain or loss.
Employee Benefits
Short-term employee benefits
Liabilities for wages and salaries, including non-monetary benefits expected to be settled wholly within 12 months of the reporting date, are measured at the amounts expected to be paid when the liabilities are settled.
Compensated absences
The Group provides annual leave and long service leave to its employees. These compensated absences are accounted for in accordance with ASC 710, Compensated Absences. The Group recognizes its liabilities for compensated absences depending on whether the obligation is attributable to employee services already rendered, rights to compensated absences vest or accumulate and payment is probable and estimable. The current and non-current compensated absences are included in Accounts payable and accrued expenses and Other non-current liabilities, respectively.
F-11
Table of Contents
Defined contribution superannuation plan
Contributions to defined contribution superannuation plans are expensed in the period in which they are incurred. The Group contributed $311,080 and $146,672 towards the superannuation plan during the years ended June 30, 2023 and 2022, respectively.
Stock-based Compensation
The Group applies the provisions of ASC 718, Compensation Stock Compensation, which requires the measurement and recognition of compensation expense for all stock-based awards made to employees and non-employees, including employee stock options, in the consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive loss. Stock-based compensation awards granted to employees are measured using the grant date fair value of the awards and the resulting expense is recognized over the period during which the employees are required to perform service in exchange for the awards.
Stock-based compensation awards issued to non-employees for goods or services, are measured at either the grant date fair value of the goods or services received, or the instruments issued in exchange for such goods or services, whichever is more readily determinable.
The fair value of stock-based compensation awards that vest based on market conditions is measured using a Monte Carlo simulation model on the date of the grant. The fair value of stock options that vest based on service conditions is measured using the Black-Scholes option pricing model on the date of the grant. The Monte Carlo simulation model and the Black-Scholes option pricing model require the input of highly subjective assumptions, including, the term of the awards, the impact of dilution, the share price at grant date and expected price volatility of the underlying share, the expected dividend yield and the risk free interest rate for the term of the option, together with non-vesting conditions that do not determine whether the Group receives the services that entitle the employees or non-employees to receive payment.
Stock-based compensation expense is recognized on a straight-line basis over the vesting period for awards that are only subject to service conditions. The cumulative charge to consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive loss is calculated based on the grant date fair value of the award, the best estimate of the number of awards that are likely to vest and the expired portion of the vesting period.
The amount recognized in consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive loss for the period is the cumulative amount calculated at each reporting date less amounts already recognized in previous periods. Stock-based compensation expense is recognized using the accelerated attribution method for awards that are subject to market conditions.
Market conditions are taken into consideration in determining the fair value. Therefore, any awards subject to market conditions are considered to vest irrespective of whether or not that market condition has been met, provided all other conditions are satisfied. In certain circumstances where there are no future performance requirements by the employees and non-employees and the stock-based compensation awards are immediately vested, the total stock-based compensation expense is recorded in the period of the measurement date.
If there are any modifications or cancellations of the underlying unvested awards, the Group may be required to accelerate or increase any remaining unearned share-based compensation expense.
Fair Value Measurements
ASC 820, Fair Value Measurement defines fair value as the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date; and assumes that the transaction will take place either: in the principal market; or in the absence of a principal market, in the most advantageous market.
F-12
Table of Contents
Fair value is measured using the assumptions that market participants would use when pricing the asset or liability, assuming they act in their economic best interests. For non-financial assets, the fair value measurement is based on its highest and best use. Valuation techniques that are appropriate in the circumstances and for which sufficient data are available to measure fair value, are used, maximizing the use of relevant observable inputs and minimizing the use of unobservable inputs.
Assets and liabilities measured at fair value are classified into three levels, using a fair value hierarchy that reflects the significance of the inputs used in making the measurements as follows:
| Level 1: | Quoted (unadjusted) prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities. |
| Level 2: | Inputs other than quoted prices included within Level 1 that are directly observable for the asset or liability or indirectly observable through corroboration with observable market data. |
| Level 3: | Unobservable inputs for the asset or liability only used when there is little, if any, market activity for the asset or liability at the measurement date. |
Classifications are reviewed at each reporting date and transfers between levels are determined based on a reassessment of the lowest level of input that is significant to the fair value measurement.
Fair value on a recurring basis
There were no material financial assets and liabilities accounted for at fair value on a recurring basis as of June 30, 2023 and 2022.
Fair value on a non-recurring basis
The Group applies the provisions of the fair value measurement standard on a non-recurring basis to its non-financial assets and liabilities, including oil and gas properties and asset retirement obligations. These assets and liabilities are not measured at fair value on an ongoing basis but are subject to fair value adjustments if events or changes in certain circumstances indicate that adjustments may be necessary. Refer to Note 7 for fair value measurement of asset retirement obligations.
Items not recorded at fair value
The carrying amounts reported on the consolidated balance sheet for cash and cash equivalents, restricted cash, accounts receivable, prepaid expenses, other assets, accounts payable, accrued expenses and other current liabilities approximate their fair values.
Income Taxes
The Group accounts for income taxes under the asset and liability method in accordance with ASC 740, Income Taxes. The asset and liability method requires the recognition of deferred tax assets and liabilities for the expected future tax consequences of temporary differences between the financial reporting and tax bases of assets and liabilities and for operating loss and tax credit carry forwards. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured using the currently enacted tax rates in effect for the years in which the differences are expected to reverse. Deferred tax is charged or credited in consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive loss, except when it is related to items credited or charged directly to equity, in which case the deferred tax is also dealt with in equity. The effect of a change in tax rates on deferred tax assets and liabilities is recognized in consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive loss in the period that includes the enactment date.
Deferred tax assets are recognized to the extent that it is probable that taxable profit will be available against which deductible temporary differences can be utilized. Deferred tax assets are reduced by a valuation allowance
F-13
Table of Contents
when, in the opinion of management, it is more likely than not that some portion or all of the deferred tax assets will not be realized. An uncertain tax position is recognized as a benefit only if it is more likely than not that the tax position would be sustained in a tax examination on the basis of the technical merits of the position. The amount recognized is the largest amount of tax benefit that is more than 50% likely of being realized on examination. For tax positions not meeting the more likely than not test, no tax benefit is recorded.
As of June 30, 2023 and 2022, the Group did not have any amounts recorded pertaining to uncertain tax positions. The Group did not have any interest or penalties related to income taxes for the years ended on June 30, 2023 and 2022.
Net Earnings/ (Loss) Per Share
Basic net earnings/ (loss) per share is calculated by dividing net earnings/ (loss) attributable to the owners of the Company by the weighted average number of common shares outstanding during the financial year, adjusted for bonus elements in common shares issued during the financial year.
Diluted earnings/ (loss) per share adjusts the figures used in the determination of basic earnings/ (loss) per share to take into account the after-income tax effect of interest and other financing costs associated with dilutive potential common shares and the weighted average number of additional common shares that would have been outstanding assuming conversion of all dilutive potential common shares.
Diluted loss per share is same as basic loss per share due to the lack of dilutive items in the Group for the financial years ended June 30, 2023 and 2022.
Concentration of Credit Risk
Credit risk represents the actual or perceived financial loss that the Group would record if its purchasers, operators, or counterparties failed to perform pursuant to contractual terms.
In the normal course of business, the Group maintains its cash in bank accounts with investment grade financial institutions. Management believes that the Groups counterparty risks are minimal based on the credit risk, reputation and history of the institutions selected.
The Group is not exposed to any significant credit risk.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
In December 2023, the FASB issued ASU 2023-09, Improvements to Income Tax Disclosures (ASU 2023-09), a final standard on improvements to income tax disclosures. The standard requires disaggregated information about a reporting entitys effective tax rate reconciliation as well as information on income taxes paid. The standard is intended to benefit investors by providing more detailed income tax disclosures that would be useful in making capital allocation decisions and applies to all entities subject to income taxes. The new standard is effective for annual periods beginning after December 15, 2024. The Group does not expect the adoption of this new guidance to have a material impact on the consolidated financial statements.
In November 2023, the FASB issued ASU 2023-07, Segment Reporting: Improvements to Reportable Segment Disclosures (ASU 2023-07). The amendments in the ASU require public business entities that disclose information on their reportable segments to provide additional information on their significant expense categories and other segment items, which represent the difference between segment revenue less significant segment expense and a segments measure of profit or loss. A description of other segment items is also required. Further, certain segment related disclosures that were limited to annual disclosure are now required at
F-14
Table of Contents
interim periods. Finally, public business entities are required to disclose the title and position of their Chief Operating Decision Maker (CODM) and explain how the CODM uses the reported measures of profit or loss to assess segment performance. This guidance is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2023, and interim periods within fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2024. The Group does not expect the adoption of ASU 2023-07 to have a material impact on the consolidated financial statements.
In October 2023, the FASB issued ASU 2023-06, Disclosure Improvements: Amendments - Codification Amendments in Response to the SECs Disclosure Update and Simplification Initiative (ASU 2023-06). The amendments in the ASU introduce changes to U.S. GAAP that originate in either SEC Regulation S-X or S-K, which are rules about the form and content of financial reports. The provisions of ASU 2023-06 are contingent upon the timing of removal of the related disclosure provisions from Regulation S-X and S-K by SEC. The Group does not expect the provisions of the standard to have a material impact on the Groups consolidated financial statements and related disclosures.
In August 2023, the FASB issued ASU 2023-05, Business Combinations - Joint Venture Formations: Recognition and Initial Measurement (ASU 2023-05), which clarifies the business combination accounting for joint venture formations. The amendments in the ASU seek to reduce diversity in practice that has resulted from a lack of authoritative guidance regarding the accounting for the formation of joint ventures in separate financial statements. The amendments also seek to clarify the initial measurement of joint venture net assets, including businesses contributed to a joint venture. ASU 2023-05 requires prospective application for all newly-formed joint venture entities with a formation date on or after January 1, 2025. Joint ventures formed prior to the adoption date may elect to apply the guidance retrospectively back to their original formation date with early adoption is permitted. The Group does not expect the adoption of ASU 2023-05 to have a material impact on the consolidated financial statements.
In March 2023, the FASB issued ASU 2023-02, Investments - Equity Method and Joint Ventures: Accounting for Investments in Tax Credit Structures Using the Proportional Amortization Method (a consensus of the Emerging Issues Task Force) (ASU 2023-02). The amendments in this update permit reporting entities to elect to account for their tax equity investments, regardless of the tax credit program from which the income tax credits are received, using the proportional amortization method if certain conditions are met. This update is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2023, including interim periods within those fiscal years. The Group does not expect the adoption of ASU 2023-02 to have a material impact on the consolidated financial statements.
In March 2023, the FASB issued ASU 2023-01, Leases: Common Control Arrangements (ASU 2023-01). The amendments in the update clarify the accounting for leasehold improvements associated with common control leases. This update is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2023, including interim periods within those fiscal years. The Group does not expect the adoption of ASU 2023-01 to have a material impact on the consolidated financial statements.
In December 2022, the FASB issued ASU 2022-06, Reference Rate Reform: Deferral of the Sunset Date of Topic 848 (ASU 2022-06). The amendments in this update defer the sunset date of Topic 848, which provides relief to entities affected by reference rate reform. The ASU defers the sunset date of Topic 848 from December 31, 2022, to December 31, 2025. The standard is effective immediately and the Group adopted the standard in December 2022 with no material financial impact on the consolidated financial statements.
In September 2022, the FASB issued ASU 2022-04, Liabilities -Supplier Finance Programs: Disclosure of Supplier Finance Program Obligations (ASU 2022-04). The amendments in the update require that buyers disclose qualitative and quantitative information about their supplier finance programs. Interim and annual requirements include disclosure of outstanding amounts under the obligations as of the end of the reporting period, and annual requirements include a rollforward of those obligations for the annual reporting period, as well as a description of payment and other key terms of the programs. This update is effective for annual periods
F-15
Table of Contents
beginning after December 15, 2022, and interim periods within those fiscal years, except for the requirement to disclose rollforward information, which is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2023. The Group does not expect the adoption of ASU 2022-04 to have a material impact on the consolidated financial statements.
In June 2022, the FASB issued ASU 2022-03, Fair Value Measurement Fair Value Measurement of Equity Securities Subject to Contractual Sale Restrictions (ASU 2022-03) which amends the guidance in Topic 820, Fair Value Measurement. The amendments in the update clarify that a contractual restriction on the sale of an equity security is not considered part of the unit of account of the equity security and, therefore, is not considered in measuring fair value. The amendments also clarify that an entity cannot, as a separate unit of account, recognize and measure a contractual sale restriction. In addition, the ASU introduces new disclosure requirements for equity securities subject to contractual sale restrictions that are measured at fair value. ASU 2022-03 is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2023, including interim periods within those fiscal years for public business entities. The Group does not expect the adoption of ASU 2022-03 to have a material impact on the consolidated financial statements.
In March 2022, the FASB issued ASU 2022-02, Financial Instruments - Credit Losses: Troubled Debt Restructurings and Vintage Disclosures (ASU 2022-02). The amendments in the update address and amend areas identified by the FASB as part of its post-implementation review of the accounting standard that introduced the current expected credit losses (CECL) model. The amendments eliminate the accounting guidance for troubled debt restructurings by creditors that have adopted the CECL model and enhance the disclosure requirements for loan refinancings and restructurings made with borrowers experiencing financial difficulty. In addition, the amendments require disclosure of current-period gross write-offs for financing receivables and net investment in leases by year of origination in the vintage disclosures. For entities that have not yet adopted the CECL accounting model in ASU 2016-13, the effective date for the amendments in ASU 2022-02 is the same as the effective date in ASU 2016-13 (i.e., fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2022, including interim periods within those fiscal years). The Group does not expect the adoption of ASU 2022-02 to have a material impact on the consolidated financial statements.
In March 2022, the FASB issued ASU 2022-01, Derivatives and Hedging: Fair Value Hedging - Portfolio Layer Method (ASU 2022-01). The amendments in the update address questions raised on ASU 2017-12, Derivatives and Hedging: Targeted Improvements to Accounting for Hedging Activities. The amendments in the update expand the currently used single-layer method of hedge accounting to allow multiple layers of a single closed portfolio under the method. ASU 2022-01 is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2022, and interim periods within those fiscal years. The Group does not expect the adoption of ASU 2022-01 to have a material impact on the consolidated financial statements.
In October 2021, the FASB issued ASU 2021-08, Business Combinations: Accounting for Contract Assets and Contract Liabilities from Contracts with Customers (ASU 2021-08). The amendments in the update requires contract assets and contract liabilities acquired in a business combination to be recognized and measured in accordance with ASC 606, Revenue from Contracts with Customers, on the acquisition date as if the acquirer had entered into the original contract at the same date and on the same terms as the acquiree. ASU 2021-08 is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2022, including interim periods within those fiscal years for public business entities. The Group does not expect the adoption of ASU 2021-08 to have a material impact on the consolidated financial statements.
Note 3 Variable Interest Entities
On September 18, 2022, Tamboran (West) Pty Ltd (West) entered into a 50/50 joint operation (VIE arrangement) with DWE to form Tamboran (B1) Pty Ltd (B1). The Company is identified as the manager of B1, and therefore has the overall responsibility to manage and carry out the day-to-day operations of B1 which most significantly impacts B1s economic performance. Pursuant to the VIE arrangement, the Company is
F-16
Table of Contents
deemed to be the primary beneficiary of B1. Accordingly, the results of B1 have been included in the accompanying consolidated financial statements. B1 has no assets that are collateral for or restricted solely to settle its obligations. The creditors of B1 do not have recourse to the Groups general credit.
A loan was provided to West from Tamboran Resources Limited. This loan was used by West to acquire its interest in B1. On November 9, 2022, B1 completed the acquisition of a 77.5% share of Beetaloo Basin assets, EP 76, EP 98, and EP 117. As a result of the VIE arrangement, the Company and Sheffield each acquired a 38.75% interest in the permits for the total undivided interest of 77.5%. Existing partner, Falcon holds the remaining undivided interest of 22.5% in the Beetaloo Basin assets.
The following table summarizes the carrying amounts of the B1s assets and liabilities included in the Companys Consolidated Balance Sheet for the year ended June 30, 2023:
| June 30, 2023 | ||||
| ASSETS |
||||
| Current assets |
||||
| Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 88,451 | ||
| Accounts receivable, net |
821,979 | |||
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
80,806 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Total current assets |
991,236 | |||
| Natural gas properties, successful efforts method: |
||||
| Unproved properties |
102,710,385 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Total non-current assets |
102,710,385 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| TOTAL ASSETS |
$ | 103,701,621 | ||
|
|
|
|||
| LIABILITIES |
||||
| Current liabilities |
||||
| Accounts payable and accrued expenses |
$ | 11,867,753 | ||
|
|
|
|||
| Total current liabilities |
11,867,753 | |||
| Asset retirement obligations |
3,650,758 | |||
| Loan from Tamboran |
46,257,798 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Total non-current liabilities |
49,908,556 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Total liabilities |
$ | 61,776,309 | ||
|
|
|
|||
Note 4 Property, Plant and Equipment & Natural Gas Properties
Natural gas properties
The Group held unproved gas properties as of June 30, 2023 and 2022 amounting to $163,385,971 and $55,469,992 respectively. These amounts reflect the Groups exploration projects, which are pending the determination of proven and probable reserves and were not being depleted for the years ended June 30, 2023 and 2022, respectively. These assets will be reclassified to proved gas properties when placed in service and then subsequently depleted.
During the years ended June 30, 2023 and 2022, the Group recognized no impairment related to unproved natural gas properties.
F-17
Table of Contents
Property, plant and equipment
| June 30, | ||||||||
| 2023 | 2022 | |||||||
| Leasehold improvements - at cost |
$ | 541,244 | $ | 562,388 | ||||
| Machinery work-in-progress - at cost |
| 10,952,384 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total property, plant and equipment |
541,244 | 11,514,772 | ||||||
| Less: Accumulated depreciation |
(343,673 | ) | (236,049 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total plant and equipment - net |
$ | 197,571 | $ | 11,278,723 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Depreciation expense for plant and equipment for the years ended June 30, 2023, and 2022 was $118,331 and $127,540, respectively.
Loss on assets classified as held for sale
On April 12, 2022, Tamboran entered into an agreement with HCI RMX, LLC to purchase rig 300, rig 301 and rig 403 (together HCI Rigs), for a total of $21,000,000, of which $10,000,000 was paid in 2022, and the remaining $11,000,000 was paid in 2023 in equal installments over the first six months of the period. On December 23, 2022, the HCI Rigs were classified as assets held for sale after Board approval.
During the year ended June 30, 2023, rig 300 and related parts were sold to a third party for $2,463,100, net of commission expenses. The loss on rig 301 was $3,336,802. Rig 301 and rig 403 remained unsold as of the balance sheet date. The Group plans to sell rig 301 and rig 403 through an online auction in the open market.
As of June 30, 2023, rig 301 and rig 403 have each been written down to the lower of their carrying amount and fair value less costs to sell. Accordingly, the loss recognized for rig 301 and rig 403 amounted to $9,247,966 for the year ended June 30, 2023.
For the year ended June 30, 2022, the Group recognized no losses on long-lived assets.
Note 5 Leases
The Groups operating lease activities consist of leases for office premises. The term of the lease is five years, with an option of three additional years. As of June 30, 2023 and 2022, the Groups leases had a weighted-average remaining lease term of 1.7 years and 2.7 years, respectively, and a weighted-average discount rate of 3.9% per annum. The discount rate used for this lease was based on a proxy of the Groups incremental borrowing rate at lease commencement.
The following table presents the classification and location of the Groups leases on the consolidated balance sheets:
| June 30, | ||||||||
| 2023 | 2022 | |||||||
| Operating leases: |
||||||||
| Operating lease right-of-use assets |
$ | 459,113 | $ | 748,471 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Current portion of operating lease obligations |
$ | 280,962 | $ | 131,391 | ||||
| Operating lease obligations |
198,743 | 636,312 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| $ | 479,705 | $ | 767,703 | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
F-18
Table of Contents
The following table presents the classification and location of the Groups lease costs in the consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive loss:
|
Statement of Operations and Comprehensive Loss |
For the years ended June 30, |
|||||||||
| 2023 | 2022 | |||||||||
| Operating lease expense |
General and administrative | $ | 289,970 | $ | 312,536 | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
The following table presents the cash flow information related to lease payments for the years ended June 30, 2023 and 2022:
| For the years ended June 30, |
||||||||
| 2023 | 2022 | |||||||
| Cash paid for amounts included in the measurement of lease liabilities: |
||||||||
| Operating cash flows for operating leases |
$ | 289,970 | $ | 312,536 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
As of June 30, 2023, the Groups undiscounted minimum cash payment obligations for its lease liabilities are as follows:
| Year ended June 30, |
||||
| 2024 |
$ | 294,734 | ||
| 2025 |
201,660 | |||
| 2026 |
| |||
| 2027 |
| |||
| Thereafter |
| |||
|
|
|
|||
| Total lease payments |
496,394 | |||
| Less: Imputed interest |
(16,689 | ) | ||
|
|
|
|||
| Present value of lease liabilities |
$ | 479,705 | ||
|
|
|
|||
Note 6 Accounts Payable and Accrued Expenses
Accounts payable and accrued expenses included in current liabilities consists of the following:
| June 30, | ||||||||
| 2023 | 2022 | |||||||
| Accounts payable |
$ | 4,205,015 | $ | 143,023 | ||||
| Accrued payroll |
435,987 | 211,258 | ||||||
| Compensated absences |
396,949 | 250,668 | ||||||
| Defined contribution superannuation payable |
7,520 | 8,456 | ||||||
| Accrued capital expenditure |
7,115,806 | 1,846,005 | ||||||
| Other |
2,310,386 | 446,247 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| $ | 14,471,663 | $ | 2,905,657 | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Note 7 Asset Retirement Obligations
The Groups recognizes the liability for an asset retirement obligation at their estimated fair value in the period in which the obligation originates. Fair value is estimated using the present value technique (level 2) based on a number of observable inputs including estimates and assumptions such as future retirement costs, future inflation rates and the Companys credit-adjusted risk-free interest rate.
F-19
Table of Contents
The Group capitalized the present value of the estimated asset retirement obligations as a part of the carrying amount of the related natural gas properties. The liability has been accreted to its present value for the year ended June 30, 2023. During the year ended June 30, 2023, the Group engaged an independent, third-party advisory firm, which reviewed the provisions recorded by the Group. The results of this review indicated the provisions recorded were in excess of what was required. As of June 30, 2023, the credit-adjusted risk-free interest rate ranged between 12.50% to 14.11% per annum considering the timing of expected settlement. As such, as of the end of the year, Tamboran has adjusted the provision to incorporate the feedback of the advisors.
The reconciliation of changes in asset retirement obligations is as follows:
| For the years ended June 30, | ||||||||
| 2023 | 2022 | |||||||
| Beginning asset retirement obligations |
$ | 903,169 | $ | 426,376 | ||||
| Associated with acquisitions |
4,143,966 | | ||||||
| Liabilities incurred |
3,842,925 | 459,021 | ||||||
| Accretion expense |
600,959 | 78,993 | ||||||
| Revision of estimates |
(2,288,427 | ) | | |||||
| Effect of changes in foreign exchange rates |
(19,853 | ) | (61,221 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Long-term asset retirement obligations |
$ | 7,182,739 | $ | 903,169 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Note 8 Other Non-current Liabilities
| June 30, | ||||||||
| 2023 | 2022 | |||||||
| Compensated absences |
$ | 137,802 | $ | 90,547 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Note 9 Stockholders Equity
|
2023 Shares |
2022 Shares |
2023 Amount |
2022 Amount |
|||||||||||||
| Common stock issued and outstanding |
1,416,010,751 | 747,359,518 | $ | 252,177,665 | $ | 167,562,860 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
Movements in common stock:
| Date | Shares | Issue price | Amount | |||||||||||||
| Balance at July 1, 2021 |
652,860,557 | $ | 143,580,043 | |||||||||||||
| Issue of ordinary shares |
November 29, 2021 | 94,498,961 | $ | 0.2642 | 24,964,736 | |||||||||||
| Less: Share issue transaction costs |
(981,919 | ) | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Balance at June 30, 2022 |
747,359,518 | 167,562,860 | ||||||||||||||
| Issue of ordinary shares |
September 29, 2022 | 186,839,878 | $ | 0.1358 | 25,370,240 | |||||||||||
| Issue of ordinary shares |
October 20, 2022 | 465,612,410 | $ | 0.1313 | 61,150,740 | |||||||||||
| Issue of ordinary shares |
October 31, 2022 | 16,198,945 | $ | 0.1348 | 2,183,942 | |||||||||||
| Less: Share issue transaction costs |
(4,090,117 | ) | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Balance at June 30, 2023 |
1,416,010,751 | $ | 252,177,665 | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
F-20
Table of Contents
Holders of common stock are entitled to participate in any dividends declared and any proceeds attributable to common stockholders should the Company be wound up, in proportions that consider both the number of shares held and the extent to which those common stock are paid up. On a show of hands, every common stockholder present at a meeting in person or by proxy shall have one vote and upon a poll each share shall have one vote.
No dividends have been declared or paid by the Company through June 30, 2023 and 2022.
Note 10 Stock-based Compensation
Historically, incentives offered to the Board, employees and consultants have included a combination of options, warrants, and employee share scheme (ESS) instruments having either fixed exercise prices or variable prices based on multiples of the fair market value of the enterprise at grant date. The issued ESS grants were supported by limited recourse loans (treasury shares) for the value of the shares as at issuance date.
Equity incentive plan
The Group has adopted the Equity Incentive Plan in order to assist in the motivation and retention of selected employees and directors. Below is a summary of the terms and conditions of the options issued under the Equity Incentive Plan.
| Total number of options issued under the Equity Incentive Plan |
Vesting condition | Exercise price and expiry date | ||
| 10,734,584 options |
Fully vested | A$0.32 per option expiring on May 20, 2026 | ||
| 7,416,667 options |
Fully vested | A$0.2367 expiring on May 20, 2026 | ||
| 39,350,000 milestone options |
(1) 25% of milestone options vest if the 90-day VWAP is greater than or equal to A$1.00 per share
(2) 25% of milestone options vest if the 90-day VWAP is greater than or equal to A$1.50 per share
(3) 25% of milestone options vest if the 90-day VWAP is greater than or equal to A$2.00 per share
(4) 25% of milestone options vest if the 90-day VWAP is greater than or equal to A$2.50 per share |
A$0.40 per milestone option expiring on May 20, 2026 or, if the milestone options vest, the day that is 5 years after the date they vest as determined by the Board. | ||
Each option entitles the optionholder a right to buy one share upon exercise of the option and is exercisable at any time on or prior to May 20, 2026. Shares issued on exercise of the options will rank equally with the then shares of the Company. The options are not transferable.
The options may be exercised by notice in writing to the Company and payment of the relevant exercise price for each option being exercised. The Company will not apply to ASX for quotation of the options however it will apply to ASX for quotation of the shares issued upon the exercise of the options.
There are no participation rights or entitlements inherent in the options and holders will not be entitled to participate in new issues of capital offered to shareholders.
F-21
Table of Contents
If the Company makes a bonus issue of common stock or other securities to existing shareholders (other than an issue in lieu or in satisfaction of dividends or by way of dividend reinvestment) the number of shares which must be issued on the exercise of an option will be increased by the number of shares which the optionholder would have received if the optionholder had exercised the option before the record date for the bonus issue.
If the Company makes an issue of shares pro rata to existing shareholders (other than an issue in lieu or in satisfaction of dividends or by way of dividend reinvestment) the exercise price of an option will be reduced according to the ASX Listing Rules.
If there is any reconstruction of the issued common stock of the Company, the rights of the optionholders may be varied to comply with the ASX Listing Rules which apply to the reconstruction at the time of the reconstruction.
The following table summarizes stock option activity for the years ended June 30, 2023 and 2022:
2023
| Grant date |
Expiry date | Exercise price |
Balance at the start of the year |
Granted |
Exercised | Expired/ |
Balance at the |
|||||||||||||||
| May 20, 2021 |
May 20, 2026 | $ | A 0.2367 | 7,416,667 | | | | 7,416,667 | ||||||||||||||
| May 20, 2021 |
May 20, 2026 | $ | A 0.3200 | 10,734,548 | | | | 10,734,548 | ||||||||||||||
| May 20, 2021 |
May 20, 2026 | $ | A 0.4000 | 16,000,000 | | | | 16,000,000 | ||||||||||||||
| October 28, 2021 |
May 20, 2026 | $ | A 0.4000 | 20,750,000 | | | (1,900,000) | 18,850,000 | ||||||||||||||
| May 17, 2022 |
May 20, 2026 | $ | A 0.4000 | 400,000 | | | | 400,000 | ||||||||||||||
| June 14, 2022 |
May 20, 2026 | $ | A 0.4000 | 1,250,000 | | | | 1,250,000 | ||||||||||||||
| November 30, 2022 |
May 20, 2026 | $ | A 0.4000 | | 2,850,000 | | | 2,850,000 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
| 56,551,215 | 2,850,000 | | (1,900,000) | 57,501,215 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
| Weighted average exercise price |
$A 0.3634 | $A 0.4000 | $A | $A 0.4000 | $A 0.3640 | |||||||||||||||||
2022
| Grant date |
Expiry date | Exercise price |
Balance at the start of the year |
Granted |
Exercised | Expired/ |
Balance at |
|||||||||||||||
| April 19, 2021 |
November 30, 2021 | $ | A 0.3200 | 2,819,290 | | | (2,819,290) | | ||||||||||||||
| May 20, 2021 |
May 20, 2026 | $ | A 0.2367 | 7,416,667 | | | | 7,416,667 | ||||||||||||||
| May 20, 2021 |
May 20, 2026 | $ | A 0.3200 | 10,734,548 | | | | 10,734,548 | ||||||||||||||
| May 20, 2021 |
May 20, 2026 | $ | A 0.4000 | 16,000,000 | | | | 16,000,000 | ||||||||||||||
| October 28, 2021 |
May 20, 2026 | $ | A 0.4000 | | 22,750,000 | | (2,000,000) | 20,750,000 | ||||||||||||||
| May 17, 2022 |
May 20, 2026 | $ | A 0.4000 | | 400,000 | | | 400,000 | ||||||||||||||
| June 14, 2022 |
May 20, 2026 | $ | A 0.4000 | | 1,250,000 | | | 1,250,000 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
| 36,970,505 | 24,400,000 | | (4,819,290) | 56,551,215 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
| Weighted average exercise price |
$A 0.3379 | $A 0.4000 | $A | $A 0.3532 | $A 0.3634 | |||||||||||||||||
Set out below are the options exercisable at the end of the financial year:
| Number at June 30, | ||||||||||||
| Grant date |
Expiry date | 2023 | 2022 | |||||||||
| 20/05/2021 |
20/05/2026 | 7,416,667 | 7,416,667 | |||||||||
| 20/05/2021 |
20/05/2026 | 10,734,584 | 10,734,584 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| 18,151,251 | 18,151,251 | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
F-22
Table of Contents
The weighted average remaining contractual life of options outstanding as of June 30, 2023 and 2022, was 2.89 years and 3.89 years, respectively.
For the milestone options granted during the year ended on June 30, 2023 and 2022, the Monte-Carlo valuation model inputs used to determine the fair value at the grant date, are as follows:
| Grant date |
Expiry date | Share price at grant date |
Exercise price |
Expected volatility |
Dividend yield |
Risk-free interest rate |
Fair value at grant date |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| October 28, 2021 |
May 20, 2026 | A$ | 0.4000 | A$ | 0.4000 | 65.0000 | % | | 1.4809 | % | A$ | 0.1815 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| October 28, 2021 |
May 20, 2026 | A$ | 0.4000 | A$ | 0.4000 | 65.0000 | % | | 1.4809 | % | A$ | 0.1630 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| October 28, 2021 |
May 20, 2026 | A$ | 0.4000 | A$ | 0.4000 | 65.0000 | % | | 1.4809 | % | A$ | 0.1381 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| October 28, 2021 |
May 20, 2026 | A$ | 0.4000 | A$ | 0.4000 | 65.0000 | % | | 1.4809 | % | A$ | 0.1188 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| May 17, 2022 |
May 20, 2026 | A$ | 0.2800 | A$ | 0.4000 | 70.0000 | % | | 3.1430 | % | A$ | 0.1050 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| May 17, 2022 |
May 20, 2026 | A$ | 0.2800 | A$ | 0.4000 | 70.0000 | % | | 3.1430 | % | A$ | 0.0861 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| May 17, 2022 |
May 20, 2026 | A$ | 0.2800 | A$ | 0.4000 | 70.0000 | % | | 3.1430 | % | A$ | 0.0700 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| May 17, 2022 |
May 20, 2026 | A$ | 0.2800 | A$ | 0.4000 | 70.0000 | % | | 3.1430 | % | A$ | 0.0577 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| June 14, 2022 |
May 20, 2026 | A$ | 0.2300 | A$ | 0.4000 | 70.0000 | % | | 3.7490 | % | A$ | 0.0807 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| June 14, 2022 |
May 20, 2026 | A$ | 0.2300 | A$ | 0.4000 | 70.0000 | % | | 3.7490 | % | A$ | 0.0651 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| June 14, 2022 |
May 20, 2026 | A$ | 0.2300 | A$ | 0.4000 | 70.0000 | % | | 3.7490 | % | A$ | 0.0528 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| June 14, 2022 |
May 20, 2026 | A$ | 0.2300 | A$ | 0.4000 | 70.0000 | % | | 3.7490 | % | A$ | 0.0432 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| November 30, 2022 |
May 20, 2026 | A$ | 0.2600 | A$ | 0.4000 | 70.0000 | % | | 3.1160 | % | A$ | 0.0871 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| November 30, 2022 |
May 20, 2026 | A$ | 0.2600 | A$ | 0.4000 | 70.0000 | % | | 3.1160 | % | A$ | 0.0677 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| November 30, 2022 |
May 20, 2026 | A$ | 0.2600 | A$ | 0.4000 | 70.0000 | % | | 3.1160 | % | A$ | 0.0529 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| November 30, 2022 |
May 20, 2026 | A$ | 0.2600 | A$ | 0.4000 | 70.0000 | % | | 3.1160 | % | A$ | 0.0419 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Note 11 Income Taxes
Deferred income taxes reflect the net tax effects of (a) temporary differences between the carrying amounts of assets and liabilities for financial reporting purposes and the amounts used for income tax purposes, and (b) operating losses and tax credit carryforwards.
Significant components of deferred tax assets (liabilities) are as follows:
| June 30, | ||||||||
| 2023 | 2022 | |||||||
| Deferred tax assets: |
||||||||
| Asset retirement obligations |
$ | 90,620 | $ | | ||||
| Transaction costs arising on shares issued |
2,640,335 | 2,587,610 | ||||||
| Tax losses carried forward |
57,624,887 | 25,220,031 | ||||||
| Leases |
6,178 | | ||||||
| Employee benefits |
160,425 | 281,736 | ||||||
| Other |
245,745 | | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total deferred tax assets |
60,768,190 | 28,089,377 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Deferred tax liabilities: |
||||||||
| Leases |
| (33,648 | ) | |||||
| Exploration assets |
(43,424,967 | ) | (16,769,158 | ) | ||||
| Other |
| (79,548 | ) | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total deferred tax liabilities |
(43,424,967 | ) | (16,882,354 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total net deferred tax assets |
17,343,223 | 11,207,023 | ||||||
| Less: Valuation allowance |
(17,343,223 | ) | (11,207,023 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Net deferred tax assets |
$ | | $ | | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
F-23
Table of Contents
The Australian statutory tax rate is 30%. The income tax provision differs from the amount of income tax determined by applying Australian income tax rate to pretax income as follows:
| For the years ended June 30, | ||||||||
| 2023 | 2022 | |||||||
| Loss before income tax expense |
$ | (32,195,616 | ) | $ | (9,622,068 | ) | ||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Tax at the Australian statutory rate of 30% (2022: 30%) |
(9,658,685 | ) | (2,886,620 | ) | ||||
| Permanent differences |
3,342,216 | 377,824 | ||||||
| Earnings in jurisdictions taxed at rates different from the statutory tax rate |
180,269 | (2,698 | ) | |||||
| Valuation allowance recognised |
6,136,200 | 2,511,494 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Income tax expense |
$ | | $ | | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
The Group has no income tax expense due to operating losses incurred for the years ended June 30, 2023 and 2022. The Group has provided a full valuation allowance on the net deferred tax asset because management has determined that it is more-likely-than-not that the Group will not earn income sufficient to realize the deferred tax assets during a foreseeable future period. Management will continue to assess the potential for realizing deferred tax assets based upon income forecast data and the feasibility of future tax planning strategies and may record adjustments to the valuation allowance against deferred tax assets in future periods, as appropriate, that could have a material impact on the statement of operations.
The Group has accumulated losses for tax purposes as of June 30, 2023, in the amount of $192,082,957 which may be carried forward and offset against taxable income in the future for an indefinite period, subject to meeting Australian tax rules around continuity of ownership or business continuity test.
Note 12 Earnings/ (Loss) per Share
Basic net earnings/ (loss) per share applicable to common stockholders is computed by dividing earnings applicable to common stockholders by the weighted average number of common shares outstanding. Diluted earnings/ (loss) per share assumes the conversion of any convertible securities using the treasury stock method.
The computations for basic and diluted loss per share are as follows:
| For the years ended June 30, | ||||||||
| 2023 | 2022 | |||||||
| Numerator: |
||||||||
| Net loss after income tax attributable to Tamboran Resources shareholders |
$ | (32,033,347 | ) | $ | (9,622,068 | ) | ||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Denominator: |
||||||||
| Weighted average number of ordinary shares outstanding, basic and diluted |
1,210,408,816 | 708,265,427 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Net loss per share, basic and diluted |
$ | (0.026 | ) | $ | (0.014 | ) | ||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
The Companys potentially dilutive shares, which include outstanding common stock options, have not been included in the computation of diluted net loss per share for the years ended June 30, 2023 and 2022 as the result would be anti-dilutive.
Note 13 Commitments and Contingencies
From time to time, the Group may be subject to various claims, title matters and legal proceedings arising in the ordinary course of business, including environmental contamination claims, personal injury and property
F-24
Table of Contents
damage claims, claims related to joint interest billings and other matters under natural gas operating agreements and other contractual disputes. The Group maintains general liability and other insurance to cover some of these potential liabilities. All known liabilities are fully accrued based on the Groups best estimate of the potential settlement amount. While the outcome and impact on the Group cannot be predicted with certainty, the Group believes that its ultimate liability with respect to any such matters will not have a significant impact or material adverse effect on its financial positions, results of operations or cash flows. Results of operations and cash flows, however, could be significantly impacted in the reporting periods in which such matters are resolved.
Capital commitments
| June 30, | ||||||||
| 2023 | 2022 | |||||||
| Committed at the reporting date but not recognised as liabilities, payable: |
||||||||
| Sweetpea Petroleum Pty Ltd |
$ | 42,465,150 | $ | 32,102,740 | ||||
| EP 161 |
2,652,000 | 1,653,360 | ||||||
| Beetaloo Joint Operation |
54,208,538 | | ||||||
Sweetpea Petroleum Pty Ltd
Sweetpea Petroleum Pty Ltds current Year 1 minimum work requirements in EP 143 include various desktop evaluations including subsurface studies, environmental assessments, design and planning of 2D seismic survey and progress of land access negotiations with pastoralist for regulated activities for a minimum expenditure of $265,200 due in April 2024.
Sweetpea Petroleum Pty Ltds current Year 5 minimum work requirements in EP 136 include the re-entry of a vertical well, side track to drill a horizontal well, stimulate and test one exploration well plus the assessment of petroleum resources potential for a minimum expenditure of $18,895,500 due on December 31, 2023. As of December 31, 2023 this work had not been completed, however, an application to vary the minimum work commitments by removing this requirement to drill the horizontal well was submitted to the Department of Industry, Tourism and Trade (DITT) on September 1, 2023. If approved, the minimum expenditure will decrease to $4,110,600 to reflect spend on the permit to date. A renewal application for EP 136 was submitted to DITT on September 28, 2023 with a proposed expected work program commitment of $14,055,600 for the next exploration term (five years). The renewal application remains under review by the DITT during which time the Group continues to have the right to explore. We have no reason to believe that the renewal will not be approved.
EP 161
For the Groups joint operations with Santos Limited, the Company must continue to contribute its proportionate share of expenditure in order to maintain its interest in the underlying EP 161 permit.
Tamborans commitment through March 2026 for the permits is approximately $2,652,000 based on the minimum work requirements.
Beetaloo Joint Operation
For the Groups joint operations with DWE and Falcon, the Company has minimum work requirements for the third term of the permits which is composed of five years through to May 2028. These commitments include an expected spend of $54,208,538 related to drilling and multi-stage hydraulic fracturing of five wells across the permits as well as subsurface studies.
F-25
Table of Contents
Environmental
The Groups operations are subject to risks normally associated with the drilling, completion and production of oil and gas, including blowouts, fires, and environmental risks such as oil spills or gas leaks that could expose the Group to liabilities associated with these risks.
In the Groups acquisition of existing or previously drilled well bores, the Group may not be aware of prior environmental safeguards, if any, that were taken at the time such wells were drilled or during such time the wells were operated. The Group maintains comprehensive insurance coverage that it believes is adequate to mitigate the risk of any adverse financial effects associated with these risks.
However, should it be determined that a liability exists with respect to any environmental cleanup or restoration, the liability to cure such a violation could still fall upon the Group. No claim has been made, nor is the Group aware of any liability which the Group may have, as it relates to any environmental cleanup, restoration, or the violation of any rules or regulations relating thereto except for the matter discussed above.
Legal proceedings
The Group is a party to legal proceedings encountered in the ordinary course of its business. While the ultimate outcome and impact to the Group cannot be predicted with certainty, in the opinion of management, it is remote that these legal proceedings will have a material adverse impact on the Groups financial condition, results of operations or cash flows.
Note 14 Related Party Transactions
During the year ended June 30, 2023, the Group entered into a strategic alliance with H&P and secured a $15,000,000 million equity investment from H&P (an entity in which a director of the Group is a member of Executive Leadership Team). The strategic alliance results in H&P supporting the Groups development plans in the Northern Territory through their investment in the business while at the same time executing on H&Ps strategy to gain more international exposure. During the current financial year, there were several transactions with H&P that are classified as related party transactions.
During the current financial year, the Group entered into a lease with H&P for the use of the FlexRig® for a two-year period with a commencement date of August 1, 2023. The minimum lease payment obligation is based on the daily operating rate from August 1, 2023 to July 31, 2025. Mobilization cost of this rig amounting to $4,219,986 is accrued and recognized as a part of accounts payable and accrued expenses in the consolidated statement of financial position as of June 30, 2023. These payables are expected to be drawn down through the convertible note facility entered into with H&P subsequent to current financial year end (Refer to Note 15).
Note 15 Subsequent Events
July 2023 Capital Raise and Share Purchase Plan
Subsequent to June 30, 2023, the Company completed a successful two-tranche placement (Placement) of approximately 295,634,390 Shares at A$0.18 per Share as follows:
| | Tranche 1 comprising the issue of 288,995,504 new fully paid ordinary shares in Tamboran to institutional, sophisticated and professional investors representing 20.4% of Tamborans pre-raise issued capital, raising approximately $34.5 million (A$52 million) and issued using Tamborans existing placement capacity under ASX Listing Rules 7.1 and 7.1A. |
| | Tranche 2 comprising the issue of 6,638,886 new fully paid ordinary shares to Tamborans investors to raise approximately $0.8 million (A$1.2 million). This tranche was approved by at the General Meeting on August 21, 2023. |
F-26
Table of Contents
As of June 30, 2023, $629,830 (A$949,970) in cash related to this capital raise had been received in the final week of the financial year. Shares for these funds were issued in August subsequent to the approval by shareholders in the General Meeting.
It is intended that funds raised under the Placement will be used by Tamboran to fund the Companys ongoing exploration and development programs in the Beetaloo Basin, for general working capital purposes and for costs of the Equity Raising.
December 2023 Capital Raise
In mid-December 2023, Tamboran announced the Company had successfully raised A$40.8 million via an Institutional Placement and institutional component of the 1 for 6.2 pro rata accelerated non-renounceable Entitlement Offer. The raise was conducted at A$0.16 per new CDI.
The Company also announced the completion of the Retail Entitlement Offer in mid-January 2024, which raised an additional A$14.2 million, completing a total raise of A$55.0 million. The funds from the capital raise aim to support Tamborans activities, including SS-1H flow testing and purchase of long lead items, to the sanctioning of the proposed Shenandoah South Pilot Project during the first half of 2024.
No other matter or circumstance has arisen since June 30, 2023 that would require disclosure in these consolidated financial statements.
Convertible notes
The Company entered into a subscription deed to issue 5-year Convertible Notes of up to $9,000,000 (A$13,505,402 at a fixed exchange rate of A$1.00:US$0.664) to H&P (related party) on July 6, 2023 (the Convertible Notes), the terms of which were approved by shareholders on August 21, 2023. The key terms of the Convertible Notes include a conversion option with a floor of A$0.21 and a ceiling of A$0.30 per share, for a maximum number of shares of 67,848,567 and a minimum number of shares of 47,493,997 respectively, although H&P can only exercise its conversion option on a change of control of the Company. Change of control is defined by the agreement as:
| (a) | a person not in Control of the Company (either alone or jointly with another person) acquires Control of the Company, or, (ii) a Group member enters into any arrangement to dispose of or transfer to one or more third parties: |
| (b) | a Group member enters into any arrangement to dispose of or transfer to one or more third parties: |
| (i) | all or substantially all of the assets of the Group or its business in any manner including by way of a restructure, asset or security sale, or |
| (ii) | more than 50% of the voting shares in the Company; |
| (c) | the Company determines that any of the events in paragraphs (a) or (b) above is likely to occur, but excluding any arrangement in respect of a solvent restructure of the Group or its business or under which there is a new holding company of the Group. |
The Convertible Notes can be drawn down as a line of credit to pay H&P for mobilization and related reimbursable costs for rig 469 plus accrued interest at 5.5% p.a. on the amount drawn down.
Tamboran has not yet issued the Convertible Notes and as such has not yet drawn down any amount under the Convertible Notes. However, Tamboran has payables outstanding which are expected to be settled through the draw down of the Convertible Notes.
F-27
Table of Contents
Scheme of Arrangement
Tamboran Resources Corporation (TRC) was incorporated in Delaware on October 3, 2023 for the purpose of effecting the Groups corporate reorganization pursuant to a scheme of arrangement under Australian law (Corporate Reorganization) between the Group and TRC. TRC is a Delaware corporation listed on the Australian Securities Exchange. On December 13, 2023, TRC acquired all of the issued and outstanding ordinary shares of Tamboran pursuant to the Corporate Reorganization. As part of the Corporate Reorganization, TRC issued to the shareholders of Tamboran one CDI (representing an interest in 1/200th of a share of TRC common stock) in exchange for one ordinary share of the Company issued and outstanding. Prior to the Corporate Reorganization, TRC had no business or operations, and following the Corporate Reorganization, TRCs business and operations consist solely of the business and operations of the Group.
Note 16 Supplemental Oil and Gas Disclosures (unaudited)
The following information was prepared in accordance with the FASBs Accounting Standards Update no. 2010-03, Extractive Activities Oil and Gas (ASC 932). The supplementary information summarized below presents the results of natural gas and oil activities for the Group in accordance with the successful efforts method of accounting for production activities.
The Groups oil and natural gas activities for financial years 2023 and 2022 were located solely in Australia.
Costs incurred in natural gas exploration and development
Costs incurred in natural gas producing activities for the years ended on June 30, 2023 and 2022 were as follows:
| For the years ended June 30, | ||||||||
| 2023 | 2022 | |||||||
| Property acquisition costs: |
||||||||
| Proved |
$ | | $ | | ||||
| Unproved |
53,205,243 | | ||||||
| Exploration costs: |
||||||||
| Geological and geophysical |
2,793,036 | 1,707,377 | ||||||
| Development costs |
30,770,172 | 25,848,994 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total cost incurred |
86,768,451 | 27,556,371 | ||||||
| Asset retirement obligations |
5,698,464 | 459,021 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total cost incurred |
$ | 92,466,915 | $ | 28,015,392 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Capitalized costs
Capitalized costs consist of Groups properties, equipment, and facilities for natural gas exploration projects, which are pending the determination of proven or probable reserves. Capitalized costs for unproved properties include costs for acquiring oil and natural gas properties where no proved reserves have been identified, including costs of exploratory wells that are in the process of drilling or in active completion, and costs of exploratory wells suspended or waiting on completion.
F-28
Table of Contents
The table below sets forth capitalized costs, impairment, and depreciation, depletion and amortization relating to the Groups oil and natural gas properties as of June 30, 2023 and 2022:
| June 30, | ||||||||
| 2023 | 2022 | |||||||
| Natural gas properties, successful efforts method: |
||||||||
| Unproved properties |
$ | 163,385,971 | $ | 55,469,992 | ||||
| Accumulated impairment to unproved properties |
| | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| $163,385,971 | $55,469,992 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
In conjunction with the capital raise in September 2022, Tamboran granted Daly Waters Royalty, LP an overriding royalty interest (ORRI) of 2.34358% to the Petroleum (as defined in the Petroleum Act 1984 (NT)) produced from each of the permits above. The payment received from Daly Waters Royalty, LP for the ORRI grant has been offset against the asset to which the payment related. While the above permits are subject to royalties, Tamboran has excluded all royalties from contingent payments and the initial measurement of the assets acquired as well as royalties for existing permits. Tamboran will recognize a liability for royalties only when the contingent payment crystallizes.
Natural gas reserves
Proved reserves are estimated quantities of natural gas that geological and engineering data demonstrate with reasonable certainty to be recoverable in future years from known reservoirs using existing economic and operating conditions. Estimating natural gas reserves is complex and inexact because of the numerous uncertainties inherent in the process. The process of estimating proved reserves requires certain economic assumptions, including, but not limited to, natural gas prices, drilling, completion and operating expenses, capital expenditures and taxes. The process relies on interpretations of available geological, geophysical, petrophysical, engineering and production data. The data for a given reservoir may also change substantially over time as a result of numerous factors including, but not limited to, additional development activity, evolving production history and continual reassessment of the viability of production under varying economic conditions.
All of the Groups exploration and evaluation projects are pending the determination of proven or probable reserves. As such, the estimates of Groups total proved reserves were nil as of June 30, 2023 and 2022.
F-29
Table of Contents

Table of Contents
PART II
INFORMATION NOT REQUIRED IN PROSPECTUS
Item 13. Other Expenses of Issuance and Distribution.
The following table sets forth the various expenses, other than underwriting discounts and commissions, payable by us in connection with the offering of our common stock contemplated by this registration statement. All of the fees set forth below are estimates, except for the SEC registration fee, the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority, Inc. (FINRA) filing fee and the NYSE listing fee.
| SEC registration fee |
$ | * | ||
| FINRA filing fee |
* | |||
| NYSE listing fees |
* | |||
| Transfer agent and registrar fees and expenses |
* | |||
| Printing fees and expenses |
* | |||
| Legal fees and expenses |
* | |||
| Accounting fees and expenses |
* | |||
| Miscellaneous |
* | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Total |
$ * | |||
|
|
|
| * | To be provided by amendment. |
Item 14. Indemnification of Directors and Officers.
Our certificate of incorporation will provide that directors and officers will not be liable to us or our stockholders for monetary damages to the fullest extent permitted by the DGCL. In addition, if the DGCL is amended to authorize the further elimination or limitation of the liability of directors and officers, then the liability of our directors or our officers, in addition to the limitation on personal liability provided for in our certificate of incorporation, will be limited to the fullest extent permitted by the amended DGCL. Our bylaws will provide that we will indemnify, and advance expenses to, any officer or director to the fullest extent authorized by the DGCL.
Section 145 of the DGCL provides that a corporation may indemnify directors and officers as well as other employees and individuals against expenses, including attorneys fees, judgments, fines and amounts paid in settlement in connection with specified actions, suits and proceedings whether civil, criminal, administrative, or investigative, other than a derivative action by or in the right of the corporation, if they acted in good faith and in a manner they reasonably believed to be in or not opposed to the best interests of the corporation and, with respect to any criminal action or proceeding, had no reasonable cause to believe their conduct was unlawful. A similar standard is applicable in the case of derivative actions, except that indemnification extends only to expenses, including attorneys fees, incurred in connection with the defense or settlement of such action and the statute requires court approval before there can be any indemnification where the person seeking indemnification has been found liable to the corporation. The statute provides that it is not exclusive of other indemnification that may be granted by a corporations certificate of incorporation, bylaws, disinterested director vote, stockholder vote, agreement or otherwise.
Our certificate of incorporation will also contain indemnification rights for our directors and our officers. Specifically, our certificate of incorporation will provide that we shall defend, indemnify and advance expenses to our officers and directors to the fullest extent authorized by the DGCL. Further, we may maintain insurance on behalf of our officers and directors against expense, liability or loss asserted incurred by them in their capacities as officers and directors.
In addition, we intend to enter into indemnification agreements, to be effective upon the completion of this offering, with our current directors and officers containing provisions that are in some respects broader than the
II-1
Table of Contents
specific indemnification provisions contained in the DGCL. The indemnification agreements will require us, among other things, to indemnify our directors and officers against certain liabilities that may arise by reason of their status or service as directors or officers and to advance their expenses incurred as a result of any proceeding against them as to which they could be indemnified. We also intend to enter into indemnification agreements with our future directors and officers.
We intend to maintain liability insurance policies that indemnify our directors and officers against various liabilities, including certain liabilities arising under the Securities Act or the Exchange Act that may be incurred by them in their capacity as such.
The proposed form of Underwriting Agreement to be filed as Exhibit 1.1 to this registration statement provides for indemnification of our directors and officers by the underwriters against certain liabilities arising under the Securities Act or otherwise in connection with this offering.
Insofar as indemnification for liabilities arising under the Securities Act may be permitted to directors, officers or persons controlling us pursuant to the foregoing provisions, we have been informed that in the opinion of the SEC, such indemnification is against public policy as expressed in the Securities Act and is therefore unenforceable.
Item 15. Recent Sales of Unregistered Securities.
Corporate Reorganization
As a result of the Corporate Reorganization, we issued 1,716,672,600 CDIs (representing interests in 8,583,363 shares of common stock) to eligible shareholders of Tamboran Resources Limited in exchange for all of the ordinary shares in our Predecessor. The information set forth in Business Corporate Reorganization of the prospectus is incorporated herein by reference.
Other Equity Issuances
In July 2021, our Predecessor completed its initial public offering on the ASX, raising approximately A$61 million through the issue of 152,510,514 ordinary shares at A$0.40 per share.
In November 2021, our Predecessor raised approximately A$35 million in gross proceeds through a private placement of 94,498,961 ordinary shares at A$0.37 per share.
In October 2022, our Predecessor raised approximately A$140 million in gross proceeds through a private placement of 668,651,233 ordinary shares at A$0.21 per share.
In August 2023, our Predecessor raised approximately A$53 million in gross proceeds through the issue of 295,634,390 ordinary shares at A$0.18 per share.
In December 2023, we completed private placements of our CDIs for approximately A$40.8 million in gross proceeds and a retail placement to Australian shareholders for approximately A$14.2 million. The proceeds of the placements will be used to fund our ongoing drilling program.
Each of the private placements was made in reliance on Section 4(a)(2) and/or Rule 902 of Regulation S of the Securities Act.
Item 16. Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedules.
(a) Exhibits: The list of exhibits set forth under Exhibit Index at the end of this registration statement is incorporated herein by reference.
II-2
Table of Contents
Item 17. Undertakings.
The undersigned registrant hereby undertakes to provide to the underwriters at the closing specified in the Underwriting Agreement certificates in such denominations and registered in such names as required by the underwriters to permit prompt delivery to each purchaser.
Insofar as indemnification for liabilities arising under the Securities Act may be permitted to directors, officers and controlling persons of the registrant pursuant to the foregoing provisions, or otherwise, the registrant has been advised that in the opinion of the SEC such indemnification is against public policy as expressed in the Securities Act and is, therefore, unenforceable. In the event that a claim for indemnification against such liabilities (other than the payment by the registrant of expenses incurred or paid by a director, officer or controlling person of the registrant in the successful defense of any action, suit or proceeding) is asserted by such director, officer or controlling person in connection with the securities being registered, the registrant will, unless in the opinion of its counsel the matter has been settled by controlling precedent, submit to a court of appropriate jurisdiction the question whether such indemnification by it is against public policy as expressed in the Securities Act and will be governed by the final adjudication of such issue.
The undersigned registrant hereby undertakes that:
(1) For purposes of determining any liability under the Securities Act, the information omitted from the form of prospectus filed as part of this registration statement in reliance upon Rule 430A and contained in a form of prospectus filed by the registrant pursuant to Rule 424(b)(1) or (4) or 497(h) under the Securities Act shall be deemed to be part of this registration statement as of the time it was declared effective.
(2) For the purpose of determining any liability under the Securities Act, each post-effective amendment that contains a form of prospectus shall be deemed to be a new registration statement relating to the securities offered therein, and the offering of such securities at that time shall be deemed to be the initial bona fide offering thereof.
II-3
Table of Contents
EXHIBIT INDEX
| Exhibit |
Description |
|
| 1.1* | Form of Underwriting Agreement | |
| 3.1* | Certificate of Incorporation of Tamboran Resources Corporation | |
| 3.2* | Bylaws of Tamboran Resources Corporation | |
| 4.1* | Form of Common Stock Certificate | |
| 5.1* | Opinion of Latham & Watkins LLP as to the legality of the securities being registered | |
| 10.1* | Form of Director Indemnification Agreement | |
| 10.3* | Form of Tamboran Resources Corporation Long-Term Incentive Plan | |
| 21.1* | List of Subsidiaries of Tamboran Resources Corporation | |
| 23.1* | Consent of Ernst & Young Global Limited | |
| 23.3* | Consent of Latham & Watkins LLP (included as part of Exhibit 5.1 hereto) | |
| 24.1* | Power of Attorney (included on the signature page of the initial filing of the Registration Statement) | |
| 107* | Filing Fee table | |
| * | To be filed by amendment. |
| | Compensatory plan or arrangement. |
| # | Portions of this exhibit (indicated by asterisks) have been omitted because the registrant has determined they are not material and would likely cause competitive harm to the registrant if publicly disclosed. |
II-4
Table of Contents
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Act, the registrant has duly caused this registration statement to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized, in the City of , State of , on , 2024.
| Tamboran Resources Corporation | ||
| By: | ||
| Name: | Joel Riddle | |
| Title: | Chief Executive Officer | |
Each person whose signature appears below appoints Joel Riddle and Eric Dyer, and each of them, any of whom may act without the joinder of the other, as his or her true and lawful attorneys-in-fact and agents, with full power of substitution and re-substitution, for him or her and in his name, place and stead, in any and all capacities, to sign any and all amendments (including post-effective amendments) to this registration statement and any registration statement (including any amendment thereto) for this offering that is to be effective upon filing pursuant to Rule 462(b) under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, and to file the same, with all exhibits thereto, and all other documents in connection therewith, with the Securities and Exchange Commission, granting unto said attorneys-in-fact and agents full power and authority to do and perform each and every act and thing requisite and necessary to be done, as fully to all intents and purposes as he or she might or would do in person, hereby ratifying and confirming all that said attorneys-in-fact and agents or any of them or their or his substitute or substitutes, may lawfully do or cause to be done by virtue hereof.
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Act, this registration statement has been signed by the following persons in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
| Signature |
Title |
Date |
||
|
Joel Riddle |
Chief Executive Officer and Sole Director (Principal Executive Officer) |
|||
|
Eric Dyer |
Chief Financial Officer (Principal Financial Officer and Principal Accounting Officer) |
|||
| *By:
|
|
|
| Attorney-in-fact |
II-5